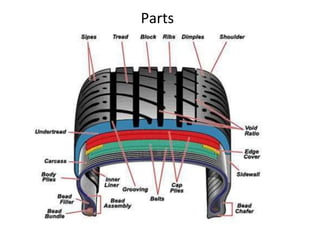
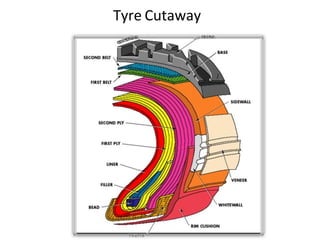
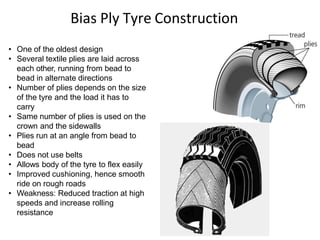
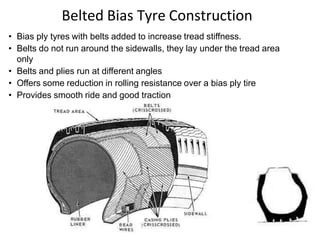
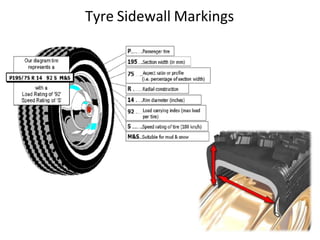
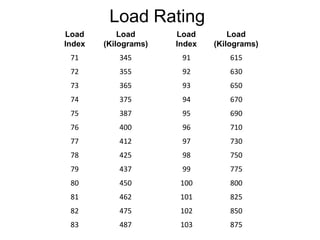
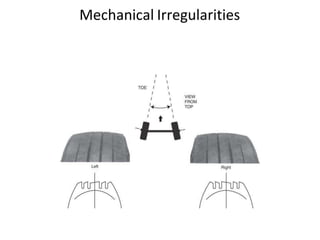
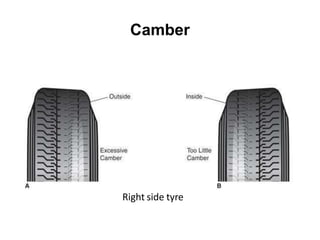
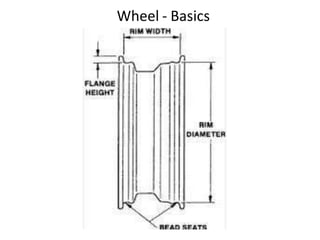
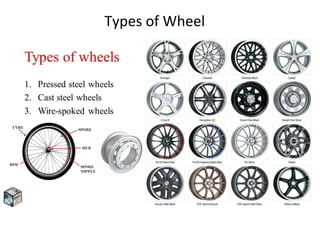
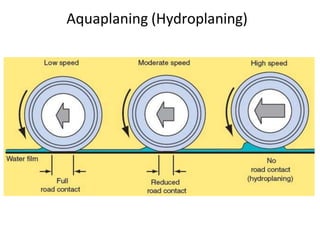
Tyres and wheels have several important functions for vehicles. Tyres provide cushioning from rough roads, allow steering and braking, and provide traction through friction with the road surface. Wheels support the vehicle's weight and allow it to move. There are different types of tyre construction like bias ply, belted bias, and radial ply. Radial ply tyres offer advantages like reduced rolling resistance and better handling. Wheels are typically made of steel or aluminum and properly torqued fasteners are needed to securely attach the wheel to the vehicle.