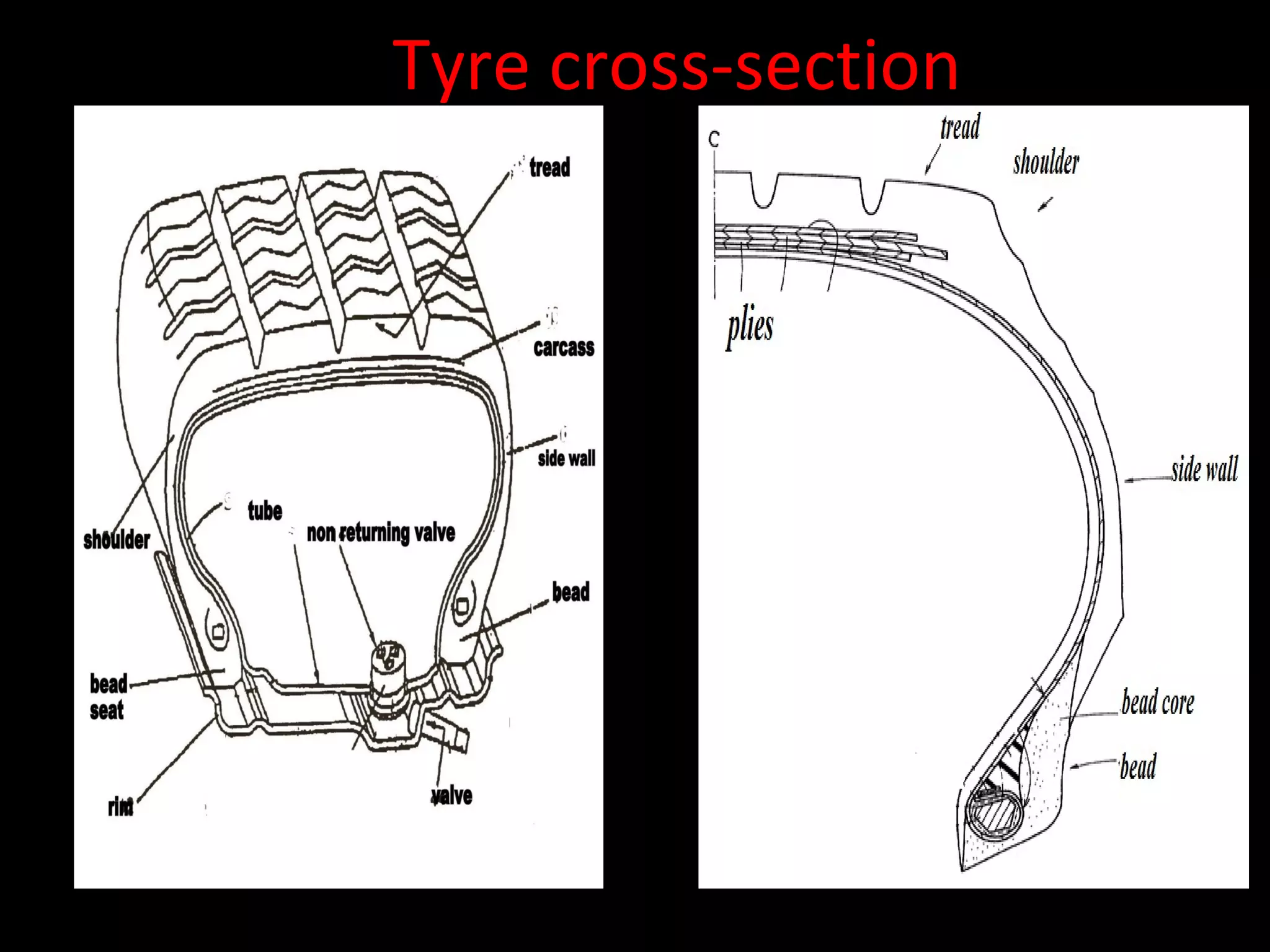
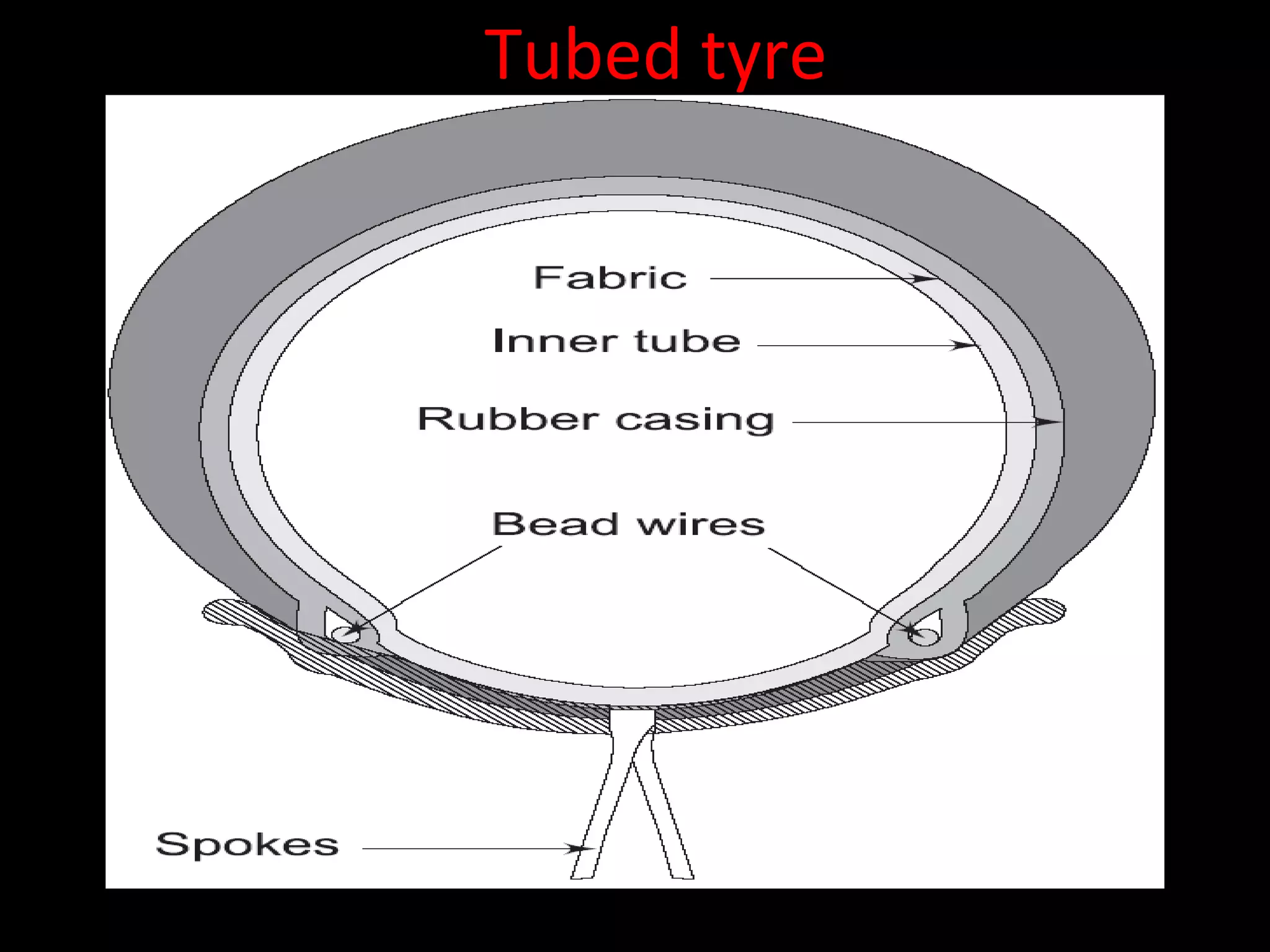
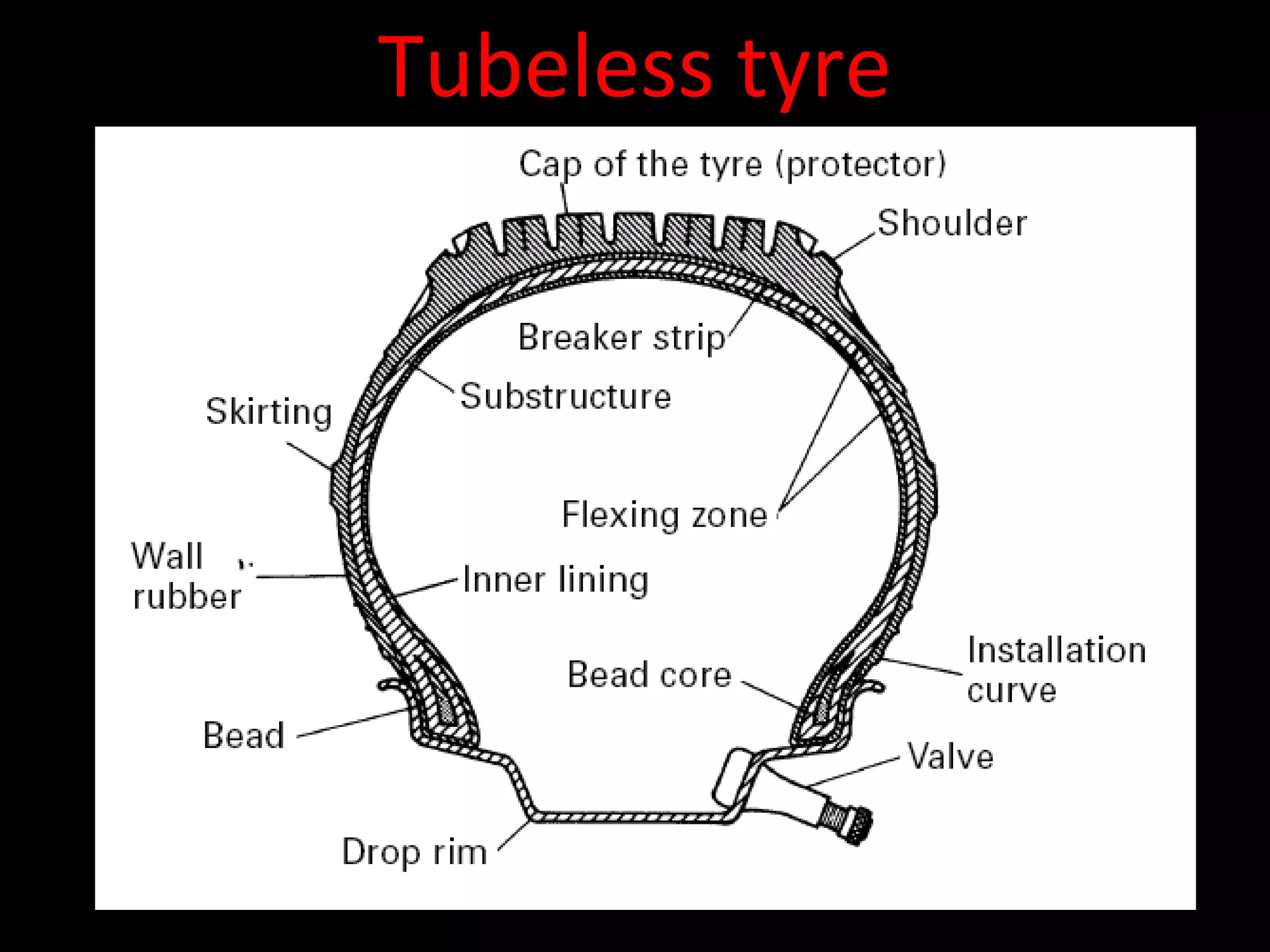
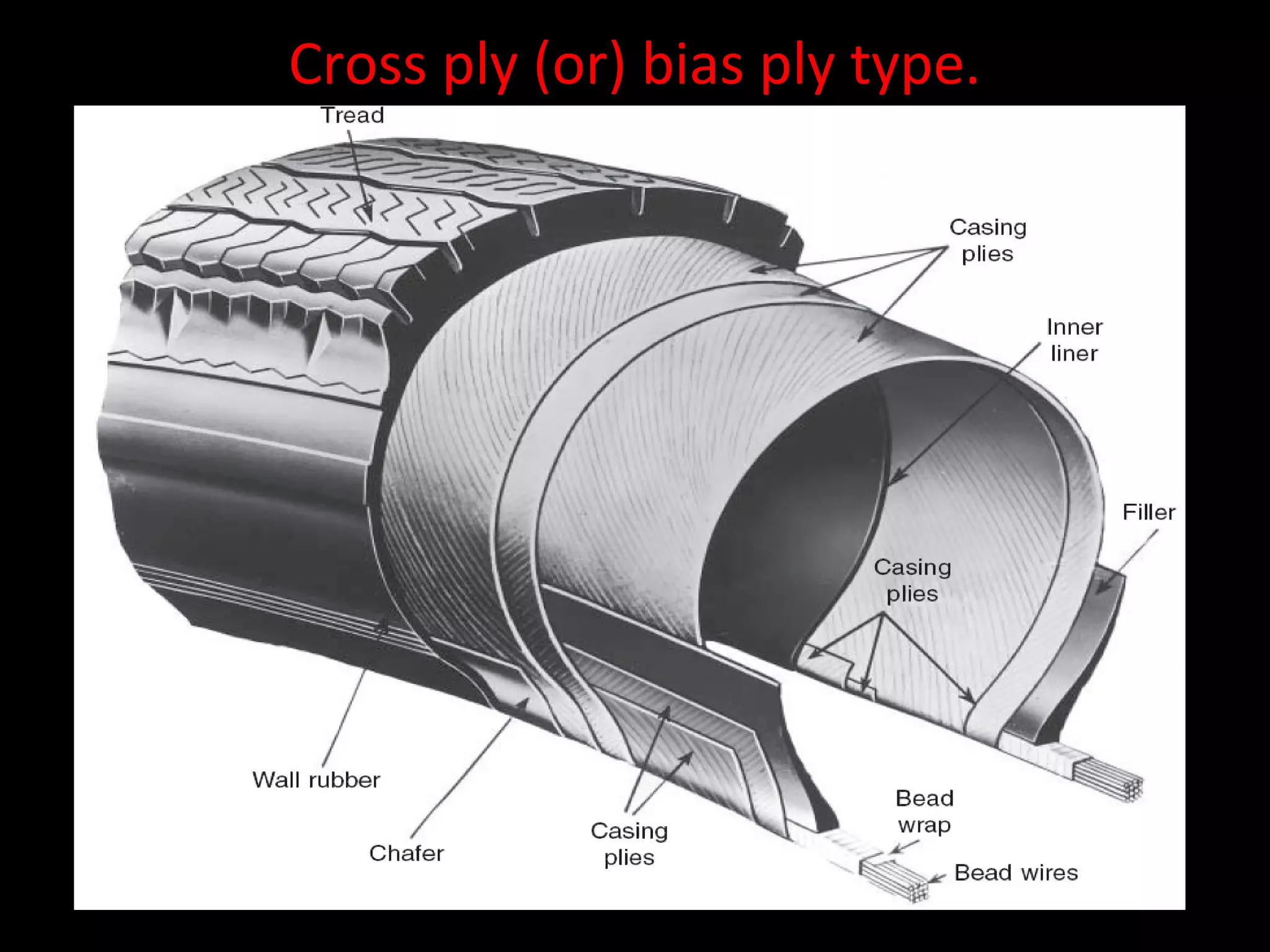
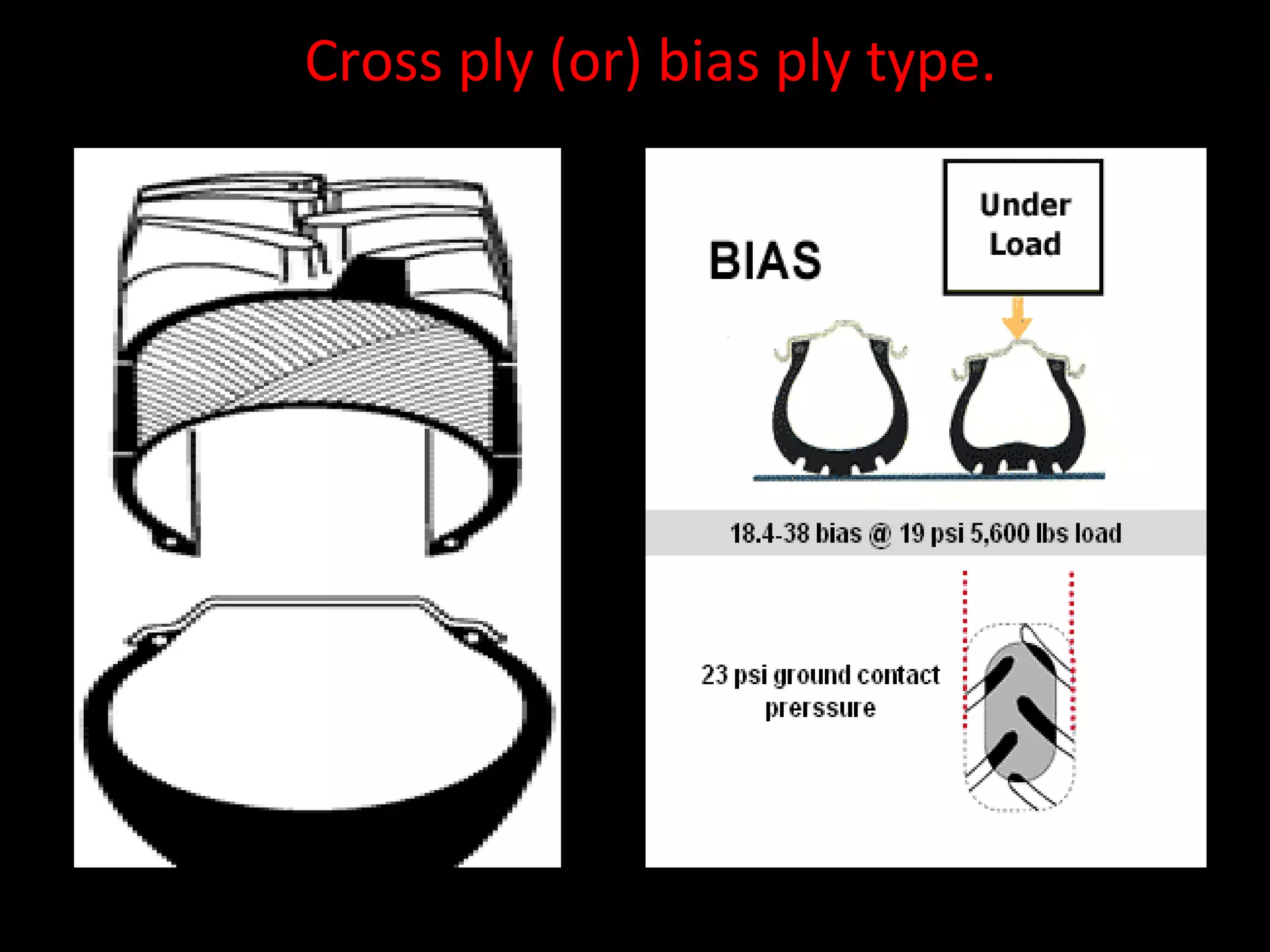
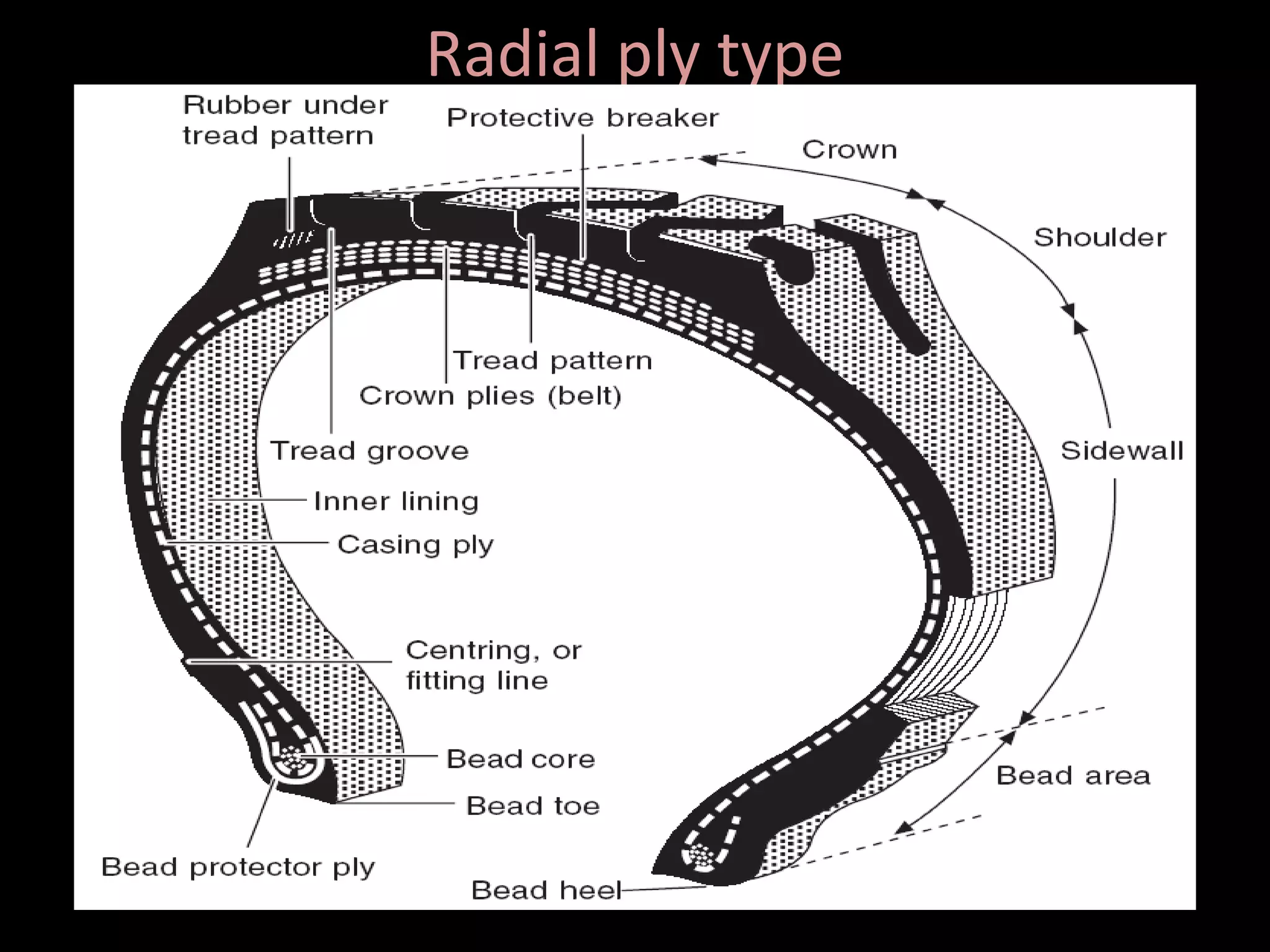
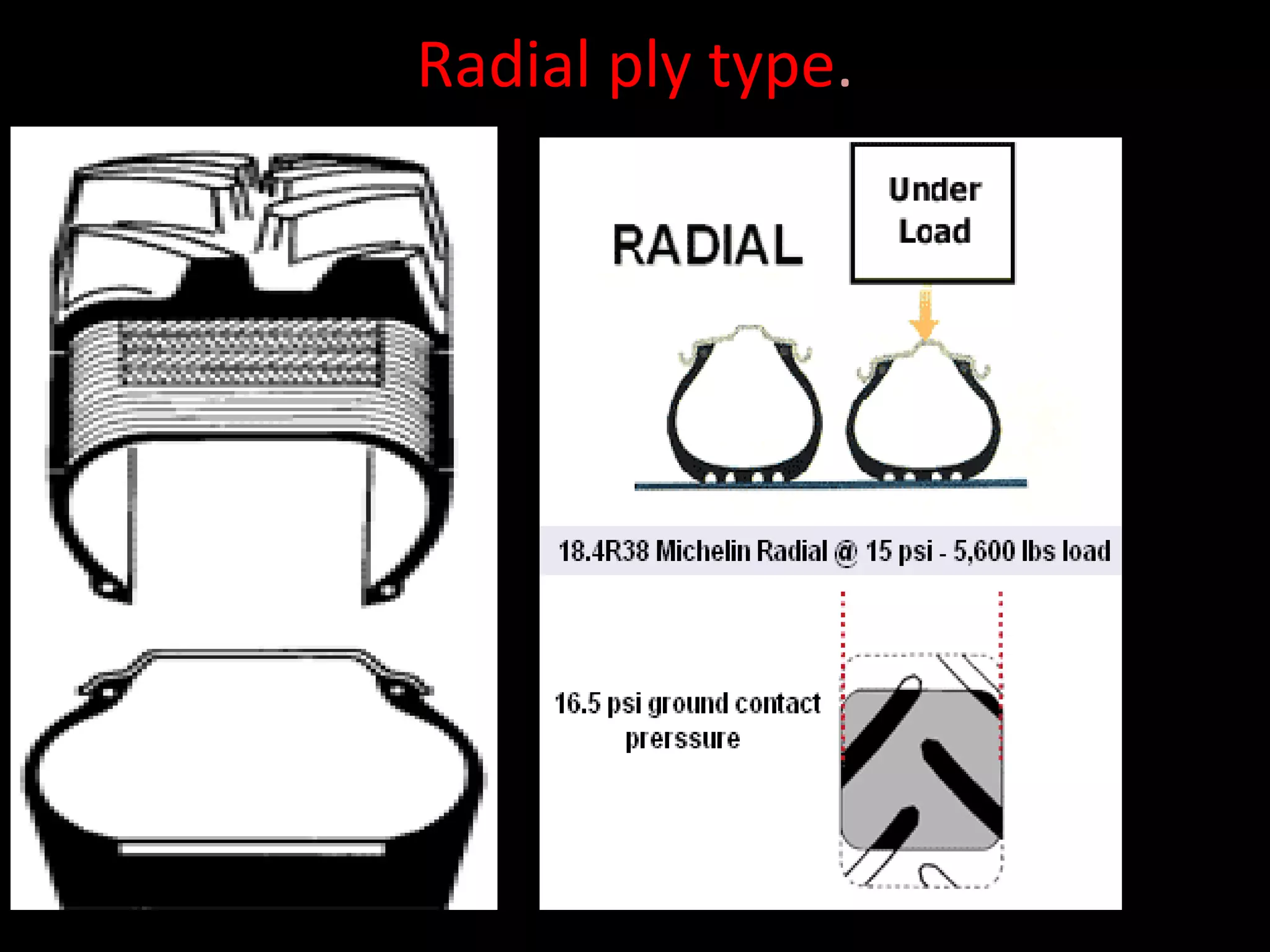
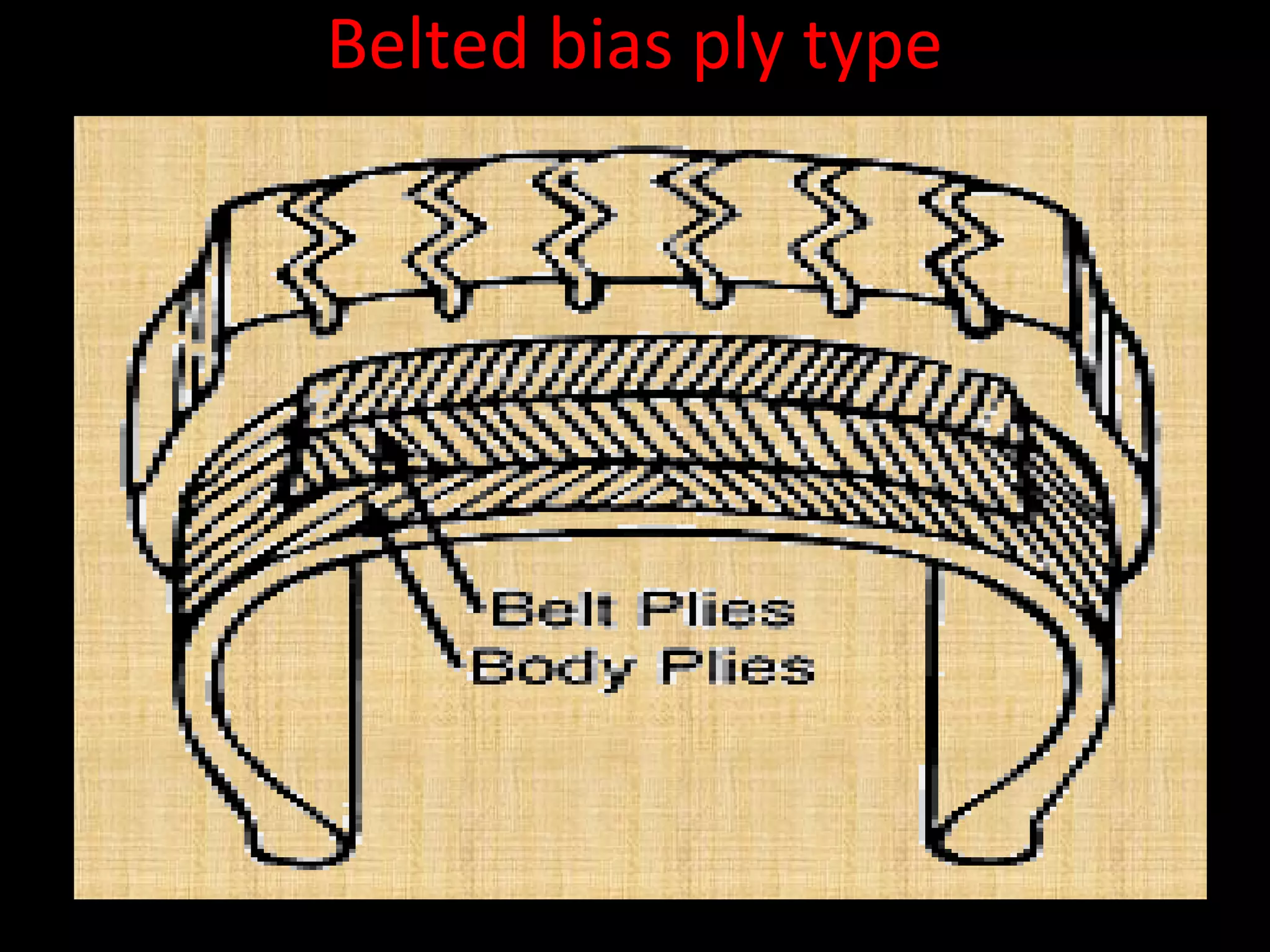
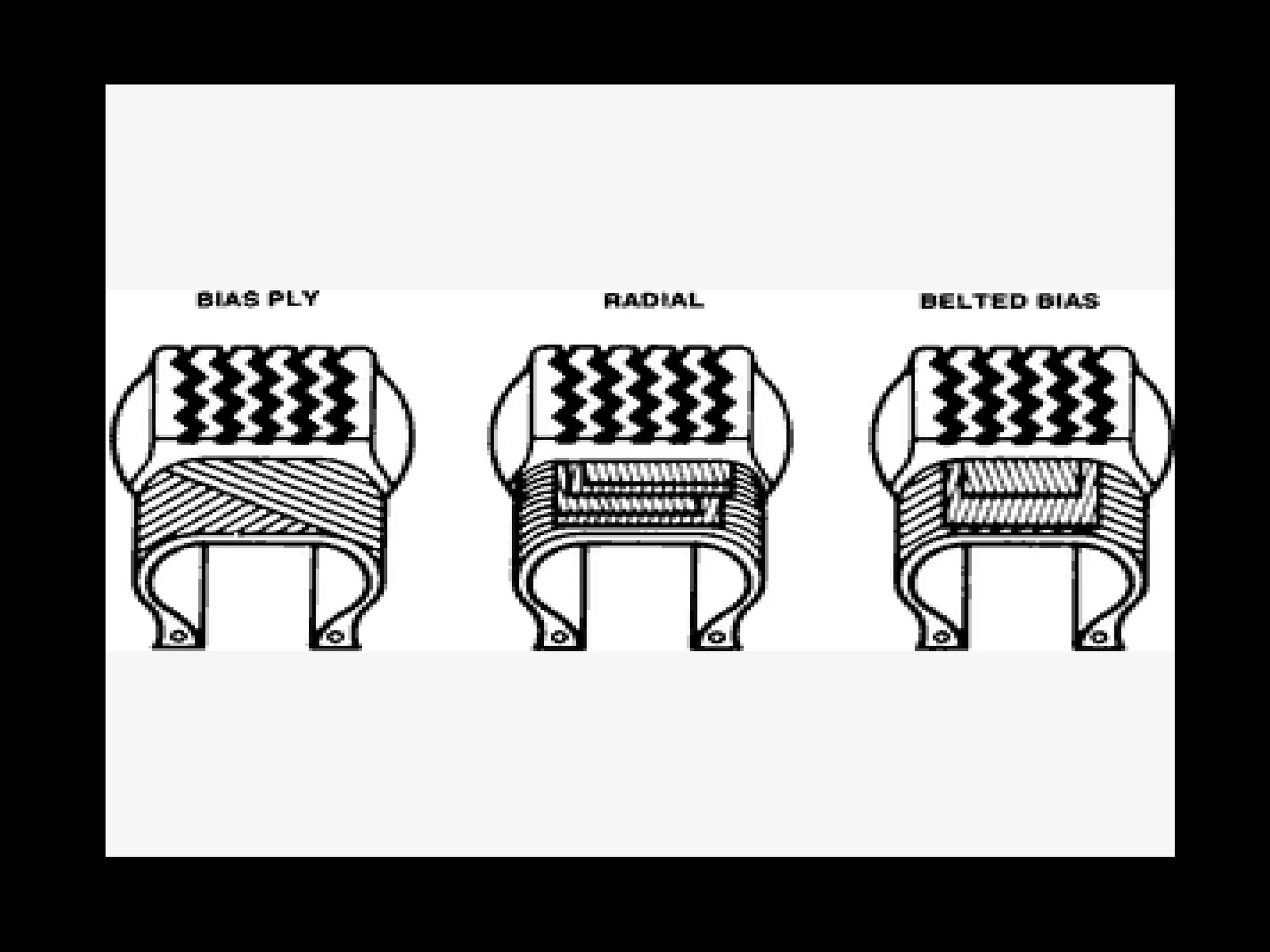
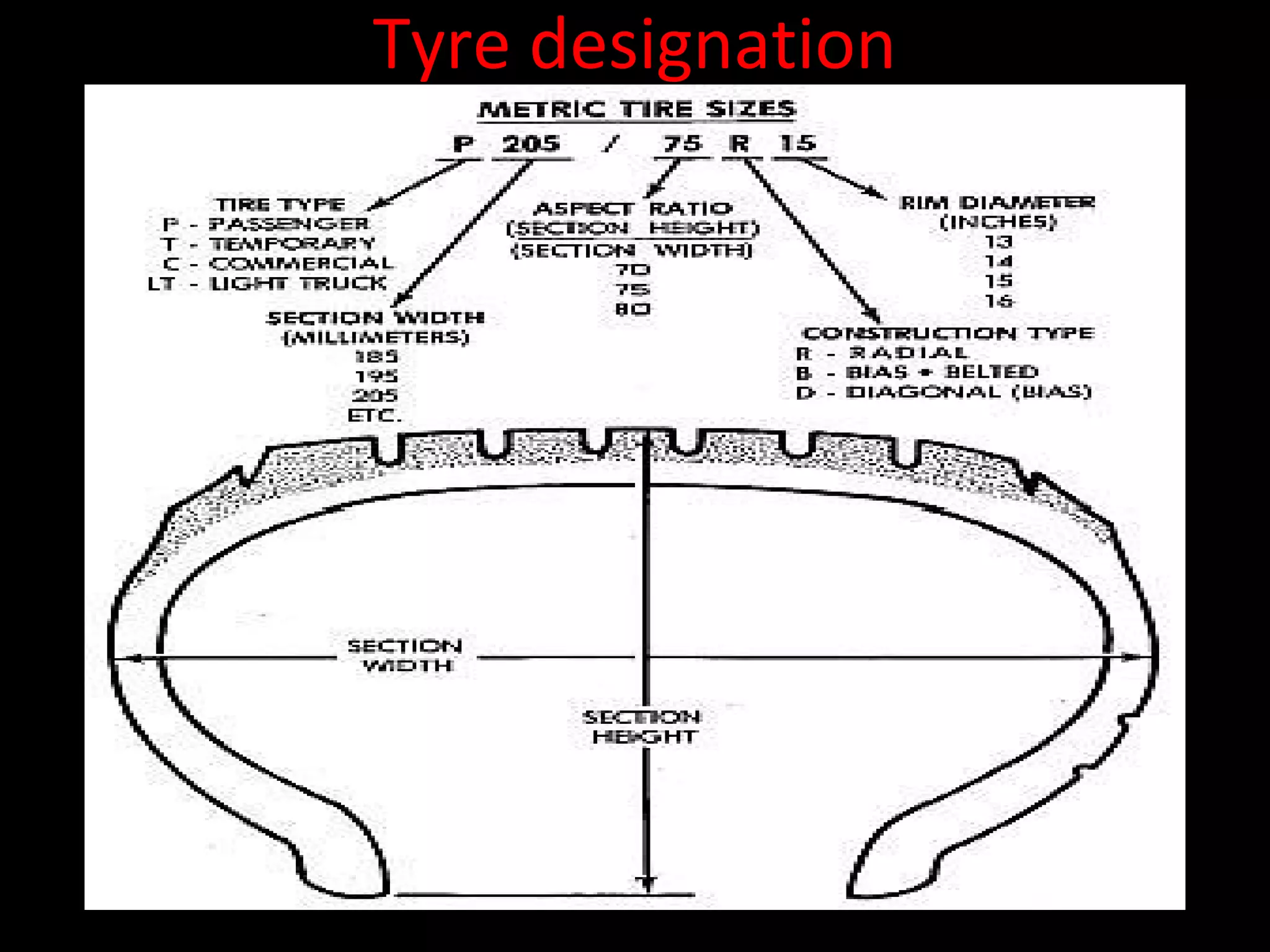
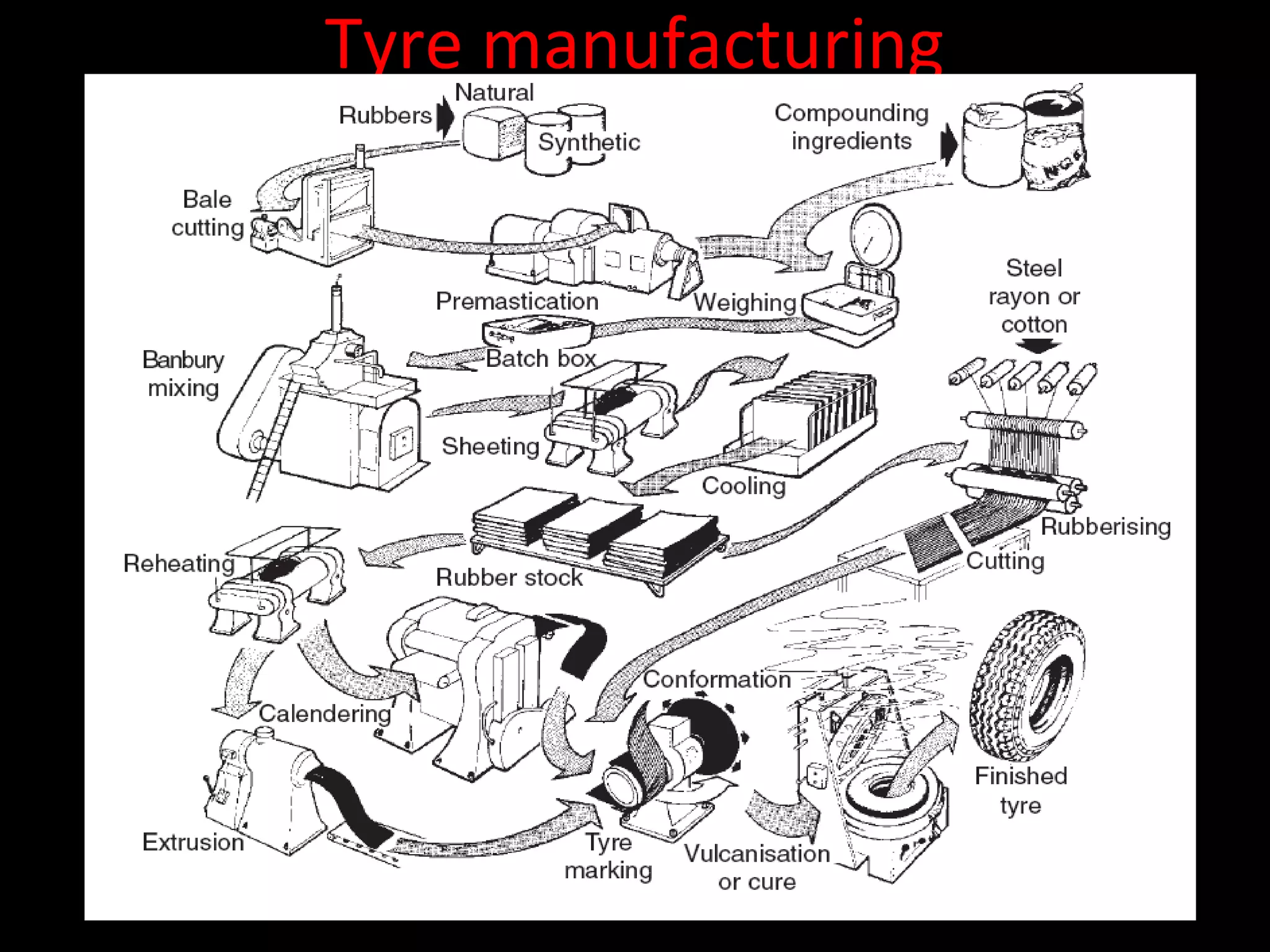
The document discusses tires (tyres) for automobiles. It describes the basic functions and components of a tire, including the outer cover and inner tube. It discusses different types of tire casings (carcasses) such as cross-ply, radial-ply, and belted bias-ply tires. Radial tires are described as having advantages over bias-ply tires like better handling and reduced rolling resistance. The document also covers tire materials, tread design considerations, tire wear factors, troubleshooting tire issues, and the tire manufacturing process.