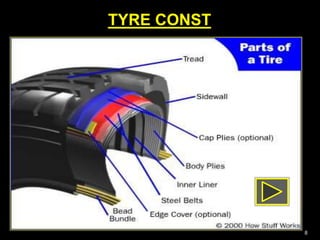
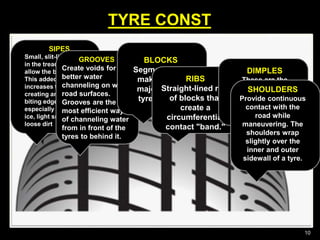
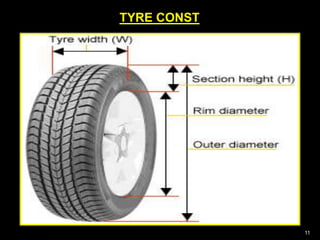
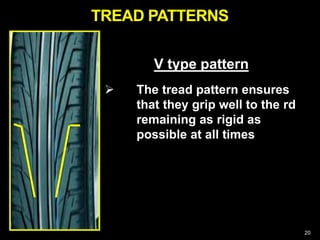
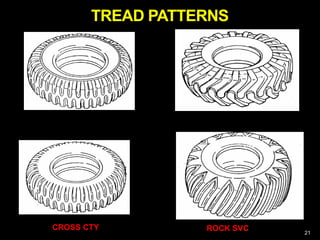
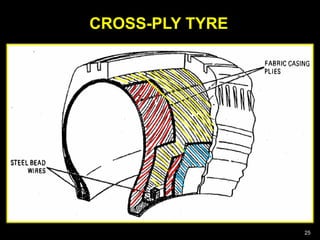
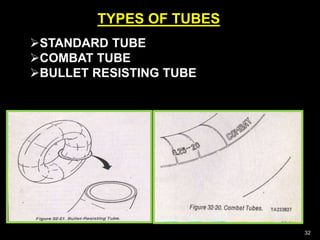
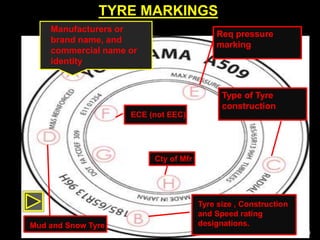
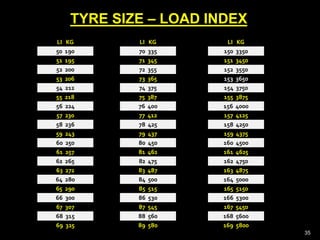
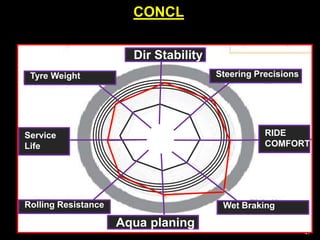
This document provides information about tyres and tubes for students. It discusses the construction of tyres, including treads, patterns, markings and ratings. It also covers the latest trends like run-flat and airless tyres. The document recommends safety measures for tyres such as checking for proper inflation and balancing to prevent hydroplaning. It concludes with reinforcing the importance of tyre safety and maintenance.