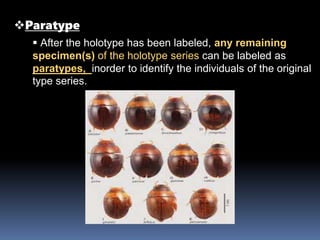
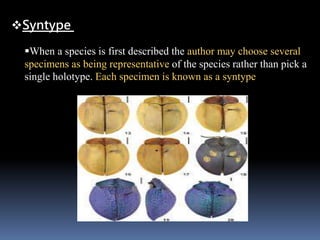
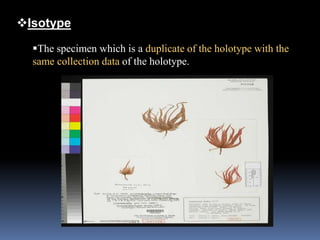
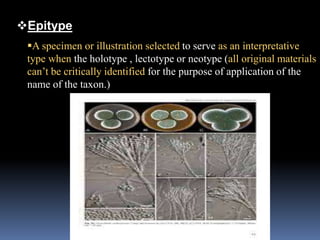
This document discusses typification and different zoological types. Typification is the process of designating a nomenclatural type, which serves as the standard to define the name of a taxon. There are several types of zoological specimens that can be designated, including holotypes, paratypes, lectotypes, and neotypes. These types provide objective references that allow taxonomists to verify the identity of described species. Designating types is important for definitively concluding whether a newly examined specimen represents a known or new species.