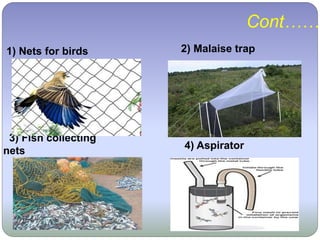
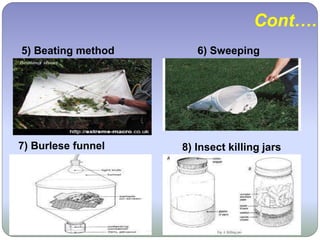
This document discusses the taxonomic procedures for collecting, preserving, and identifying specimens. It outlines the key steps as collection, preservation, curetting, and identification. For collection, it describes various techniques like nets, traps, and digging. Preservation methods include wet preservation in formalin or alcohol and dry preservation for some specimens. Curetting involves cataloging and storing specimens. Identification determines the species of each organism based on morphology. The overall goal of these taxonomic procedures is to systematically classify organisms.