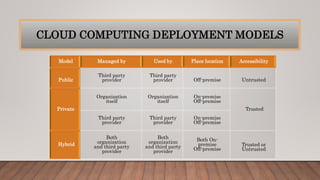
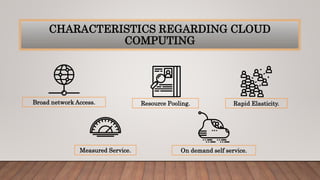
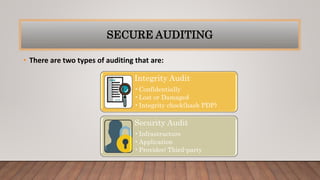
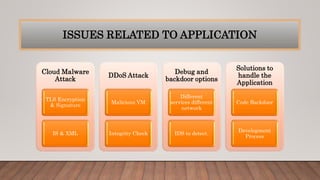
The document discusses optimizing quality of service and security issues in cloud computing. It begins with an introduction to cloud computing and its benefits. It then covers cloud service models (IaaS, PaaS, SaaS), deployment models (public, private, hybrid), characteristics, architectures, transparency, energy management, security and privacy issues. It discusses solutions to security issues like access control, encryption and regional data restrictions. It also addresses application security concerns and potential solutions.