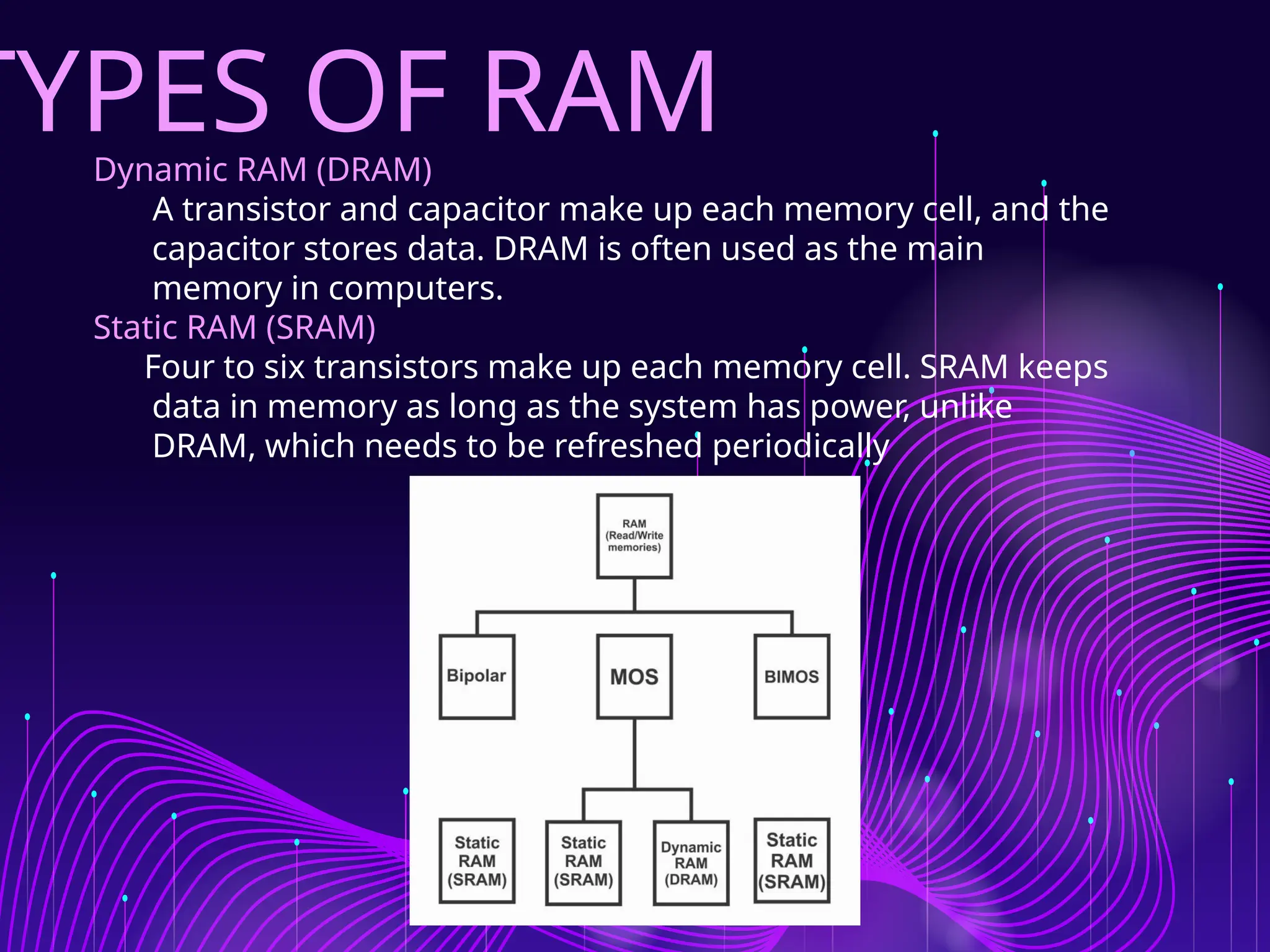
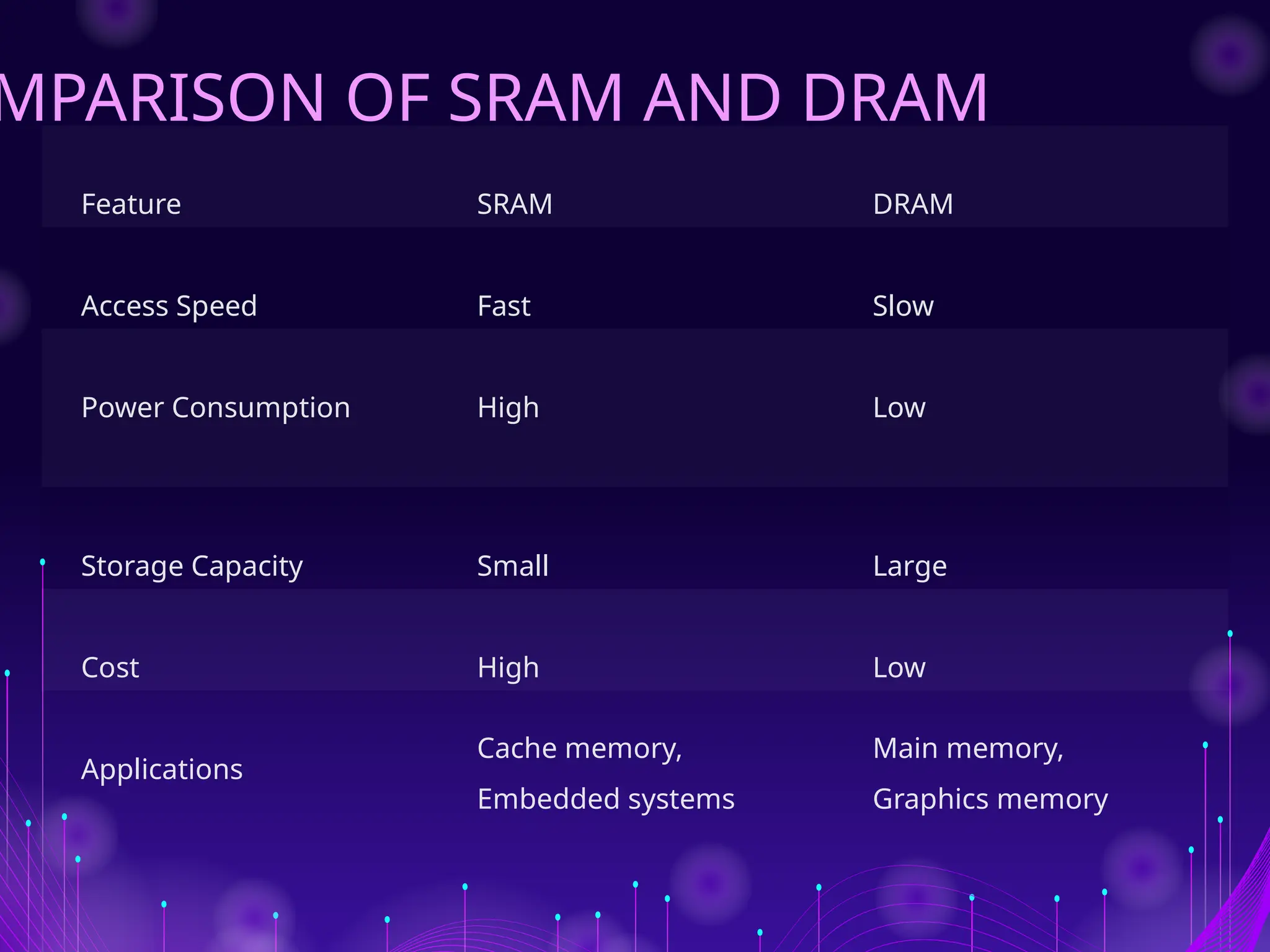
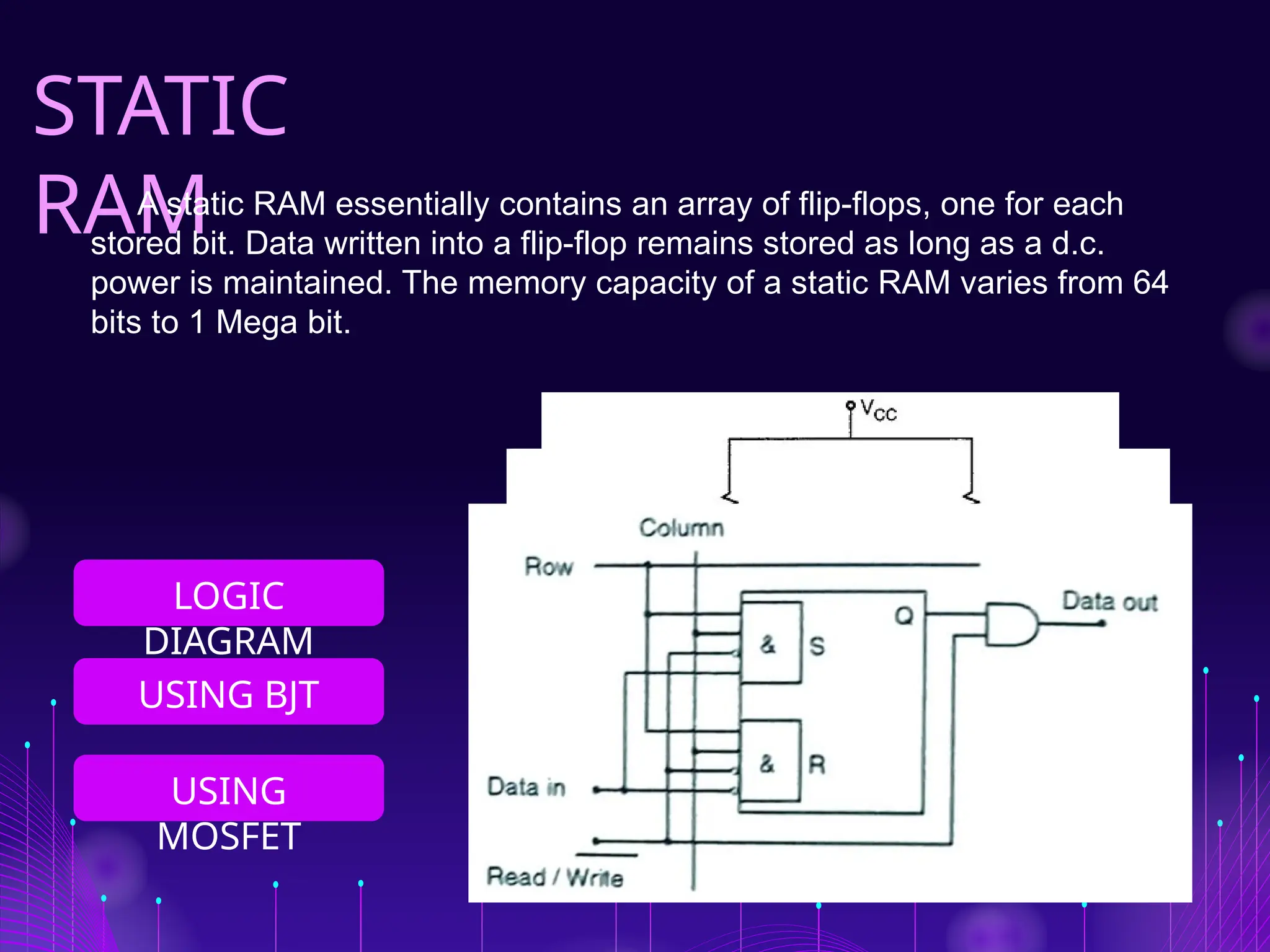
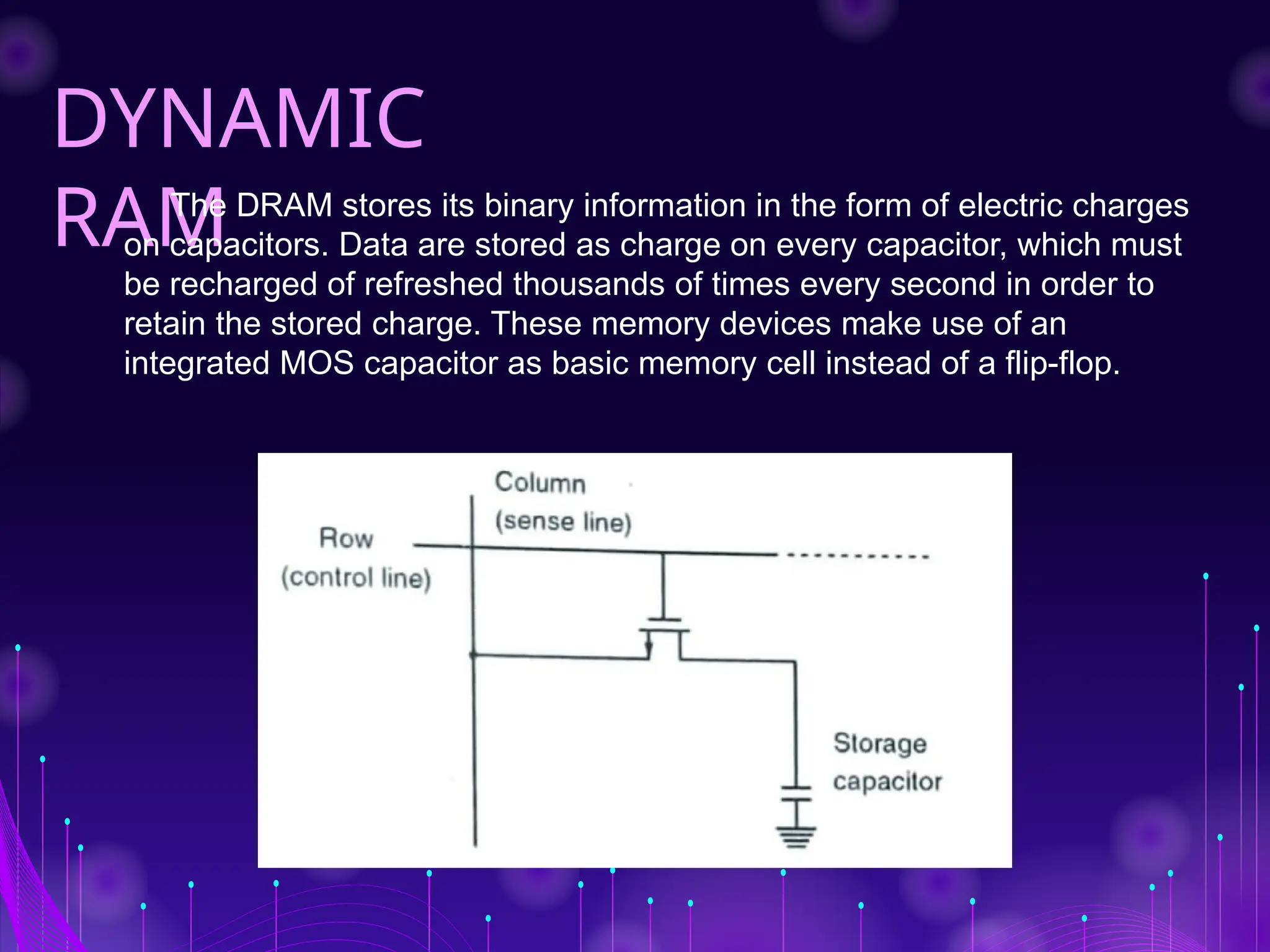
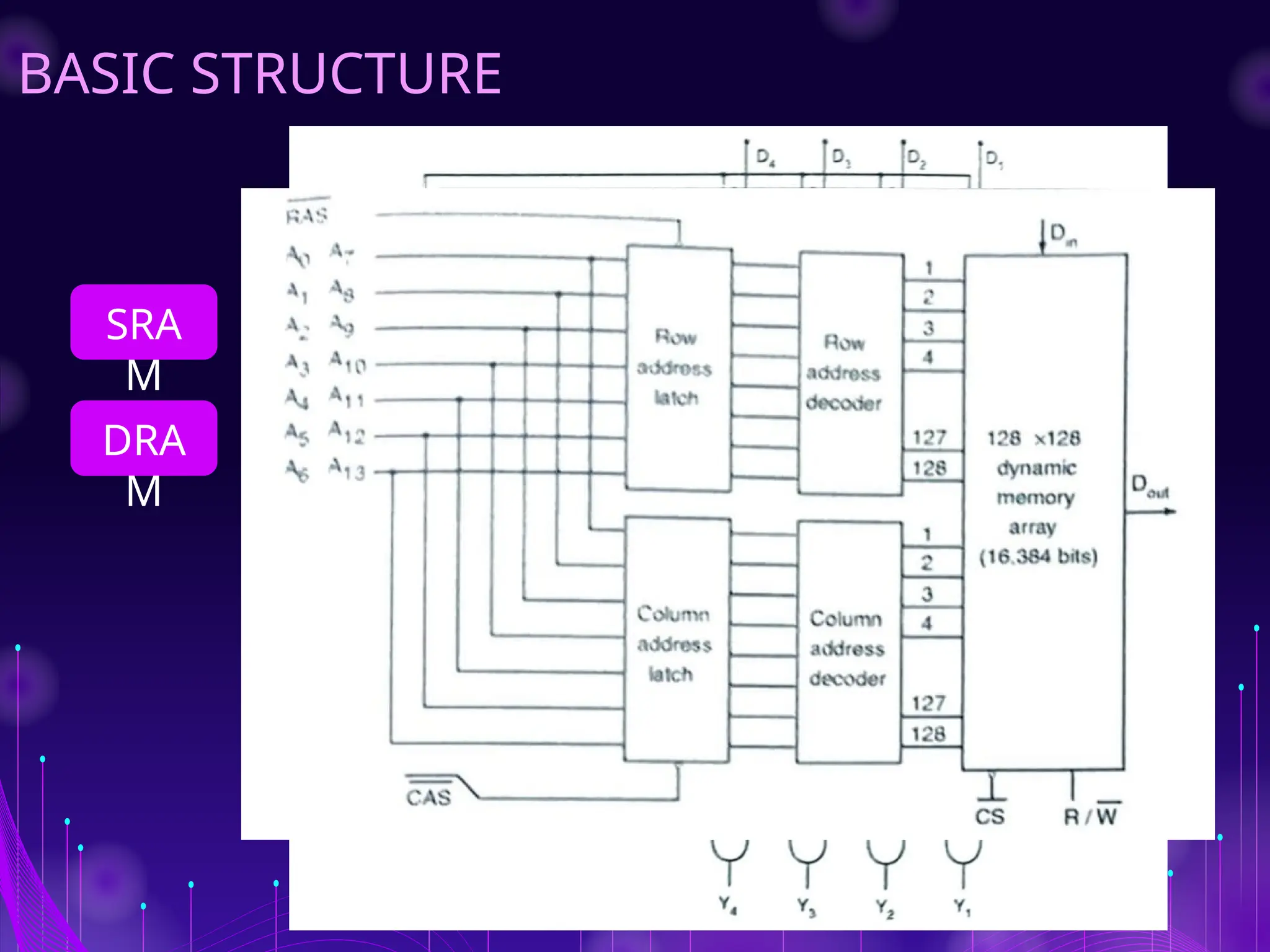
The document discusses Random Access Memory (RAM), detailing its importance in digital electronics for storing data and instructions. It contrasts two primary types of RAM: Static RAM (SRAM), which offers fast access but has higher power consumption and costs, and Dynamic RAM (DRAM), which has slower access speeds but greater storage capacity and efficiency. Overall, SRAM is suited for applications requiring quick data retrieval, while DRAM is commonly used as main memory in computers.