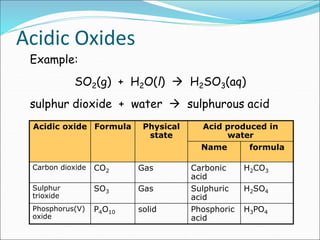
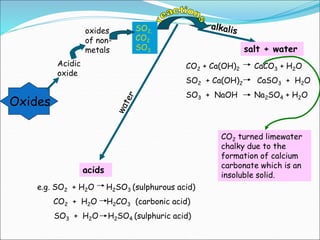
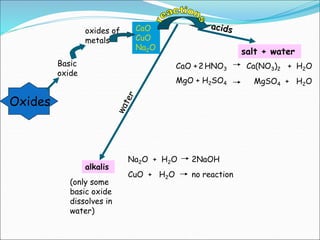
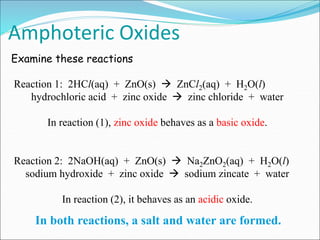
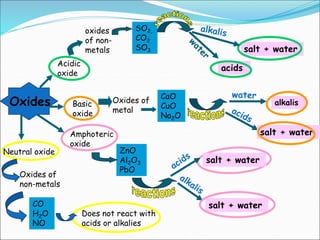
An oxide is a compound formed from oxygen and another element. There are four main types of oxides: acidic, basic, amphoteric, and neutral. Acidic oxides dissolve in water to form acids, basic oxides are insoluble in water and react with acids to form salts, amphoteric oxides react with both acids and bases, and neutral oxides do not react with acids or bases. Common examples of each type and their reactions are provided.