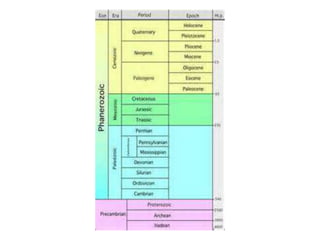
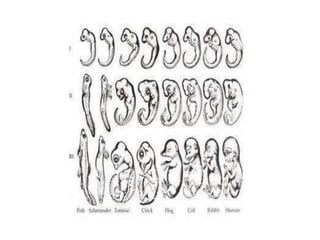
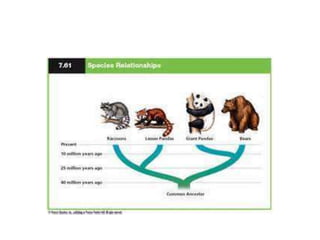
Charles Darwin developed the theory of evolution by natural selection based on observations he made during a 5-year voyage as the naturalist on the HMS Beagle. Some of his most important observations included the diversity of life in South America and the Galapagos Islands, as well as adaptations and differences between similar species on different islands. These observations, combined with his knowledge of selective breeding, led him to propose natural selection as the mechanism of evolution. Natural selection results from overproduction of offspring, competition for limited resources, and inherited variations between individuals that influence survival and reproduction.