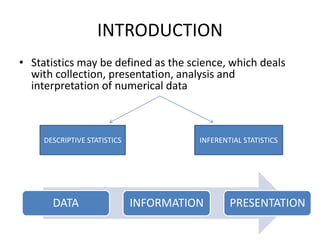
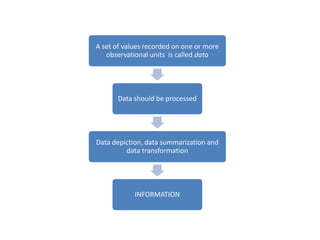
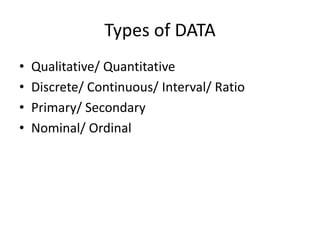
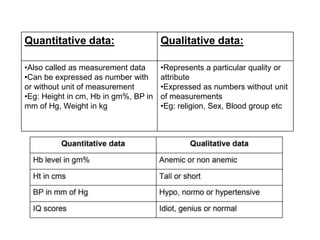
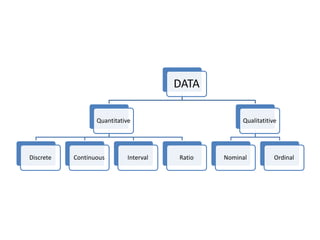
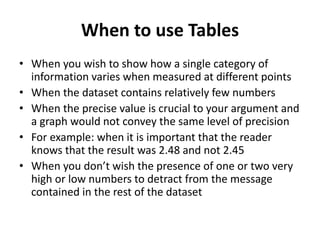
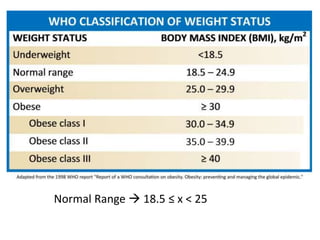
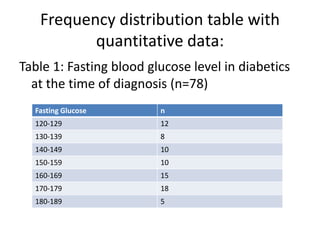
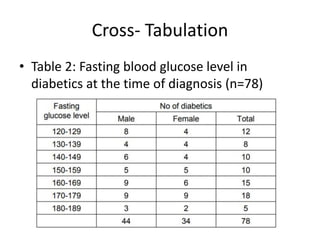
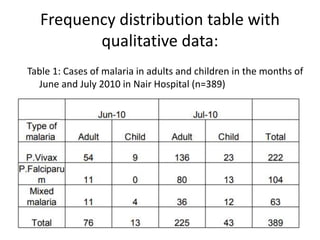
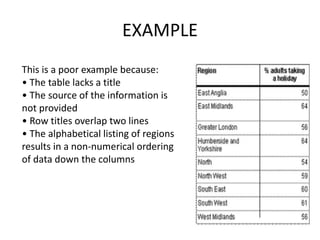
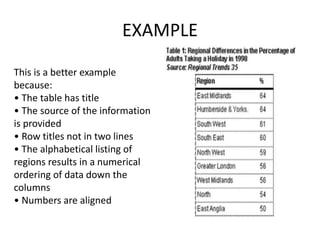
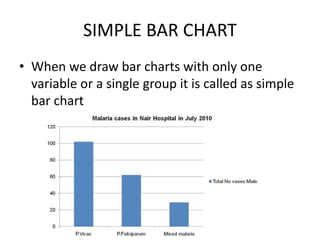
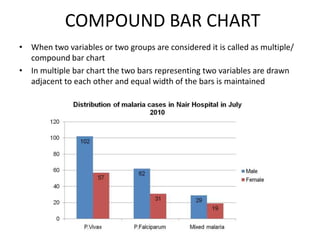
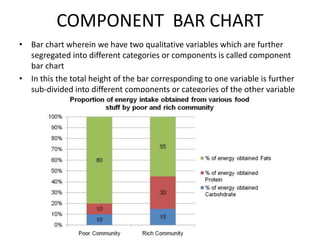
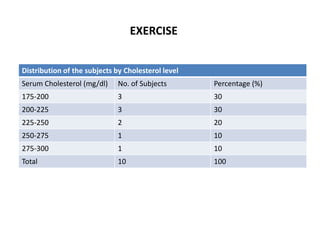
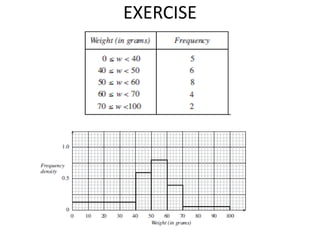
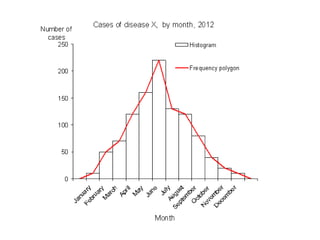
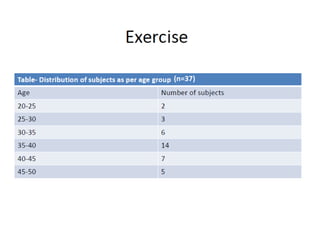
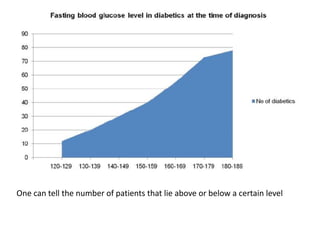
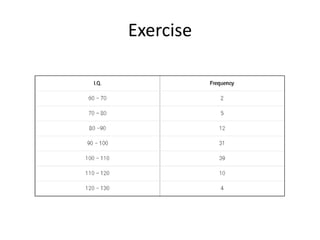
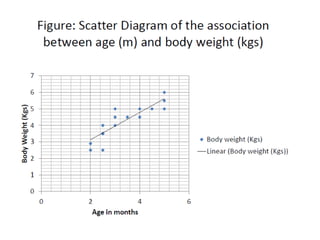
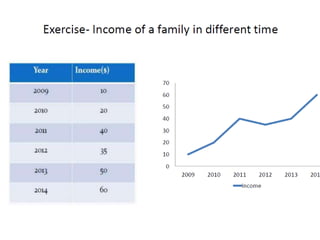
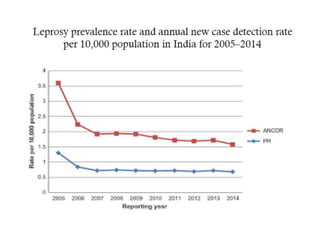
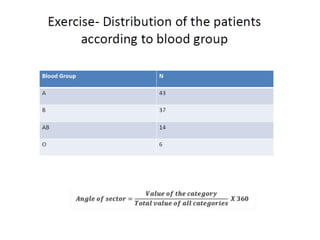
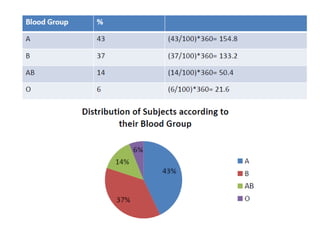
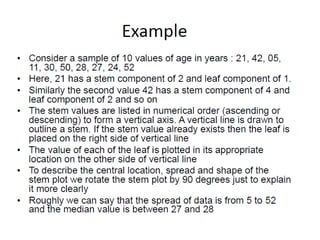
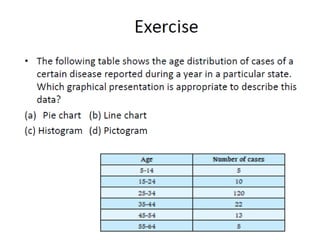
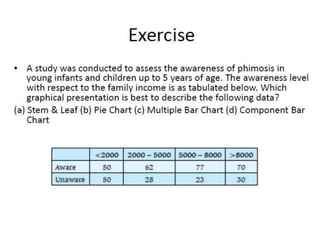
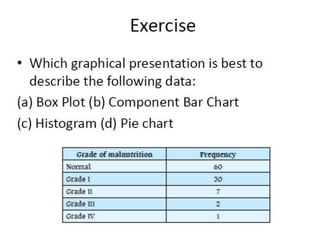
This document discusses different types of data and ways to represent data graphically and tabularly. It defines qualitative and quantitative data, as well as discrete, continuous, interval and ratio data. Primary and secondary data and nominal and ordinal data are also defined. Common ways to represent data include tables, bar charts, histograms, frequency polygons, cumulative frequency curves, scatter diagrams, line diagrams and pie charts. General principles for effective graphical representation are outlined.