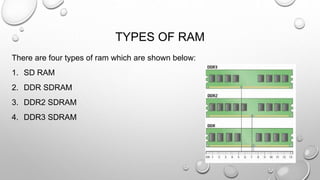
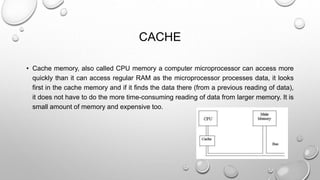
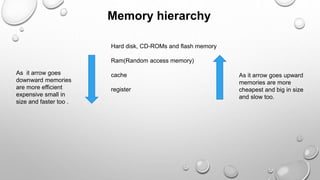
There are two main types of computer memory: volatile and non-volatile. Volatile memory, like RAM, loses its stored data when power is removed but is fast, while non-volatile memory, like ROM, retains data without power but is slower. RAM is the primary memory for running programs and comes in types like SDRAM, DDR SDRAM, DDR2 SDRAM, and DDR3 SDRAM that have faster data transfer speeds. Caches and registers are even faster but smaller memory types close to the CPU. Non-volatile memory includes ROM for long-term storage and flash memory for rewritable storage.