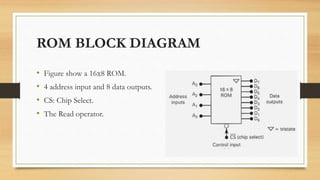
The document discusses RAM and ROM memory. RAM (random access memory) is the main memory of a computer system, used to temporarily store data and instructions. It is volatile memory that allows reading and writing. ROM (read only memory) is permanent memory where instructions cannot be changed; it is used to store basic input/output functions. The document outlines the structure of memory chips and different types of RAM like DRAM and SRAM and ROM.