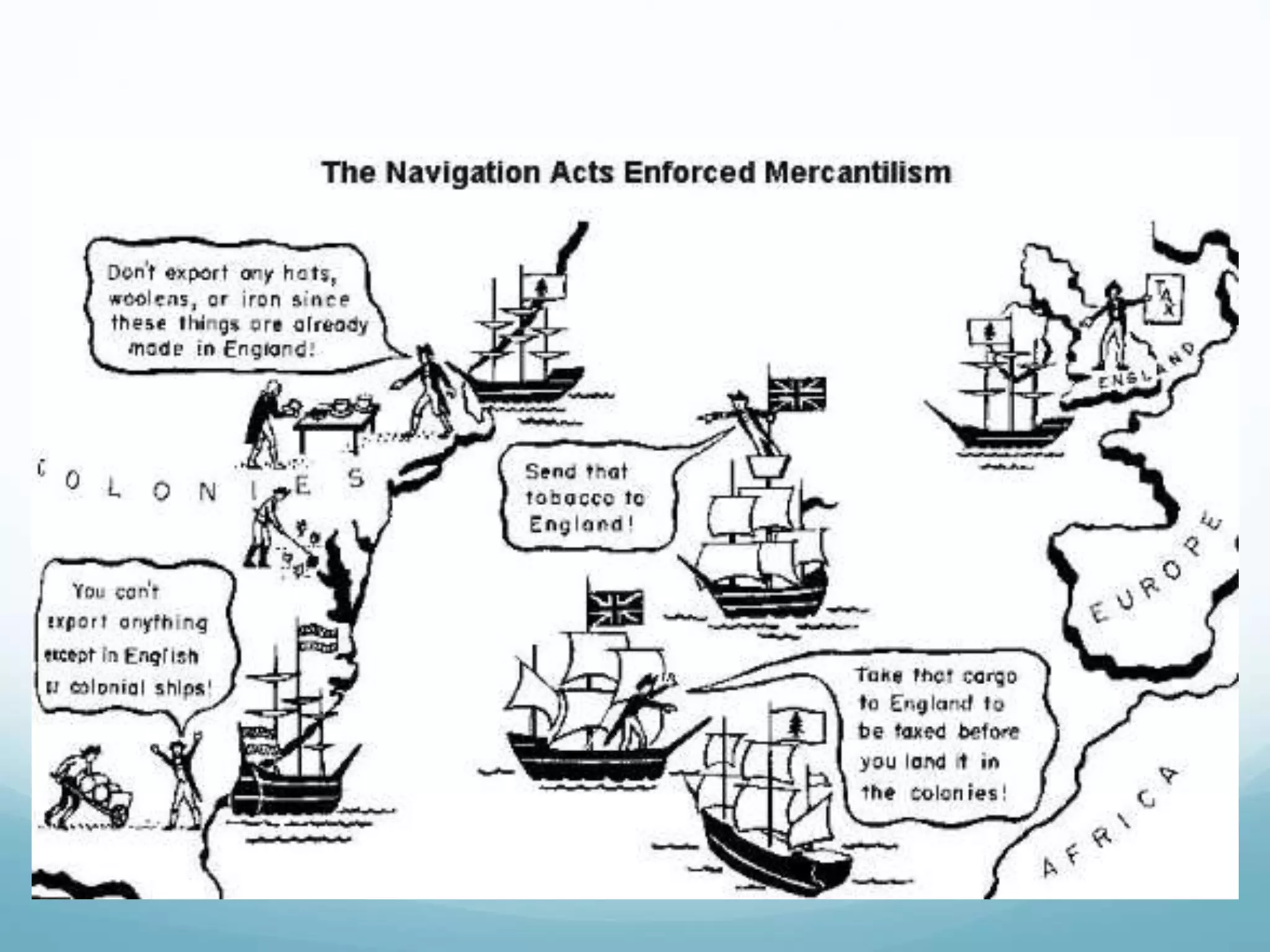
The document discusses Britain's mercantilist policies toward the American colonies from the 17th century. It explains that the main purpose of the colonial system was to enrich Britain by establishing strict control over colonial trade. The colonies were required to export raw goods to Britain and import finished British manufactures. The Navigation Acts regulated colonial trade by restricting it to British and colonial ships. While beneficial to Britain, these policies led to resentment in the colonies and unrest grew as colonial prosperity increased Britain's control.