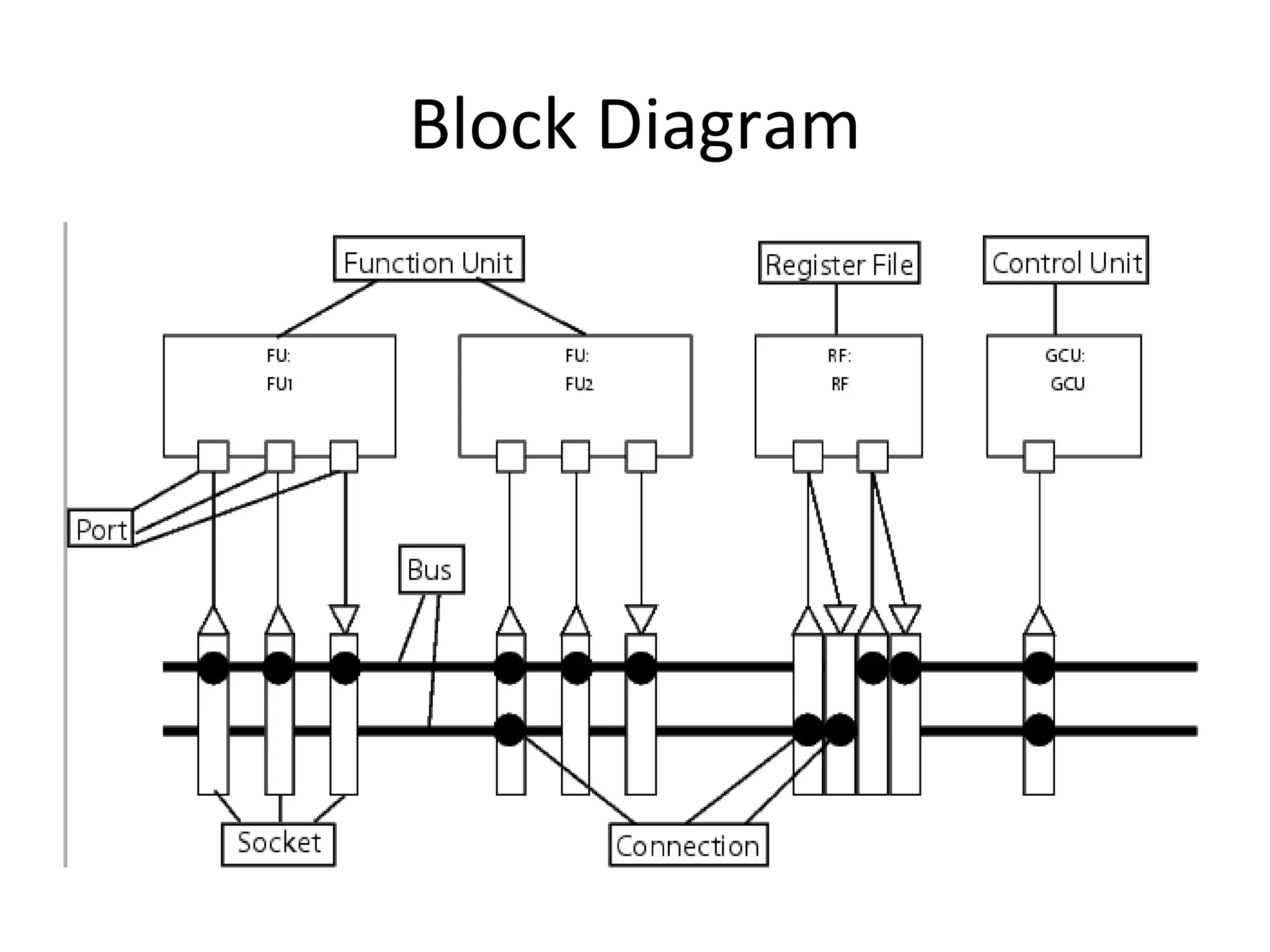
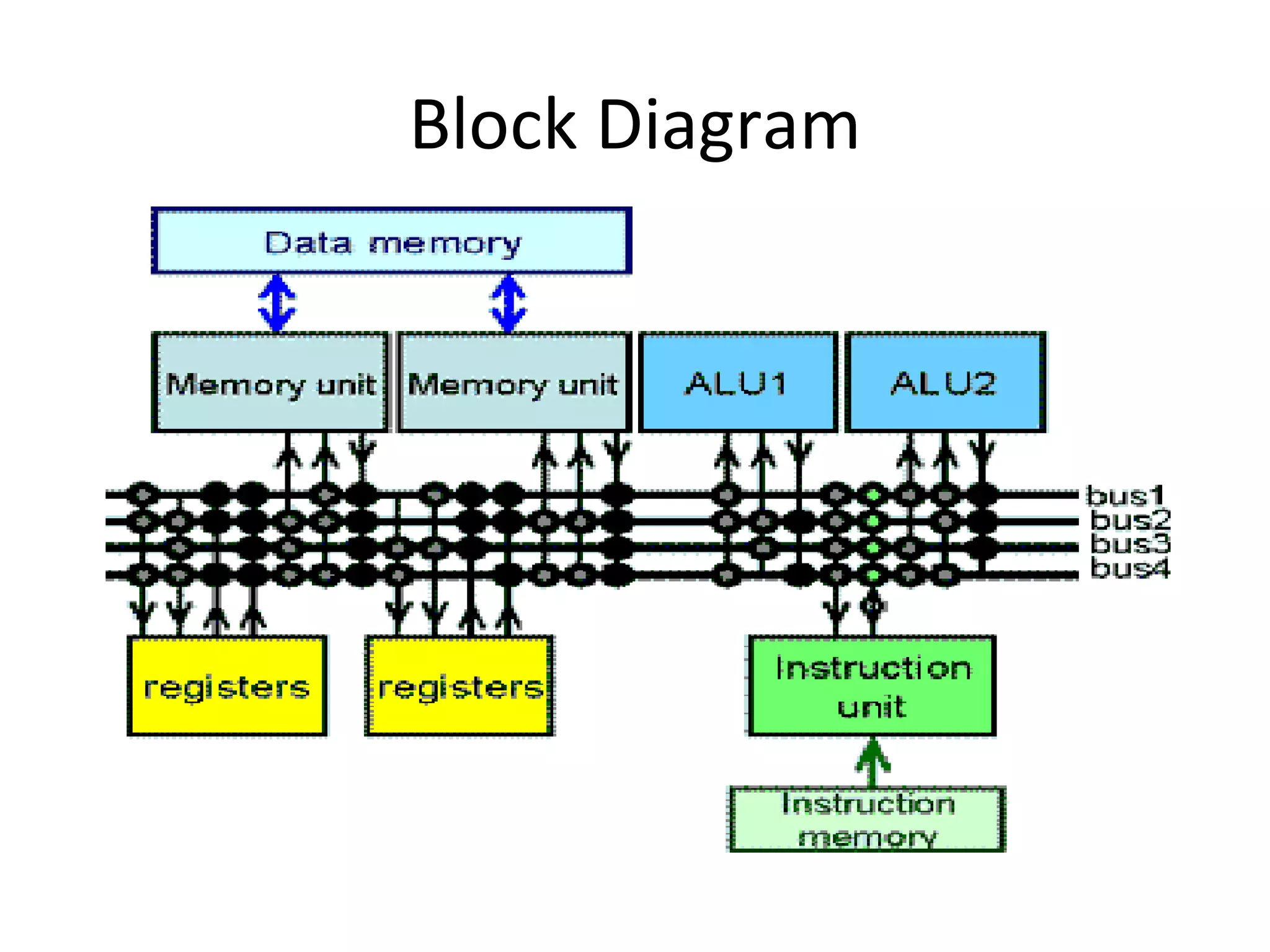
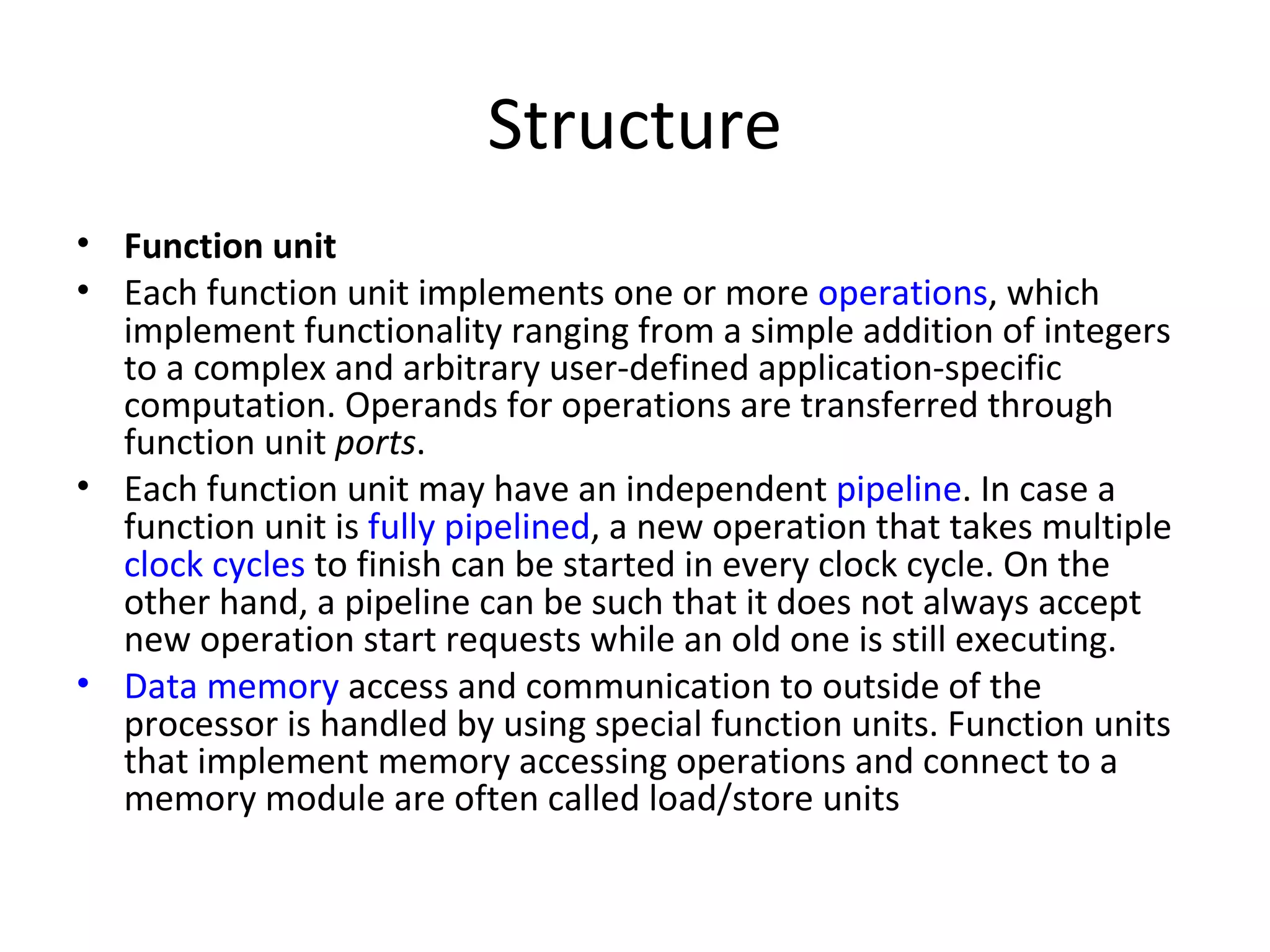
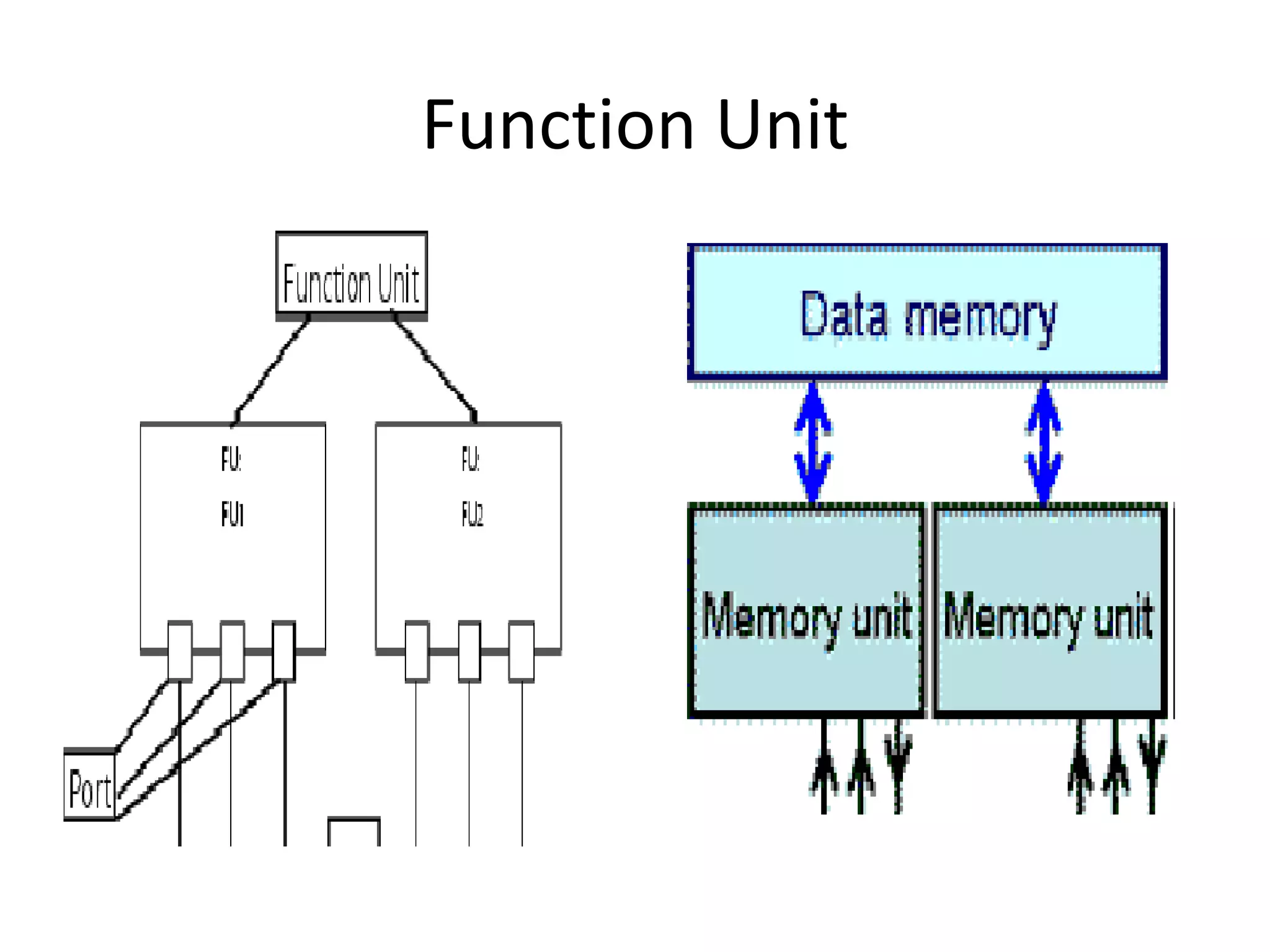
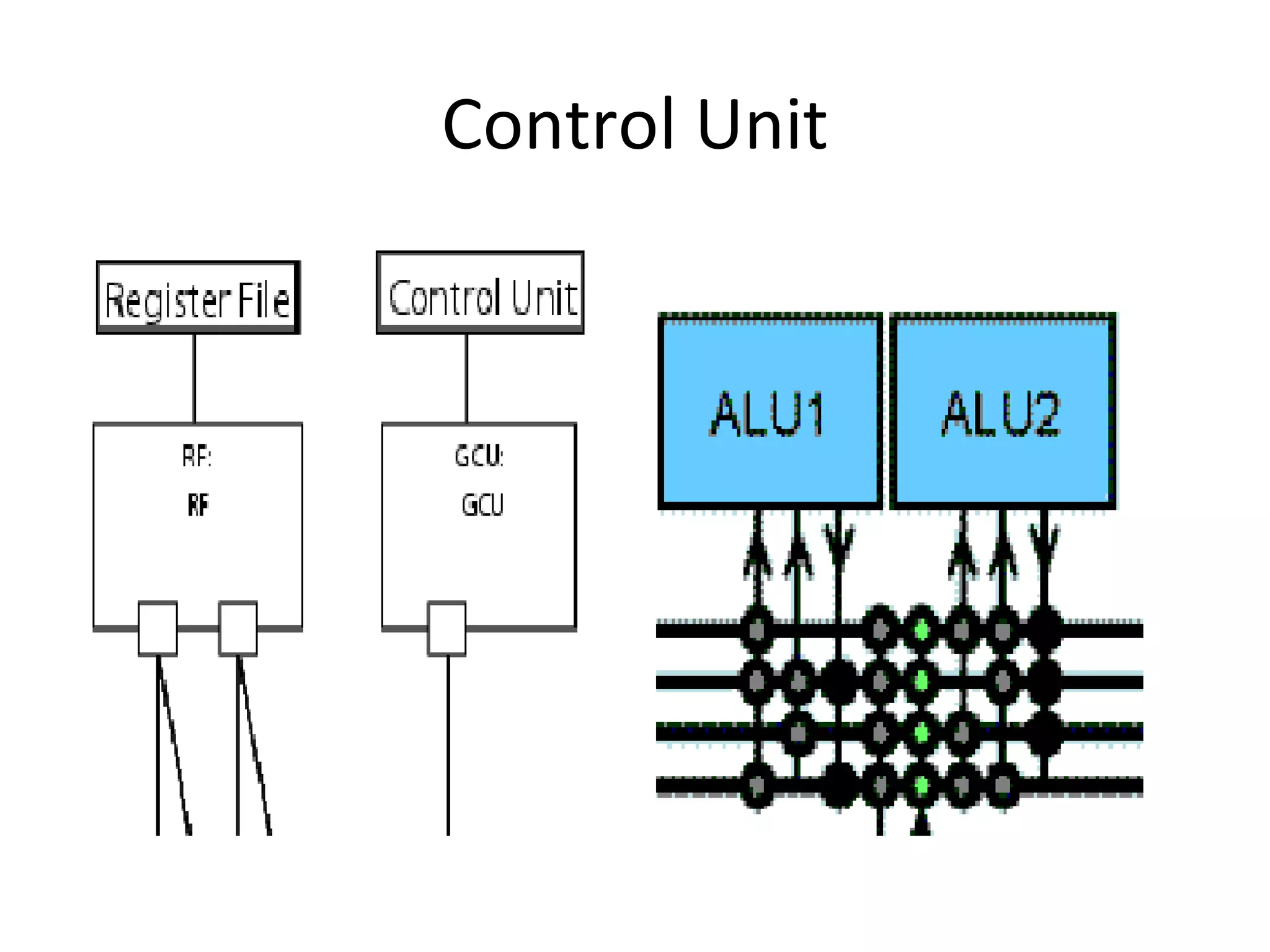
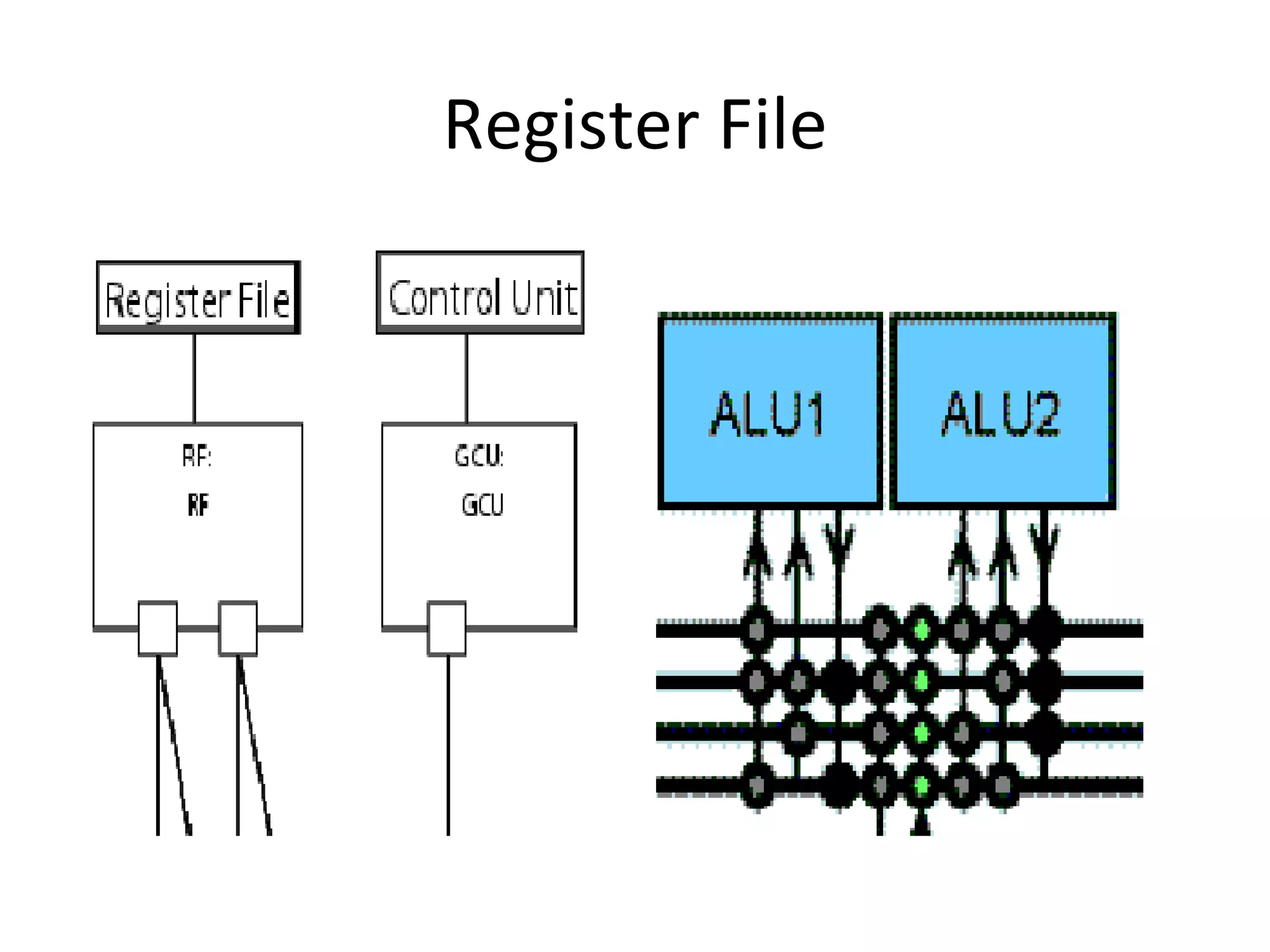
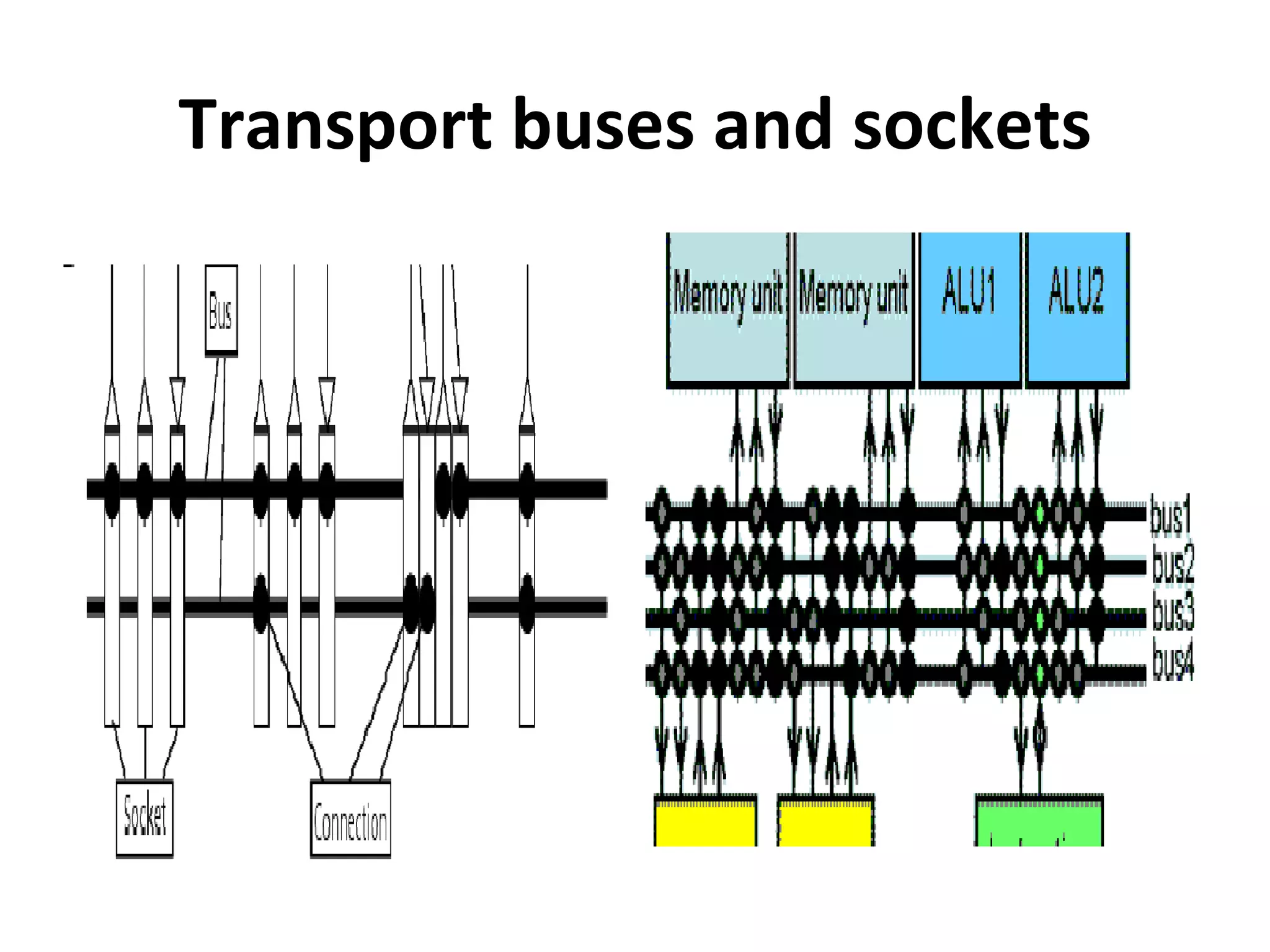
Transport triggered architecture uses function units, a control unit, and register files connected by transport buses and sockets. Each function unit implements operations like addition or user-defined computations. The control unit fetches and executes instructions from instruction memory. Register files store variables. Data and instructions are transferred between components through the transport buses and sockets.