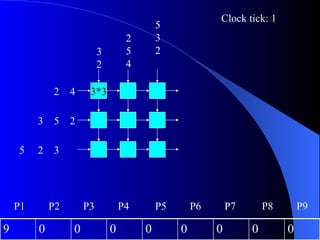
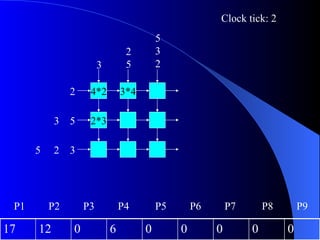
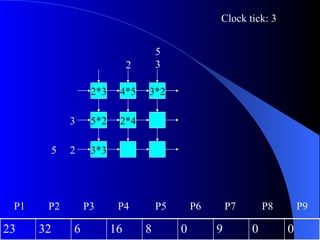
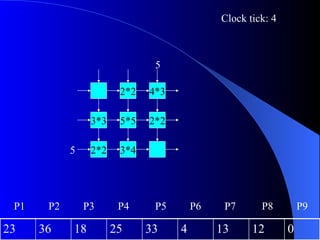
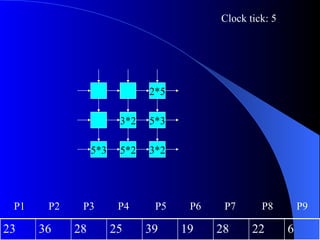
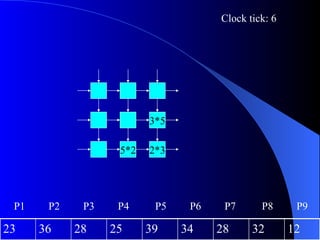
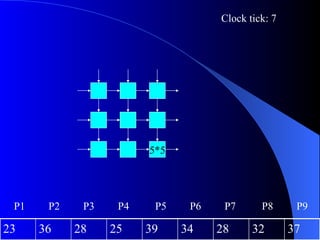
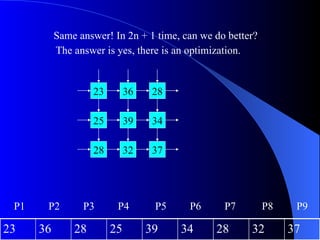
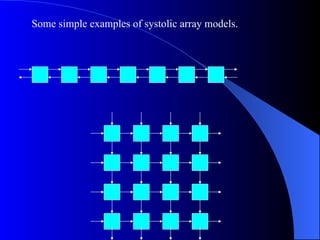
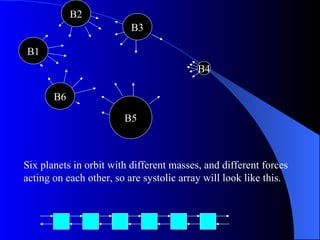
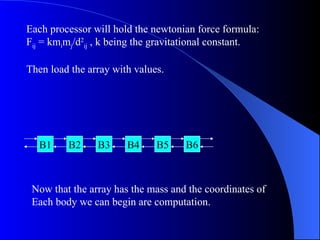
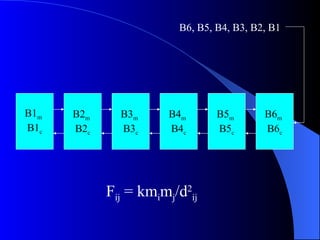
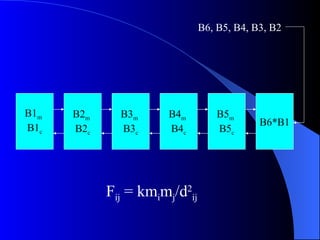
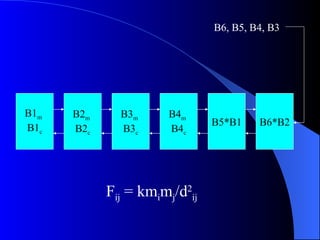
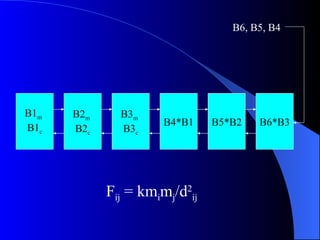
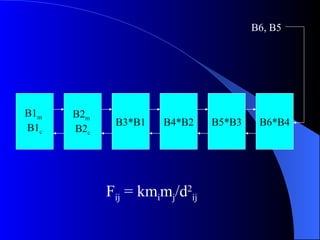
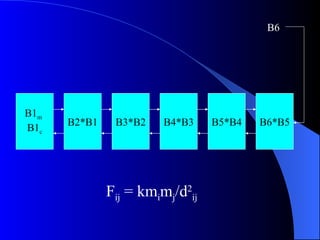
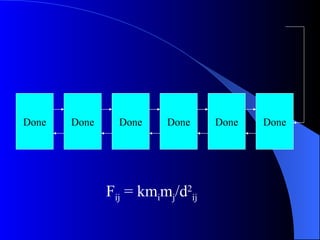
Systolic arrays are arrangements of processors where data flows synchronously between neighboring processors. Each processor receives data from neighbors, processes it, and outputs results to opposite neighbors. This allows certain problems to be solved much more efficiently, such as reducing the n-body problem from n^2 to n time. Matrix multiplication can also be performed in linear rather than cubic time using a systolic array. While powerful for specific applications, systolic arrays are also expensive and specialized, and not needed for most problems.






![Matrix Multiplication
a11 a12 a13 b11 b12 b13 c11 c12 c13
a21 a22 a23
a31 a32 a33 * b21 b22 b23
b31 b32 b33
= c21 c22 c23
c31 c32 c33
Conventional Method: N3
For I = 1 to N
For J = 1 to N
For K = 1 to N
C[I,J] = C[I,J] + A[J,K] * B[K,J];](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/lec2-final-120404001346-phpapp02/85/Lec2-final-18-320.jpg)