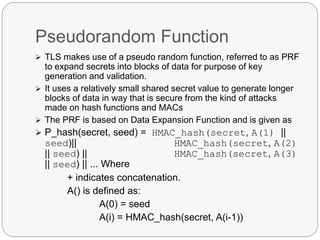
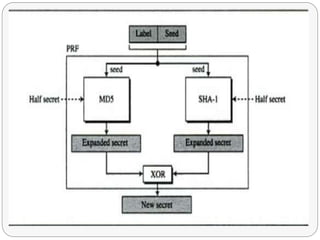
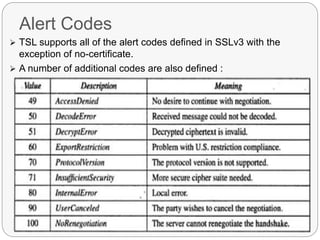
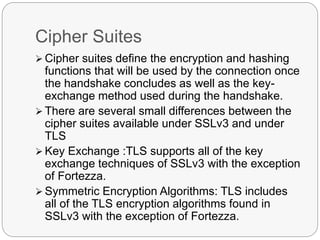
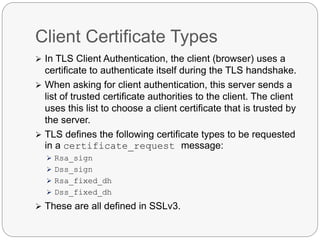
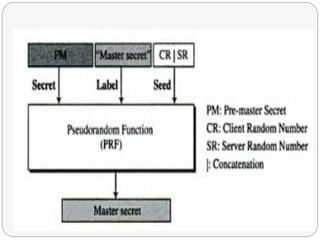
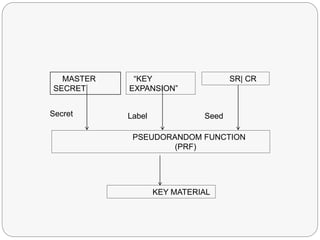
TLS is an IETF standard similar to SSL that provides cryptographic security and secure connections between parties through the establishment of a secure session. It aims to securely transmit data via record layer encapsulation and encryption, using techniques like cryptographic computations, MACs, and the generation of secrets through pseudorandom functions and data expansion. TLS supports various cipher suites, certificate types, and alert codes while making some changes compared to SSL in areas like record formatting, PRF usage, and handshake messaging.







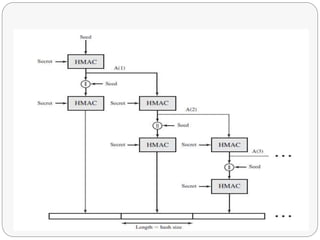
![Message Authentication Code
The Message Authentication Code (MAC) used for TLS is
HMAC
HMAC is expressed by the following equation,
HMACK(M) = H[(K+ opad)||H[(K+ ipad)||M]]
Where:
: is concatenation
M : is the plain-text to be encrypted
H : is the hashing function (either MD-5 or SHA-1)
K+ : secret key padded with zeros on the left so that the result
is equal to the block length of the hash code (for MD-5 and SHA-
1 block length is 512 bits)
ipad : 00110110 (36 in hexa decimal) repeated 64 times (512
bits)
opad : 01011101 (5c in hexa decimal) repeated 64 times (512
bits)](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/transportlayersecurity-140807005600-phpapp01/85/Transport-layer-security-11-320.jpg)