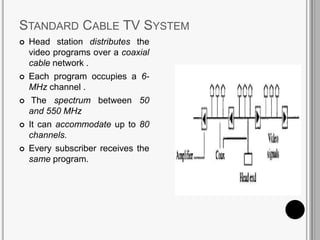
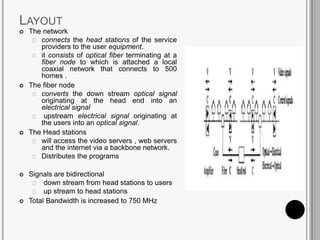
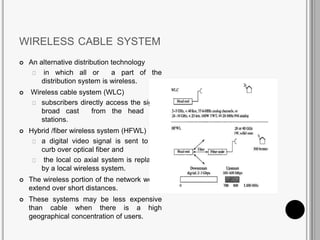
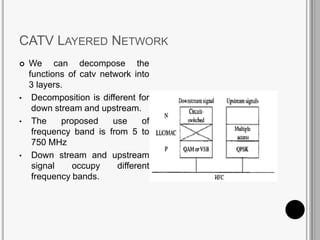
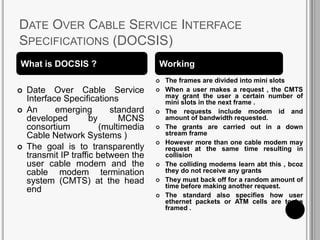
CATV systems distribute television programs via coaxial cables or fiber optic networks from a head end station to subscribers. Signals are transmitted downstream from the head end to users and upstream from users back to the head end. The cable distribution network consists of head end stations connected through coaxial cables or fiber optic lines to neighborhoods, where the signal is distributed to subscribers. CATV networks can support up to 80 channels in the 50-550 MHz bandwidth and provide internet and telephone services in addition to television programming.