Embed presentation
Downloaded 47 times


![SYSTEM
An input-output relationship is called a
system if there is a unique output for
any given input.
Y(n1,n2) = T[X(n1,n2)]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/twodimensionalsignalsandsystems-140125013135-phpapp02/75/Two-dimensional-signals-and-systems-7-2048.jpg)
![LINEAR SYSTEMS
The linearity of a system T is defined as
Linearity:
T[a X1(n1,n2) + b X2(n1,n2)] = a Y1 + b
Y2
(i.e., principle of superposition holds).](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/twodimensionalsignalsandsystems-140125013135-phpapp02/75/Two-dimensional-signals-and-systems-8-2048.jpg)
![LINEAR SHIFT INVARIENT
SYSTEMS
Shift Invariance:
T[X(m-k, n-l)] = Y(m-k, n-l) where
Y(m,n) = T[X(m,n)].](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/twodimensionalsignalsandsystems-140125013135-phpapp02/75/Two-dimensional-signals-and-systems-9-2048.jpg)
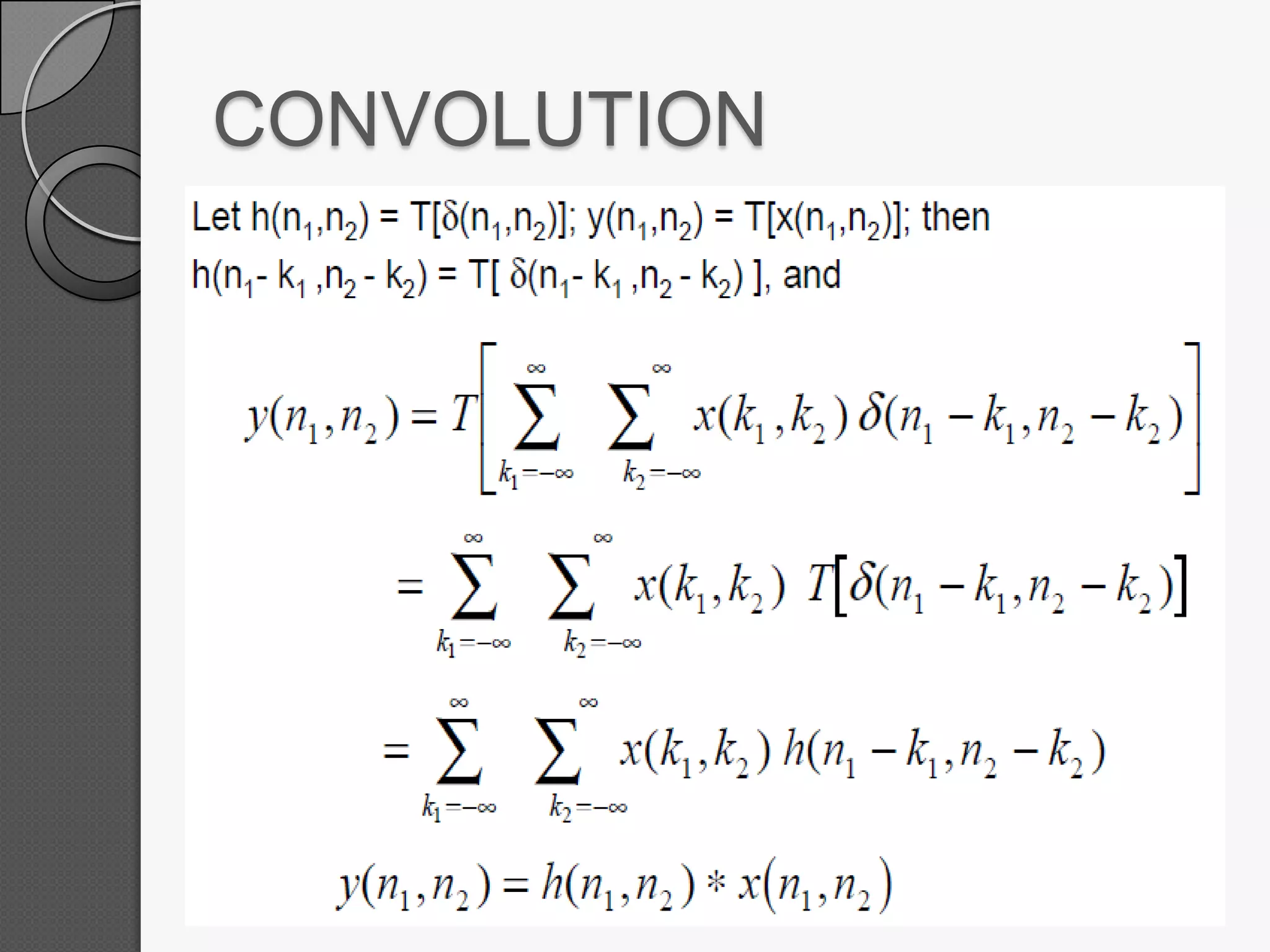
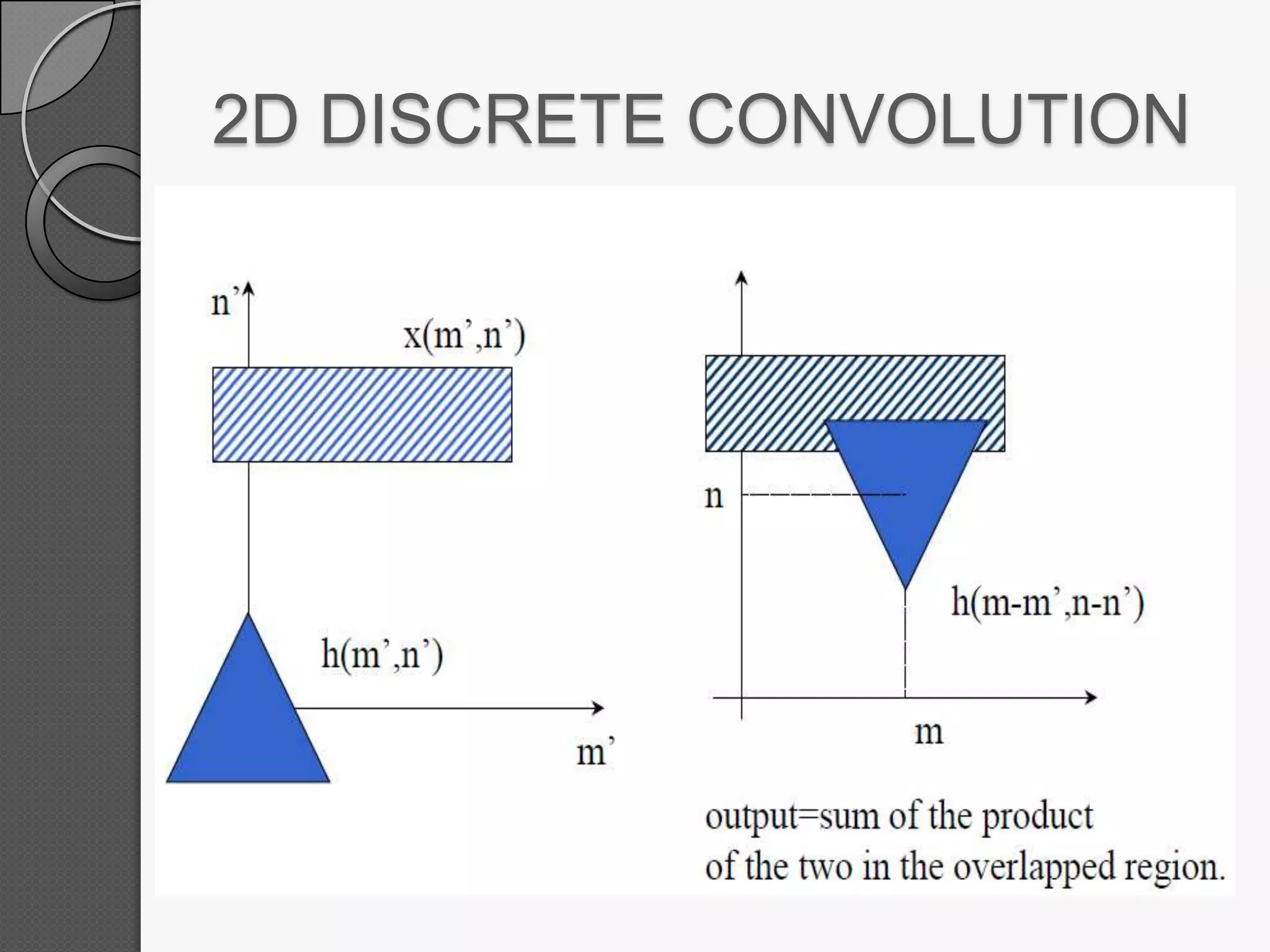
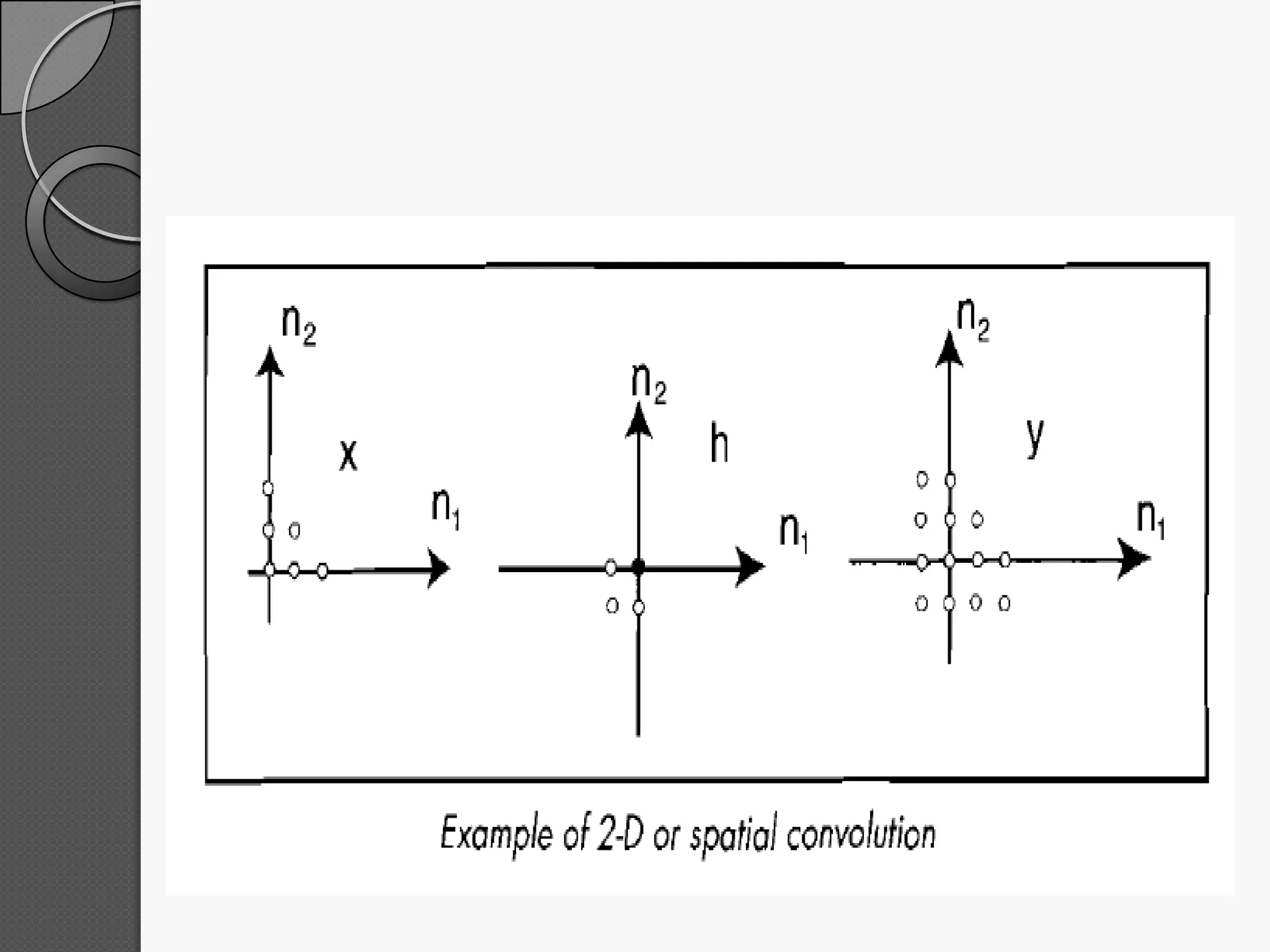


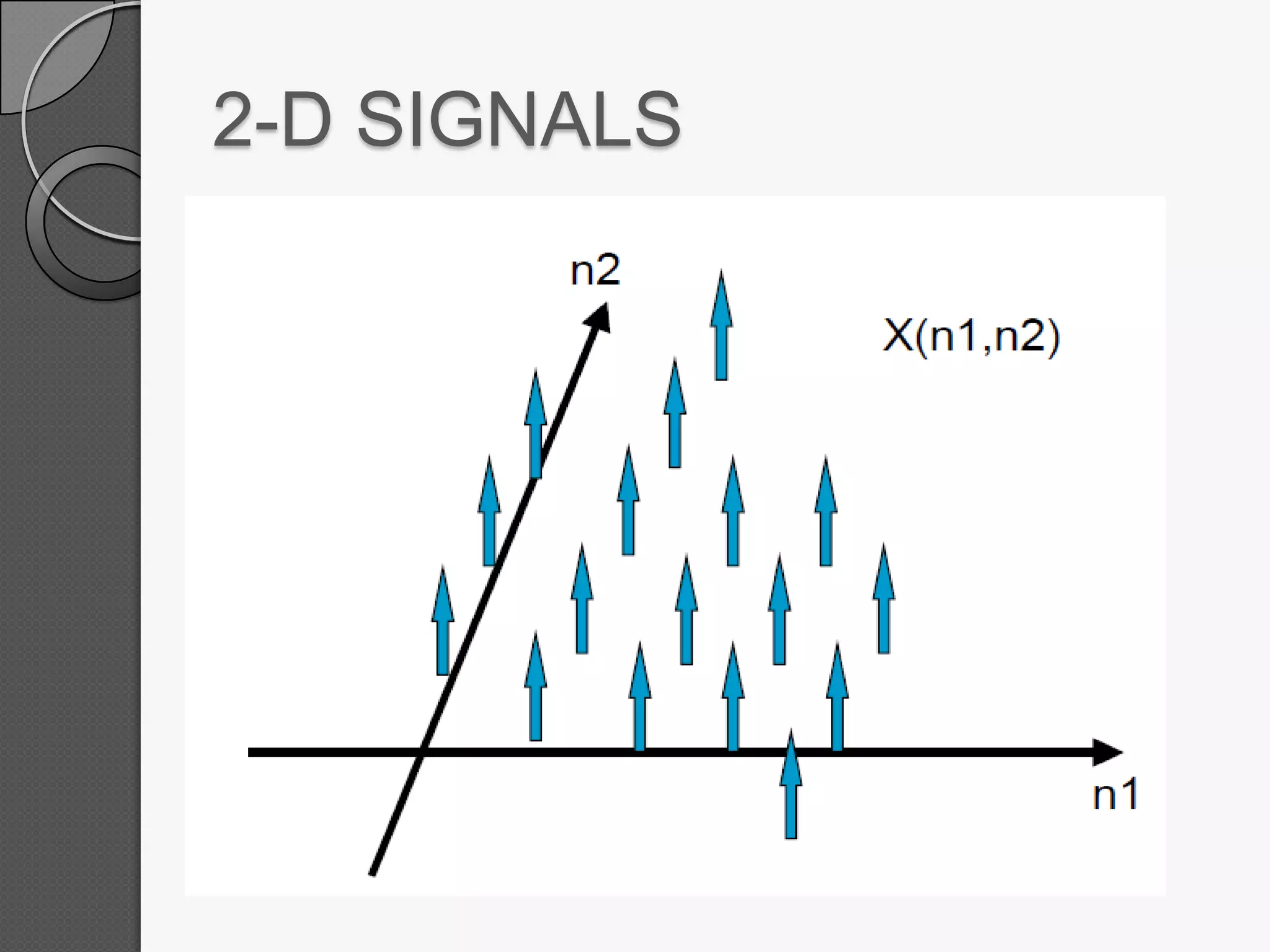
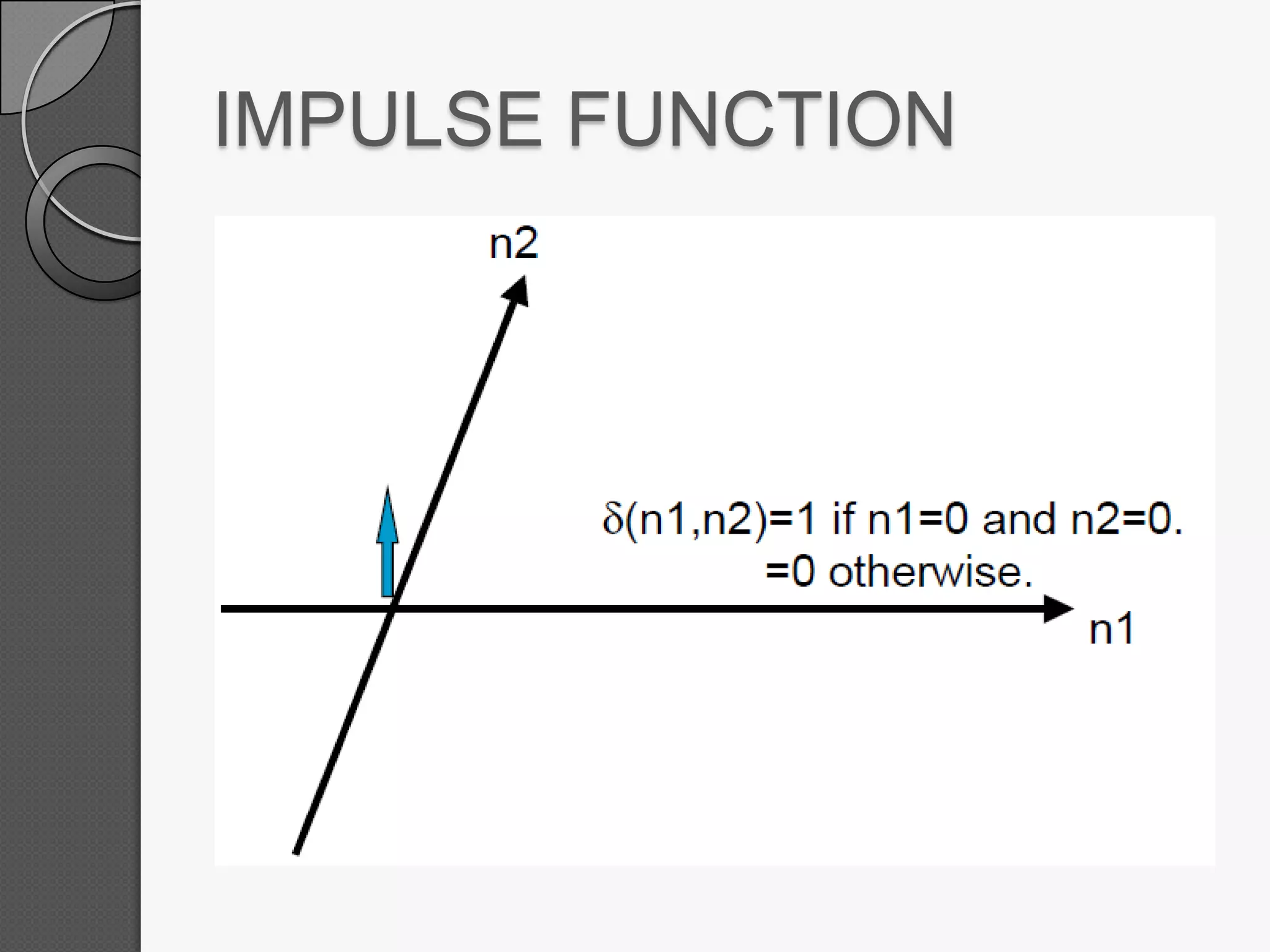
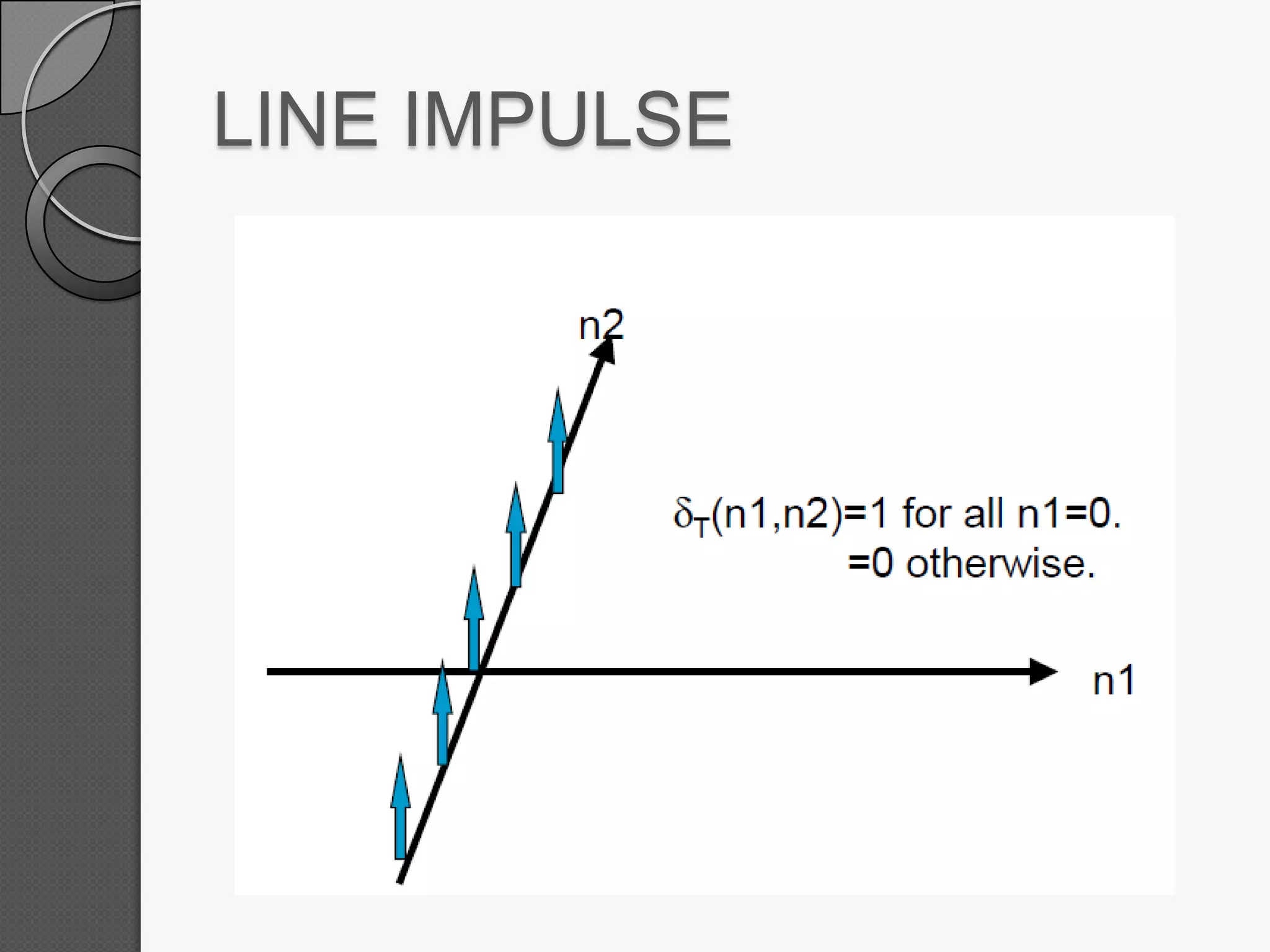
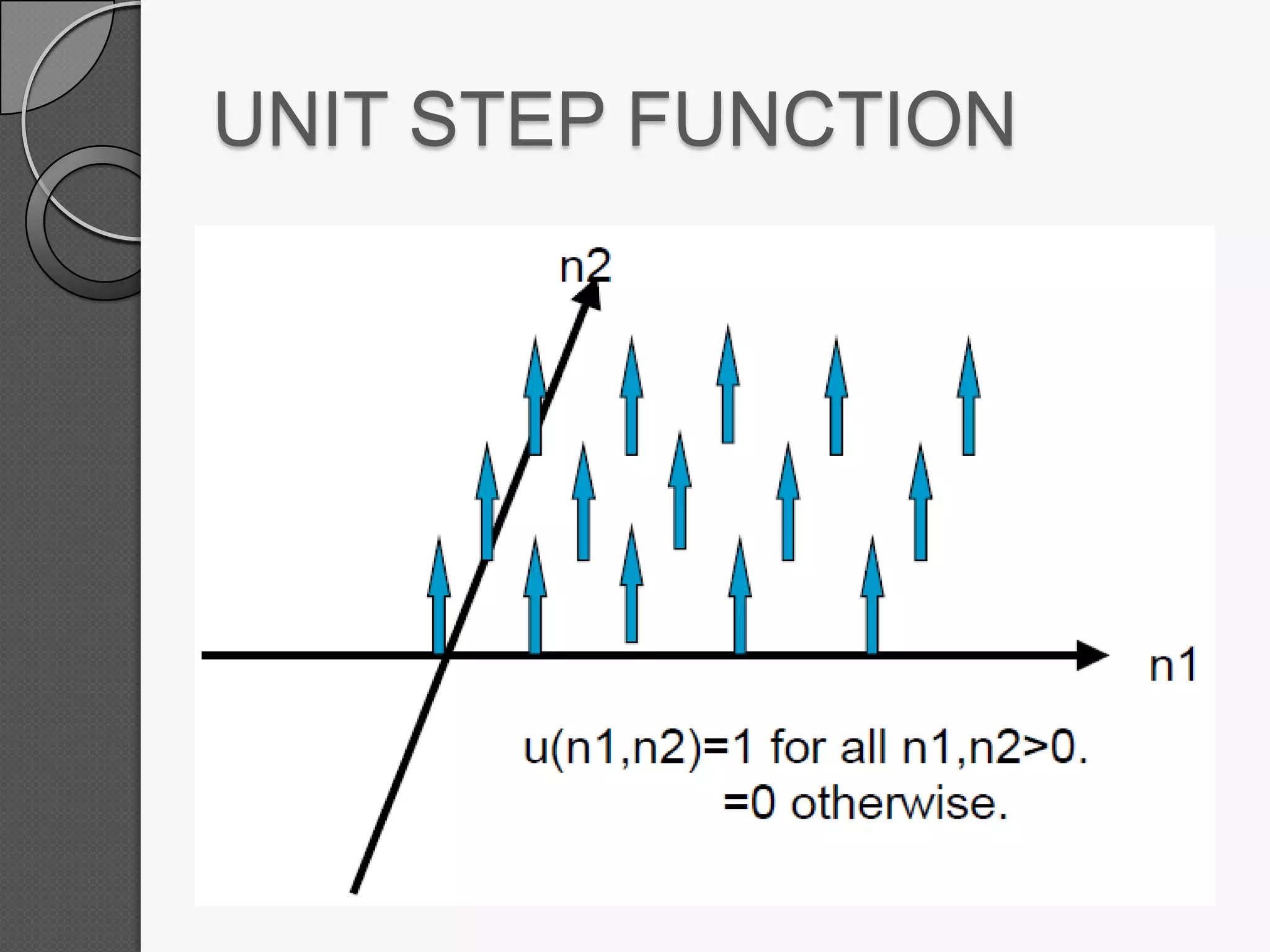
This document discusses two-dimensional signals and systems. It defines 2D signals as having two independent variables, like f(x,y), compared to 1D signals which have one variable like f(t). It also defines key concepts for 2D systems like impulse functions, step functions, linearity, shift-invariance, and 2D discrete convolution. Linear systems follow the principle of superposition and produce unique outputs from given inputs.






![SYSTEM
An input-output relationship is called a
system if there is a unique output for
any given input.
Y(n1,n2) = T[X(n1,n2)]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/twodimensionalsignalsandsystems-140125013135-phpapp02/75/Two-dimensional-signals-and-systems-7-2048.jpg)
![LINEAR SYSTEMS
The linearity of a system T is defined as
Linearity:
T[a X1(n1,n2) + b X2(n1,n2)] = a Y1 + b
Y2
(i.e., principle of superposition holds).](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/twodimensionalsignalsandsystems-140125013135-phpapp02/75/Two-dimensional-signals-and-systems-8-2048.jpg)
![LINEAR SHIFT INVARIENT
SYSTEMS
Shift Invariance:
T[X(m-k, n-l)] = Y(m-k, n-l) where
Y(m,n) = T[X(m,n)].](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/twodimensionalsignalsandsystems-140125013135-phpapp02/75/Two-dimensional-signals-and-systems-9-2048.jpg)



