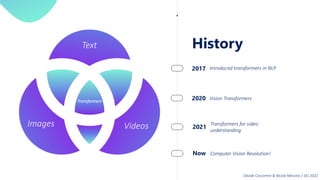
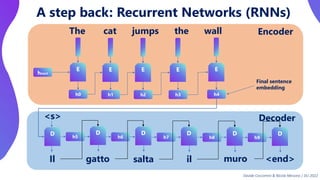
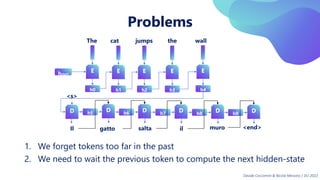
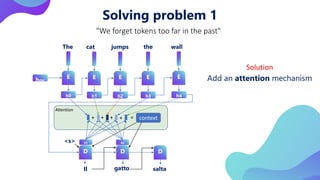
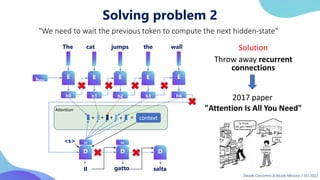
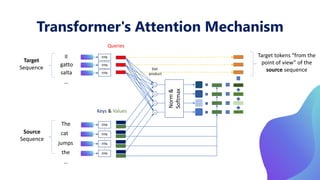
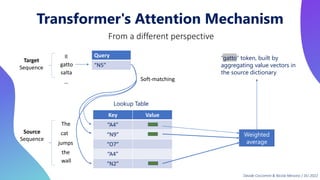
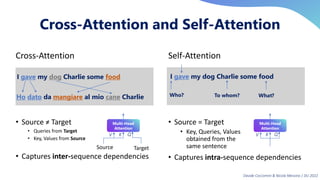
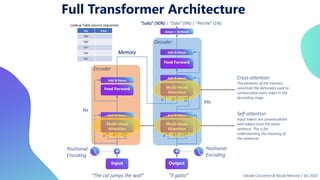
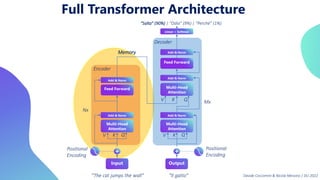
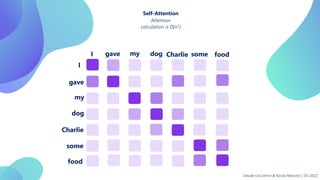
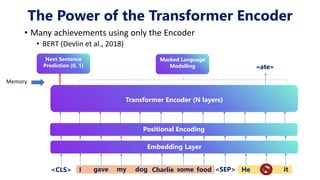
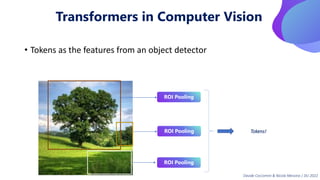
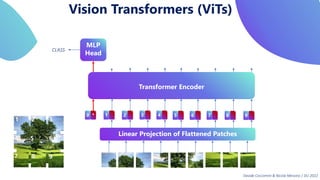
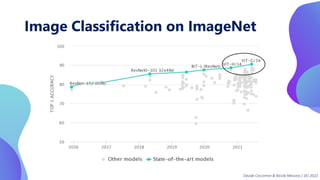
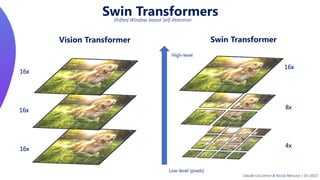
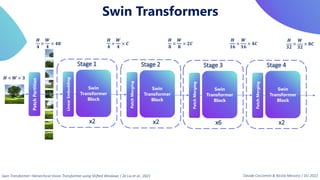
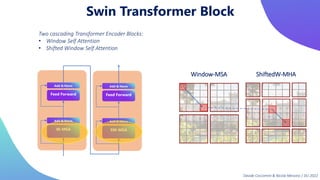
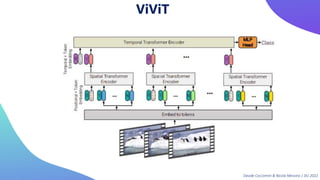
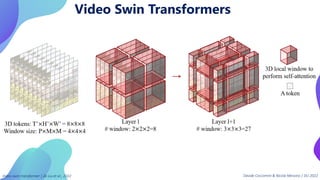
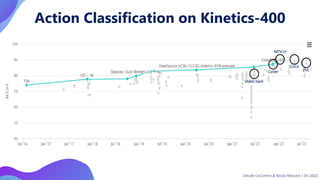
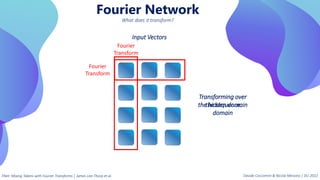
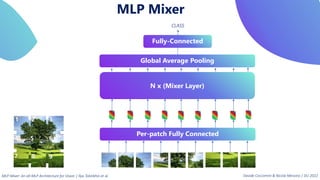
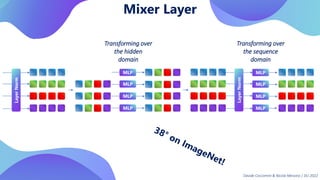
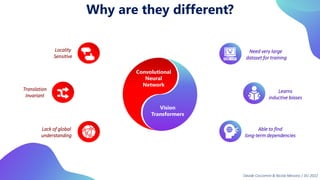
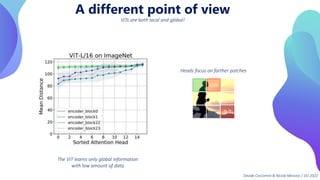
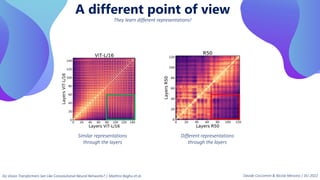
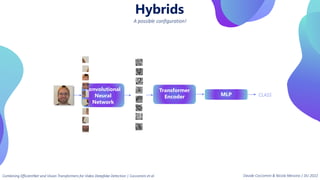
This document provides an overview of transformers in computer vision. It discusses how transformers were originally developed for natural language processing using attention mechanisms instead of recurrent connections. Vision transformers apply this approach to images by treating patches as tokens and using self-attention. Early vision transformers achieved strong results on image classification tasks. Recent developments include Swin transformers which use shifted windows to incorporate positional information, and models that combine convolutional and transformer architectures. Transformers are also being applied to video understanding tasks. The document explores different transformer architectures and applications of vision transformers.