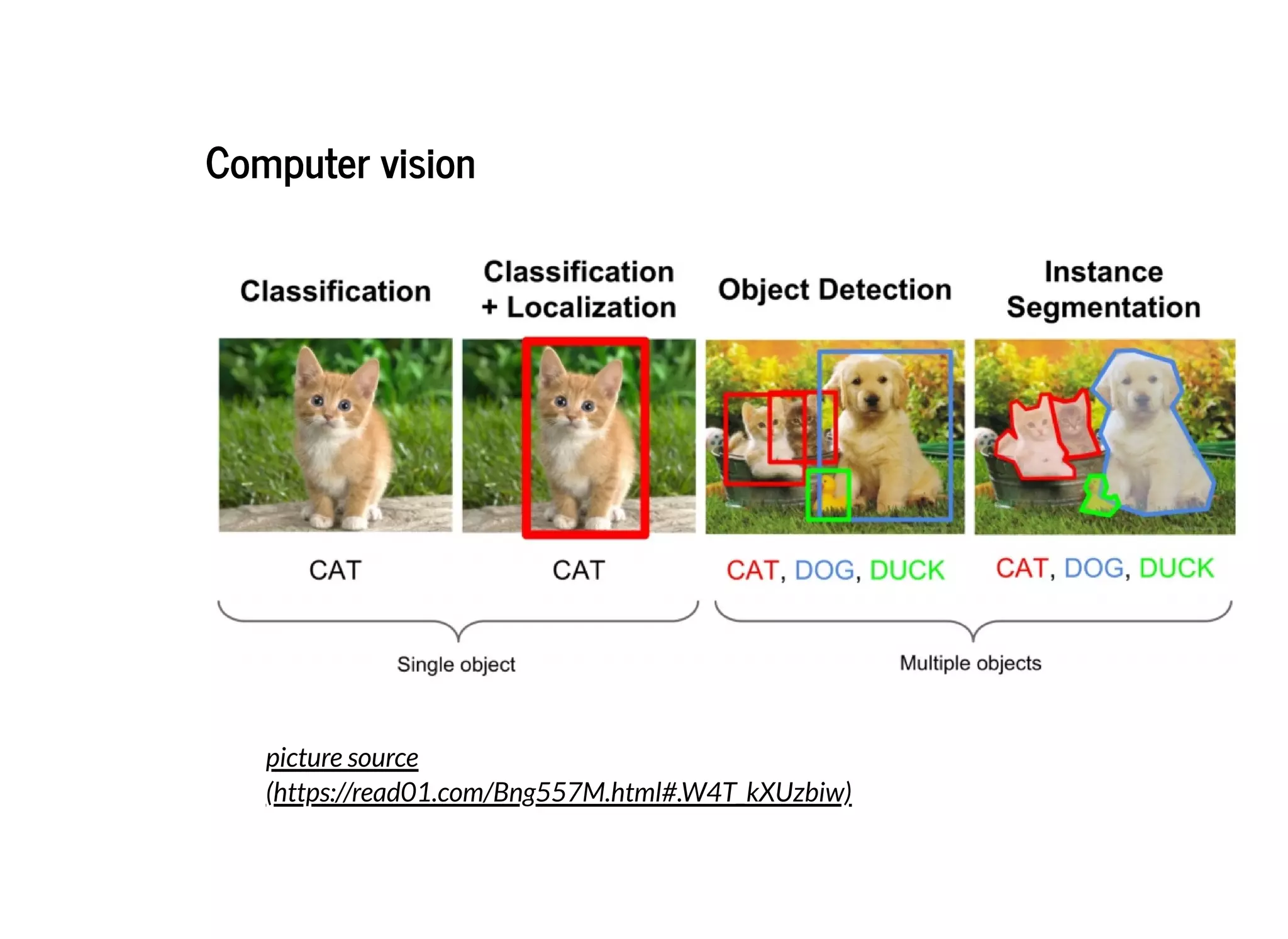
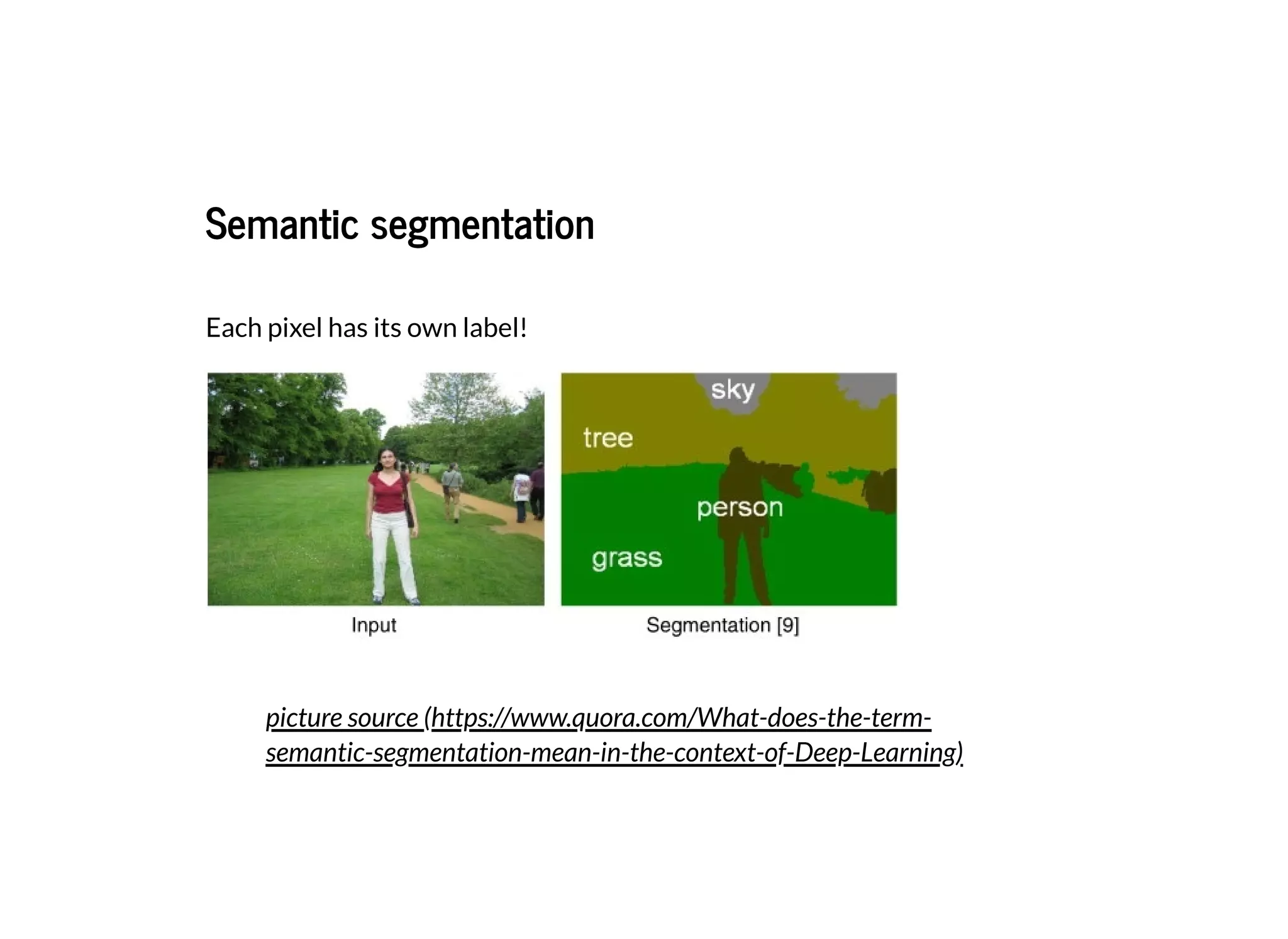
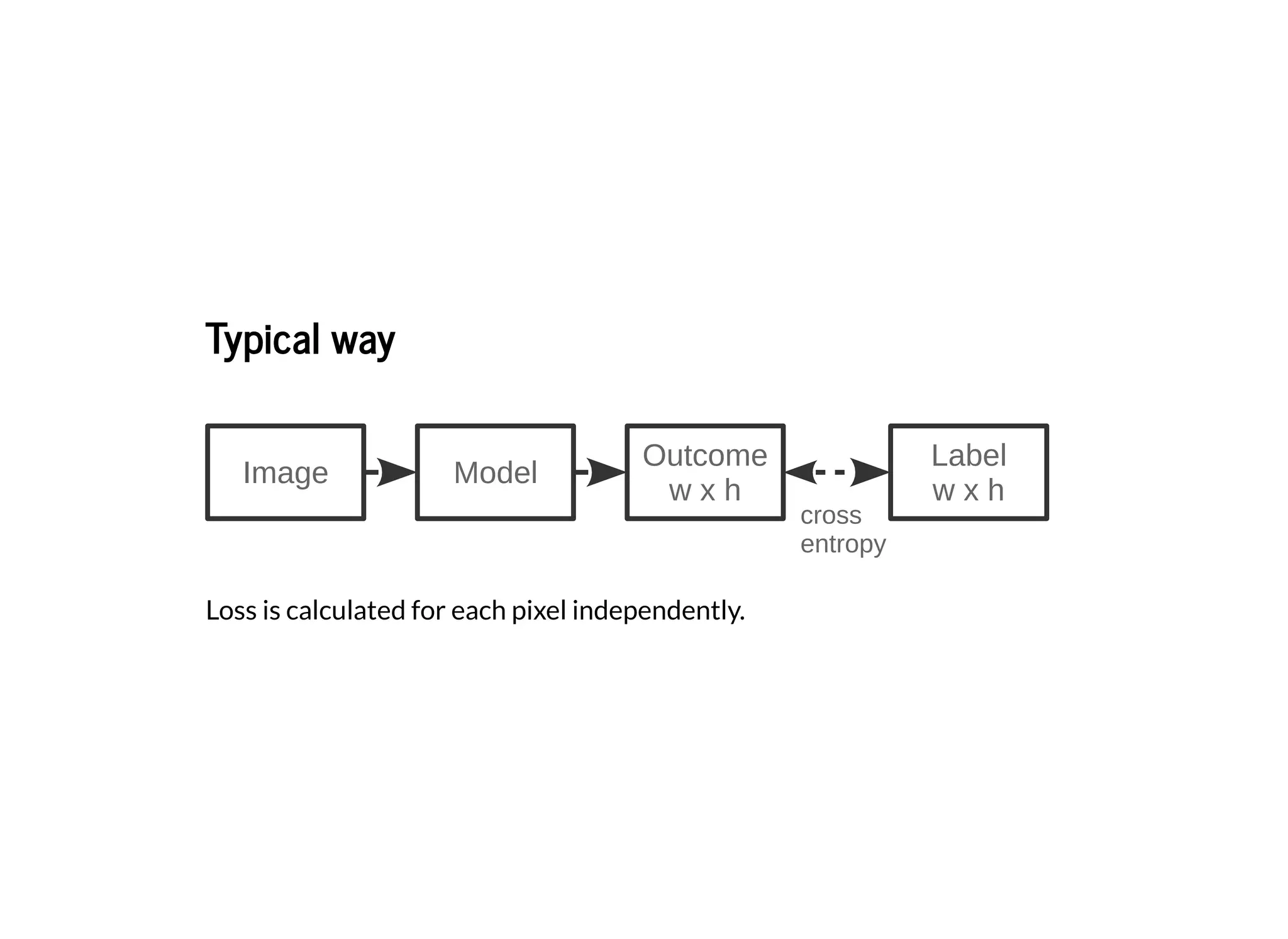
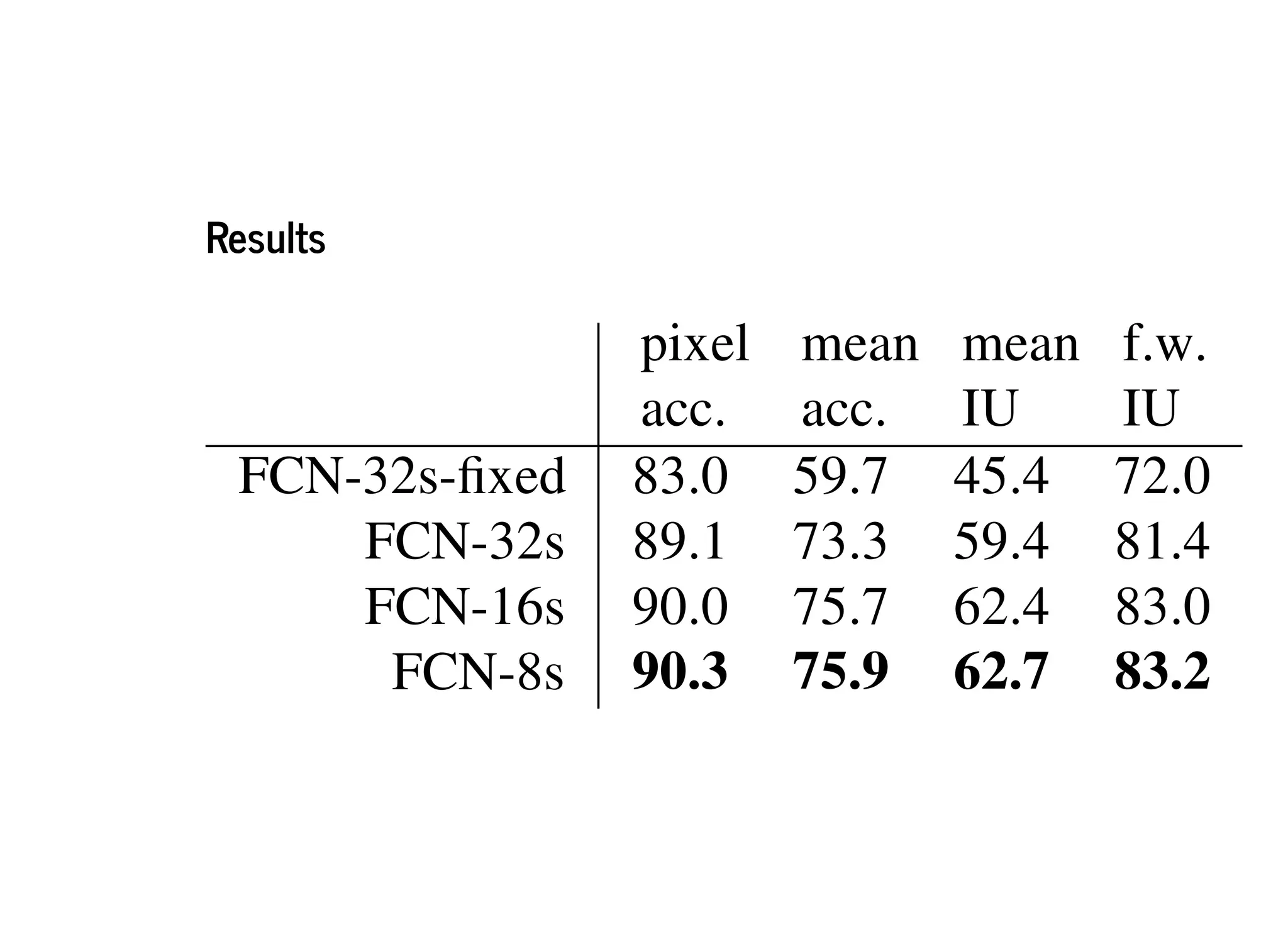
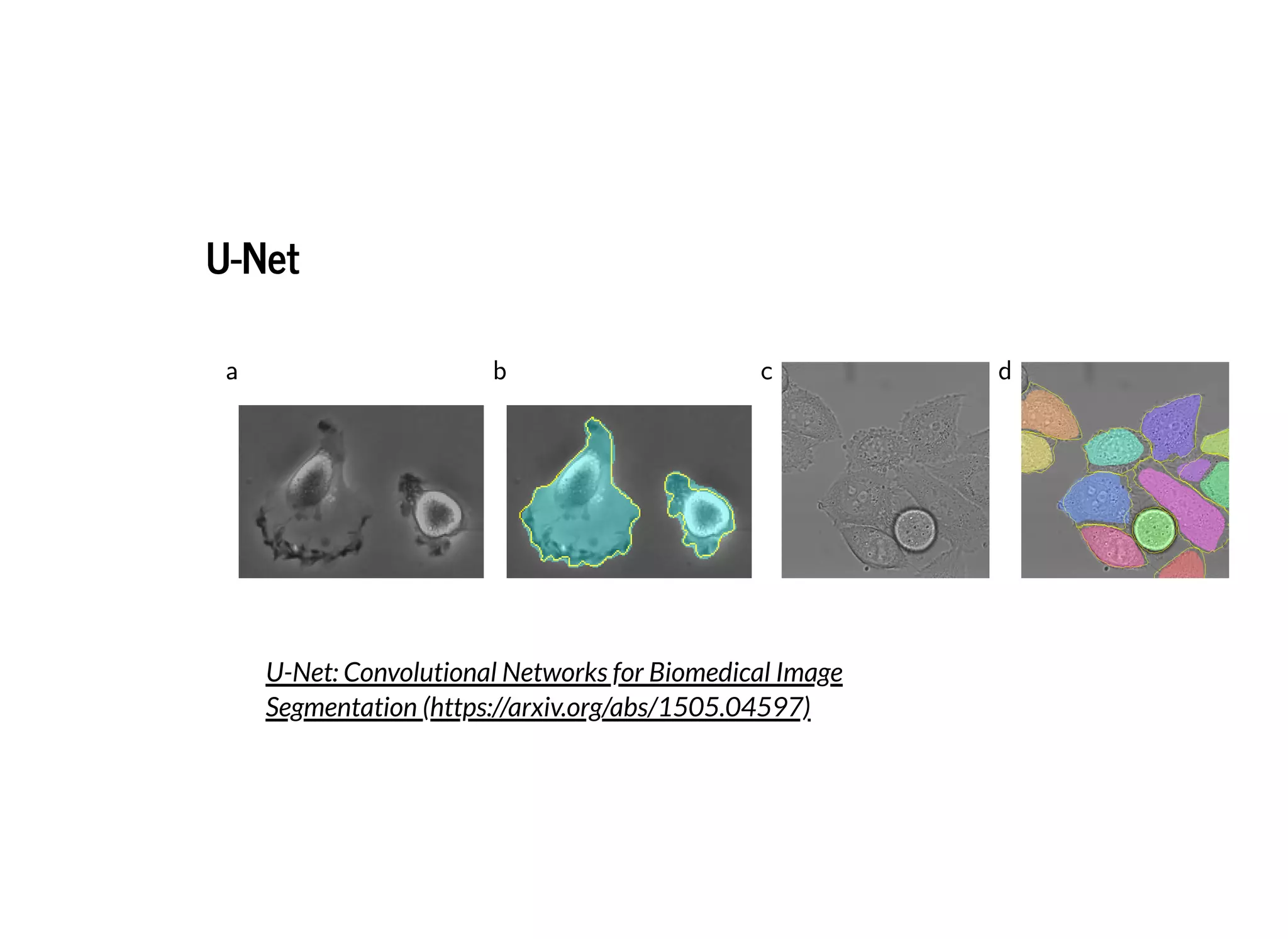
This document discusses several semantic segmentation methods using deep learning, including fully convolutional networks (FCNs), U-Net, and SegNet. FCNs were among the first to use convolutional networks for dense, pixel-wise prediction by converting classification networks to fully convolutional form and combining coarse and fine feature maps. U-Net and SegNet are encoder-decoder architectures that extract high-level semantic features from the input image and then generate pixel-wise predictions, with U-Net copying and cropping features and SegNet using pooling indices for upsampling. These methods demonstrate that convolutional networks can effectively perform semantic segmentation through dense prediction.

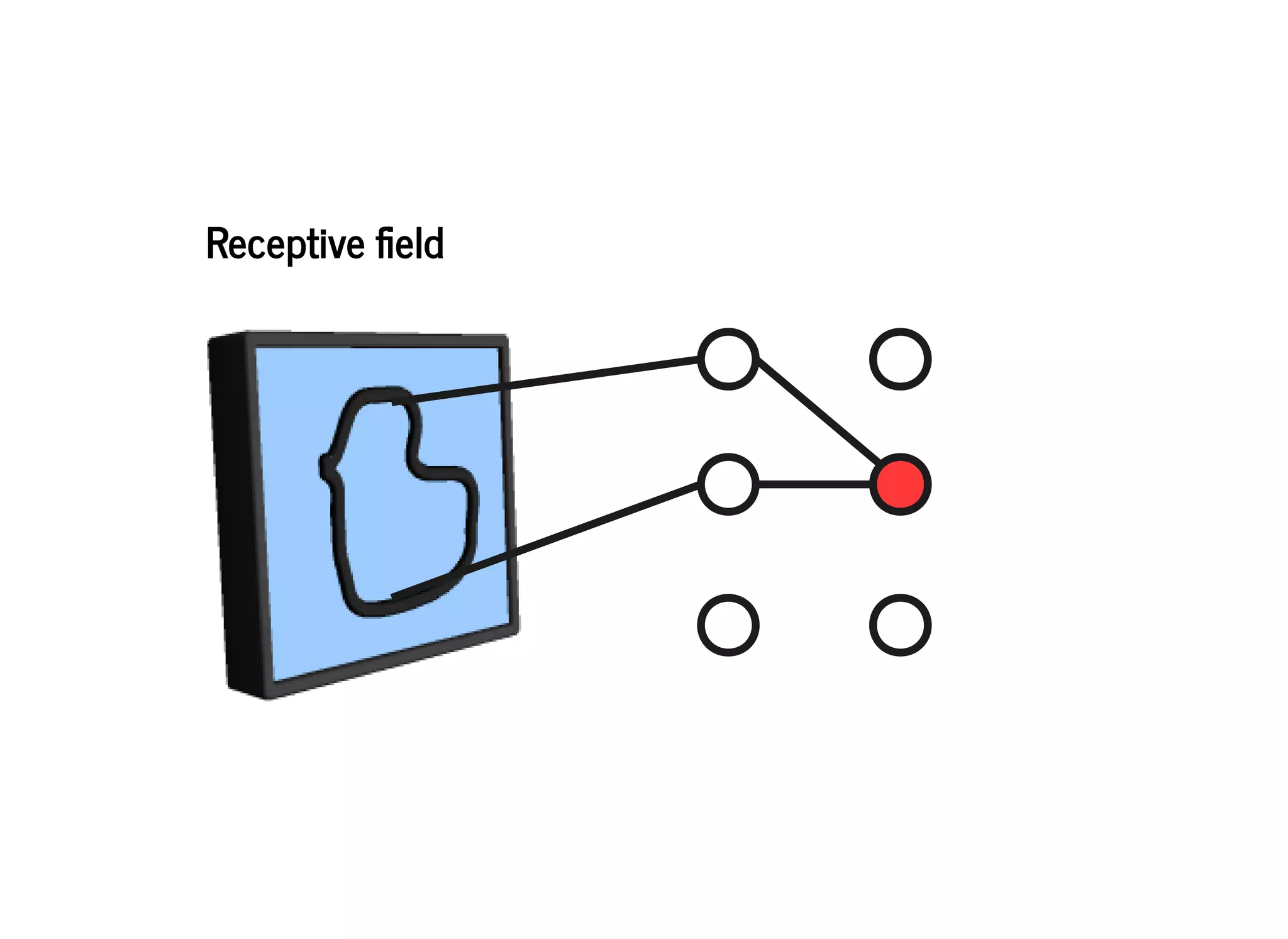


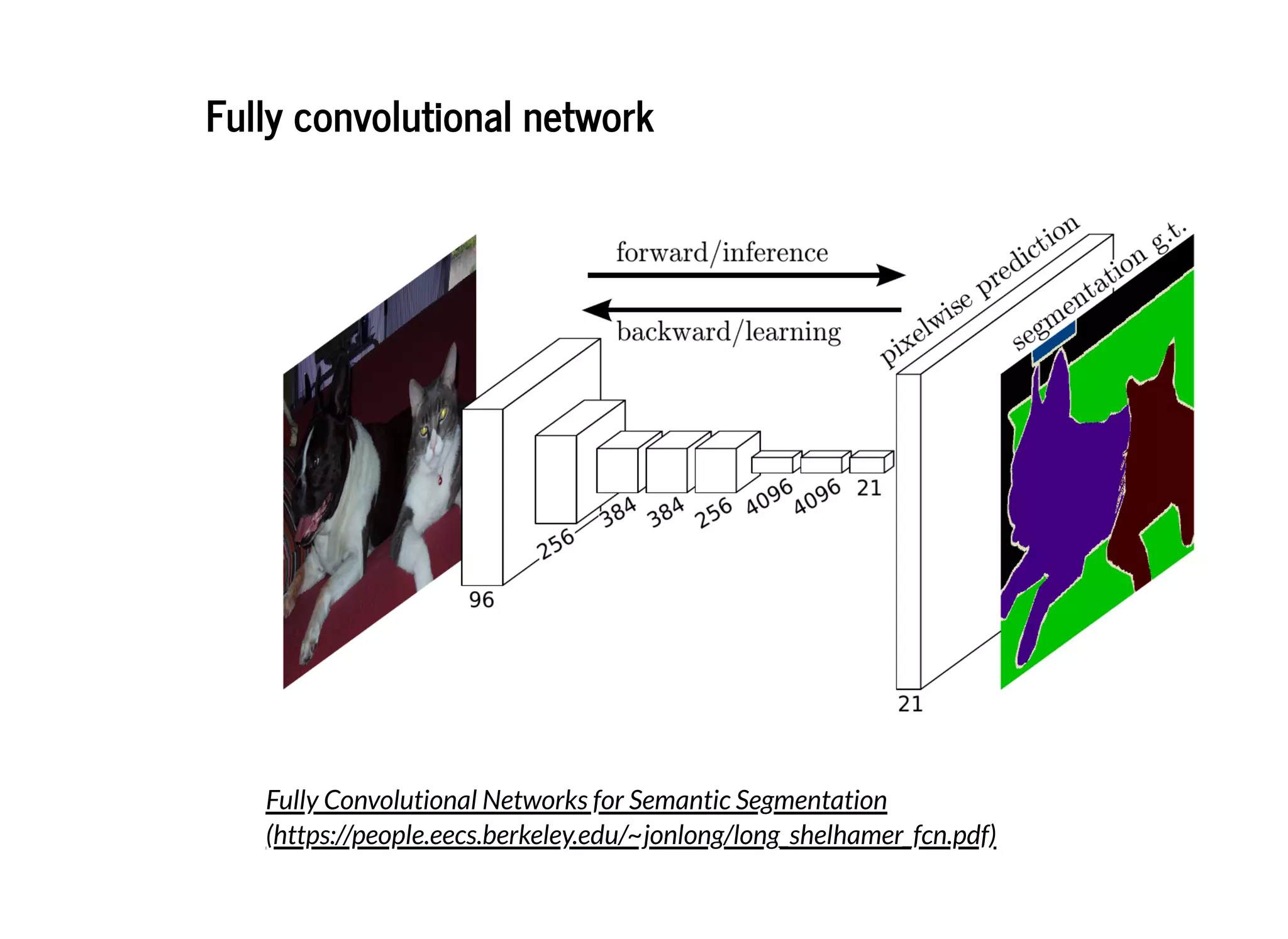
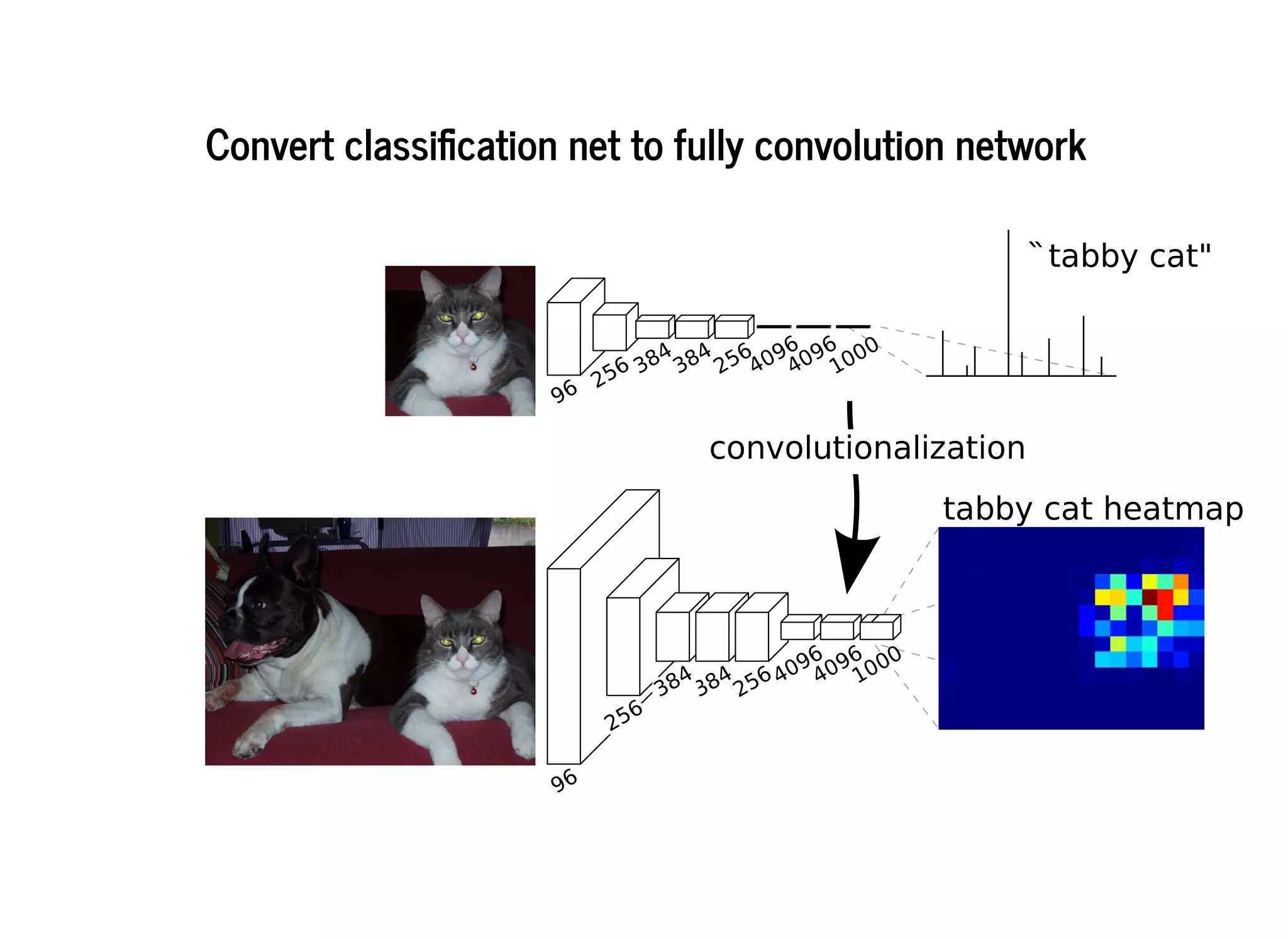

![DeconvolutionDeconvolution
Deconvolutional network [2015]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/semanticsegmentationslides-181218144057/75/Semantic-Segmentation-Fully-Convolutional-Networks-for-Semantic-Segmentation-13-2048.jpg)

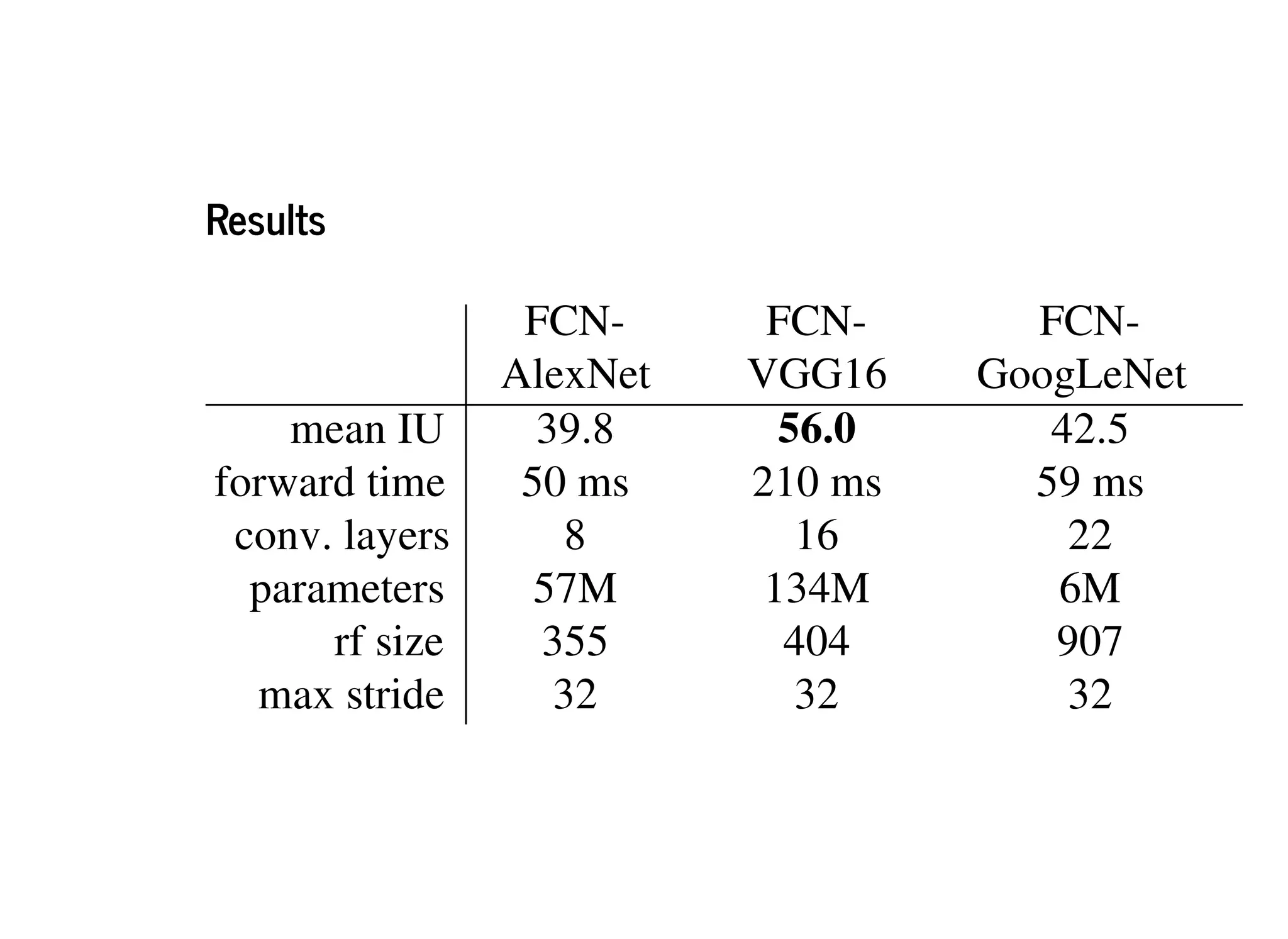
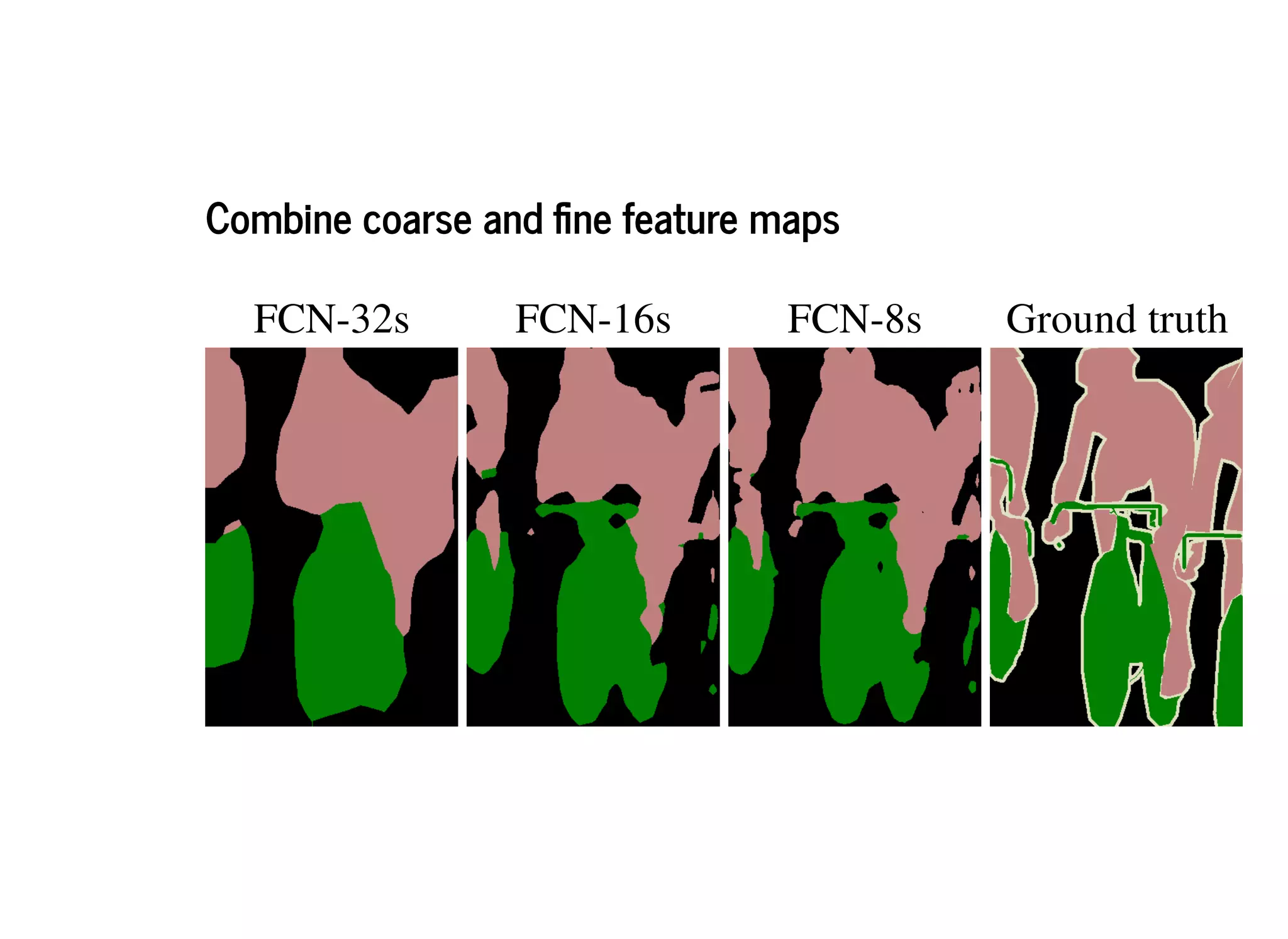
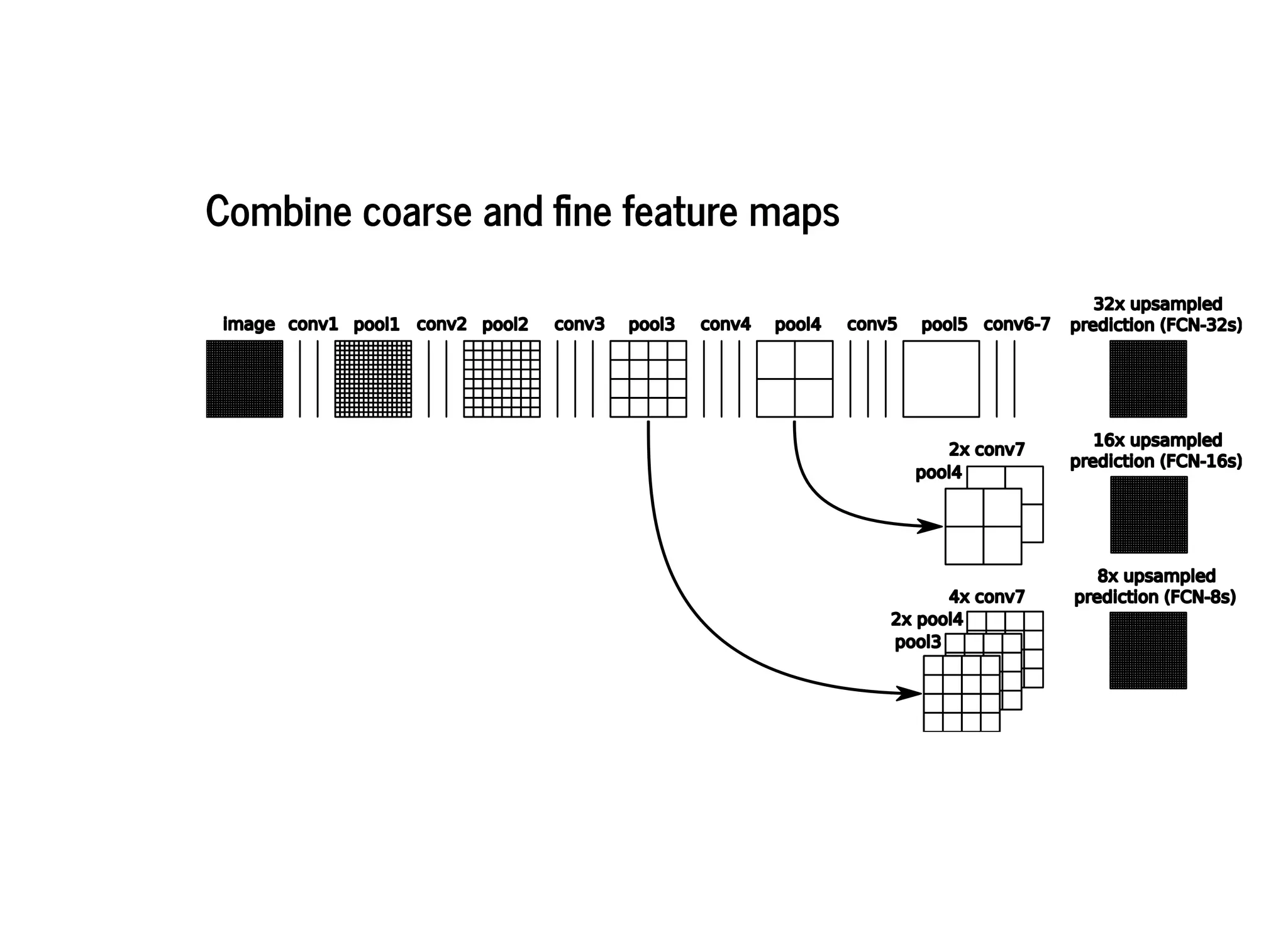
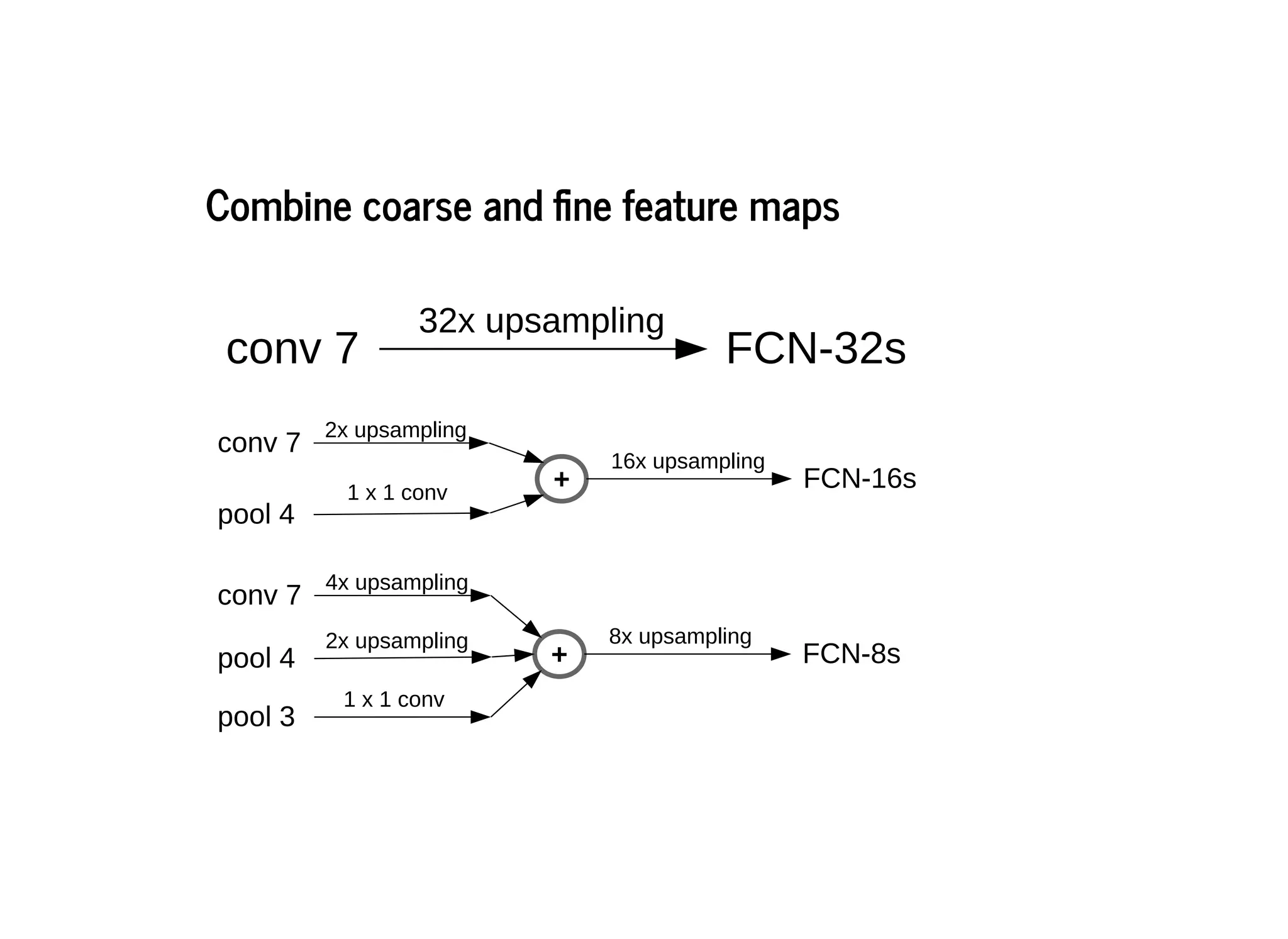
![FCN-8s SDS [17] Ground Truth Image](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/semanticsegmentationslides-181218144057/75/Semantic-Segmentation-Fully-Convolutional-Networks-for-Semantic-Segmentation-20-2048.jpg)


![Deconvolutional network [2015]Deconvolutional network [2015]
Learning Deconvolution Network for Semantic Segmentation
(https://arxiv.org/abs/1505.04366)](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/semanticsegmentationslides-181218144057/75/Semantic-Segmentation-Fully-Convolutional-Networks-for-Semantic-Segmentation-23-2048.jpg)
![Deconvolutional networkDeconvolutional network
[1]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/semanticsegmentationslides-181218144057/75/Semantic-Segmentation-Fully-Convolutional-Networks-for-Semantic-Segmentation-24-2048.jpg)
![U-Net [2015]U-Net [2015]
copy and crop
input
image
tile
output
segmentation
map
641
128
256
512
1024
max pool 2x2
up-conv 2x2
conv 3x3, ReLU
572x572
284²
64
128
256
512
570x570
568x568
282²
280²140²
138²
136²68²
66²
64²32²
28²
56²
54²
52²
512
104²
102²
100²200²
30²
198²
196²392x392
390x390
388x388
388x388
1024
512 256
256 128
64128 64 2
conv 1x1](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/semanticsegmentationslides-181218144057/75/Semantic-Segmentation-Fully-Convolutional-Networks-for-Semantic-Segmentation-25-2048.jpg)

![SegNet [2015, University of Cambridge]SegNet [2015, University of Cambridge]
Convolutional Encoder-Decoder Architecture
Convolutional Encoder-Decoder
Pooling Indices
Input
Segmentation
Output
Conv + Batch Normalisation + ReLU
Pooling Upsampling Softmax
RGB Image](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/semanticsegmentationslides-181218144057/75/Semantic-Segmentation-Fully-Convolutional-Networks-for-Semantic-Segmentation-28-2048.jpg)


![Q & AQ & A
ReferenceReference
[1]
[2]
[3]
A brief introduction to recent segmentation methods
(https://www.slideshare.net/mitmul/a-brief-introduction-to-recent-
segmentation-methods)
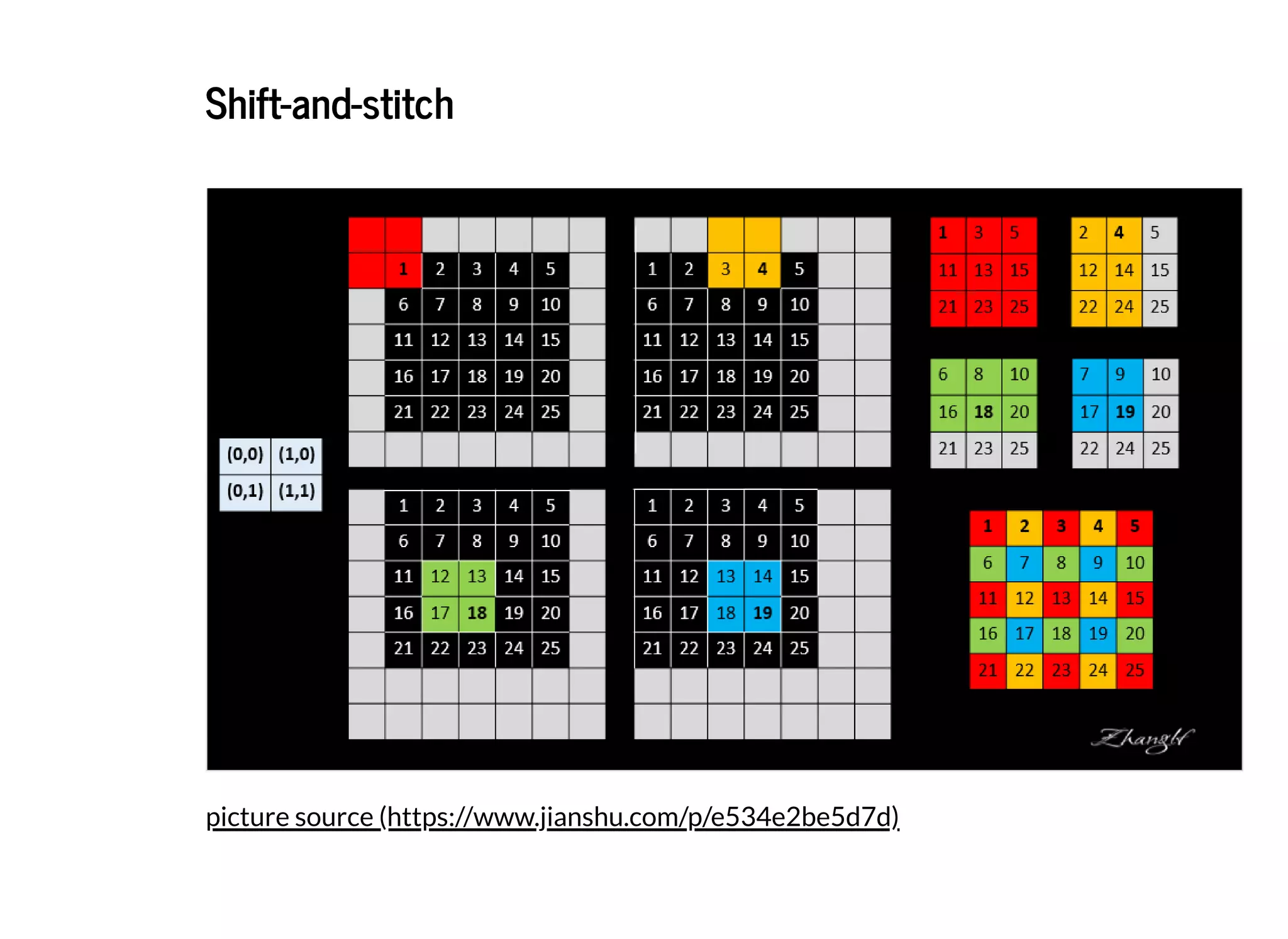
关于FCN 论⽂中的Shift-and-stitch 的详尽解释
(https://www.jianshu.com/p/e534e2be5d7d)
A 2017 Guide to Semantic Segmentation with Deep Learning
(http://blog.qure.ai/notes/semantic-segmentation-deep-learning-review)](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/semanticsegmentationslides-181218144057/75/Semantic-Segmentation-Fully-Convolutional-Networks-for-Semantic-Segmentation-31-2048.jpg)