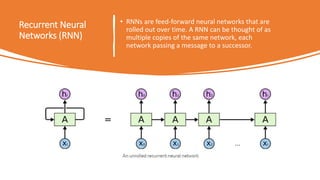
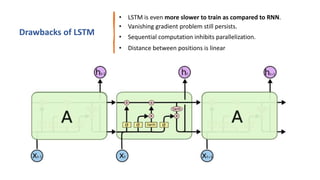
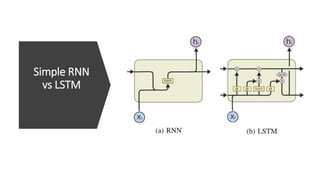
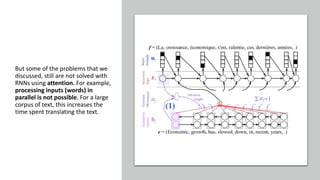
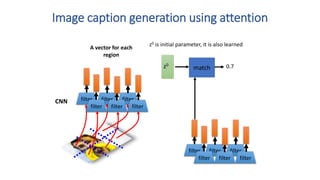
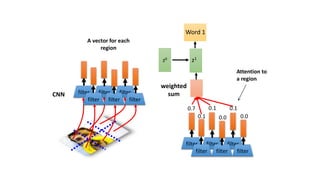
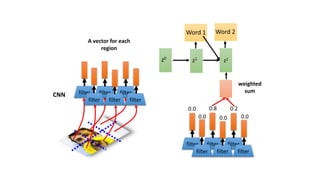
1) Transformers use self-attention to solve problems with RNNs like vanishing gradients and parallelization. They combine CNNs and attention.
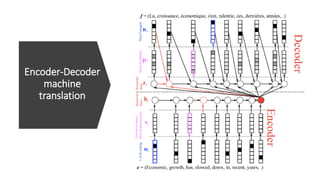
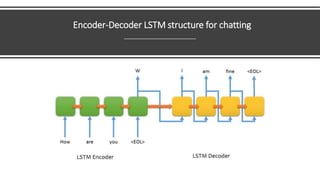
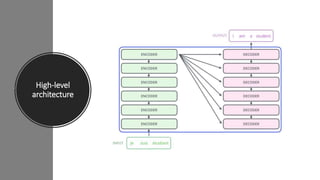
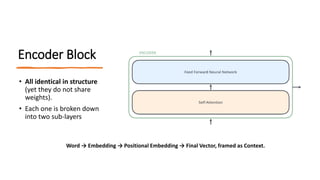
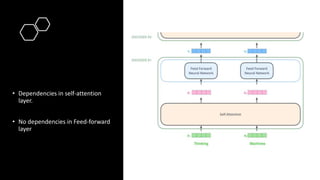
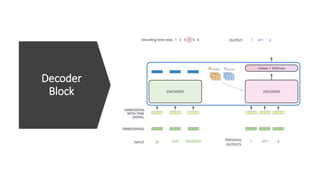
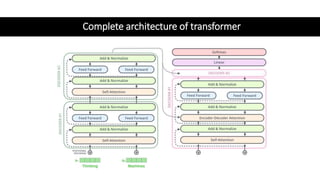
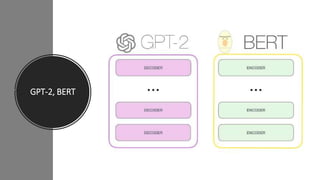
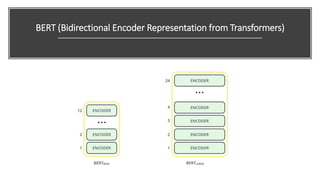
2) Transformers have encoder and decoder blocks. The encoder models input and decoder models output. Variations remove encoder (GPT) or decoder (BERT) for language modeling.
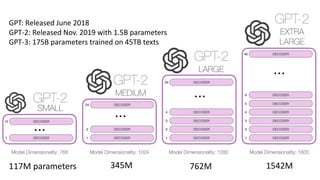
3) GPT-3 is a large Transformer with 175B parameters that can perform many NLP tasks but still has safety and bias issues.