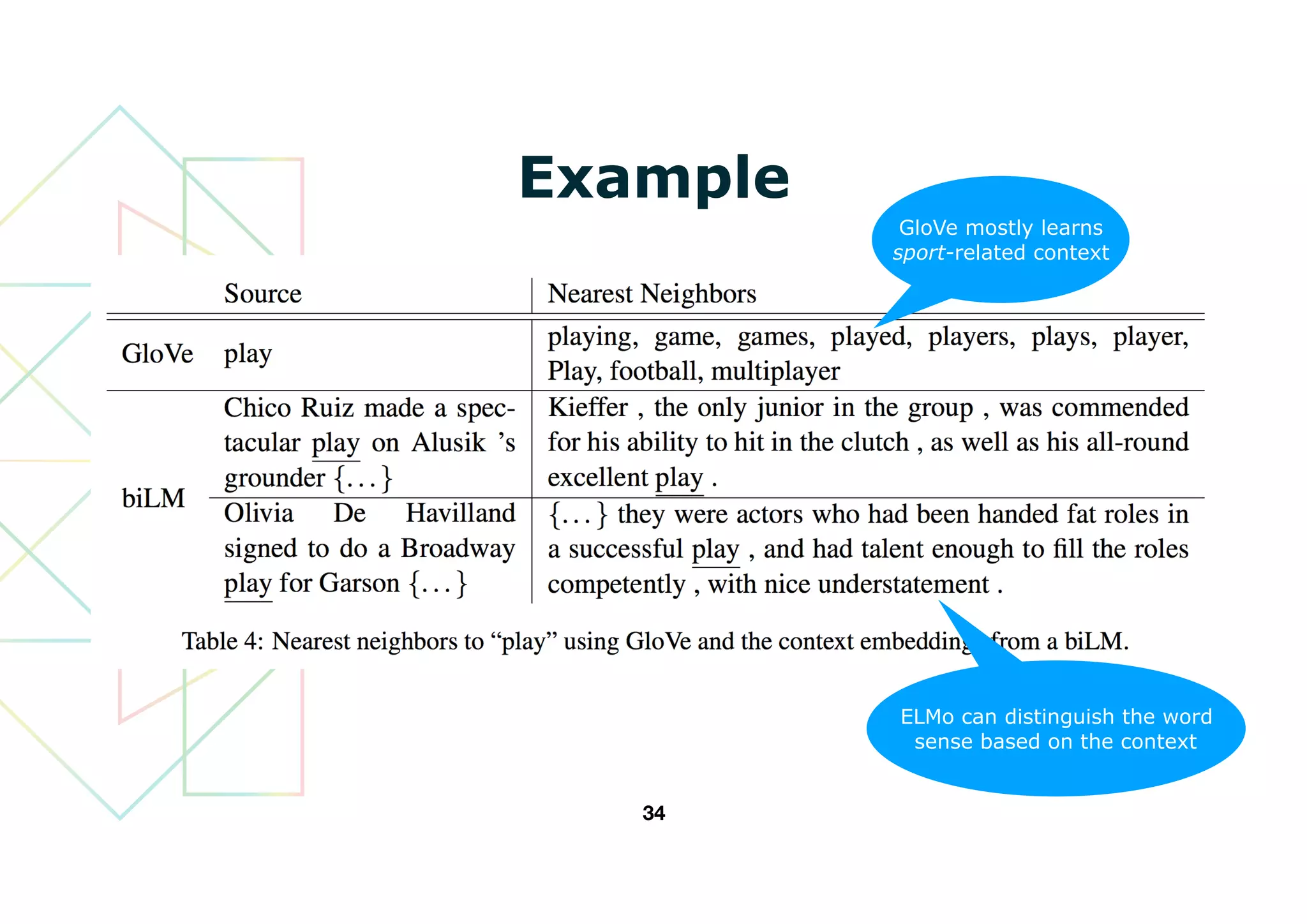
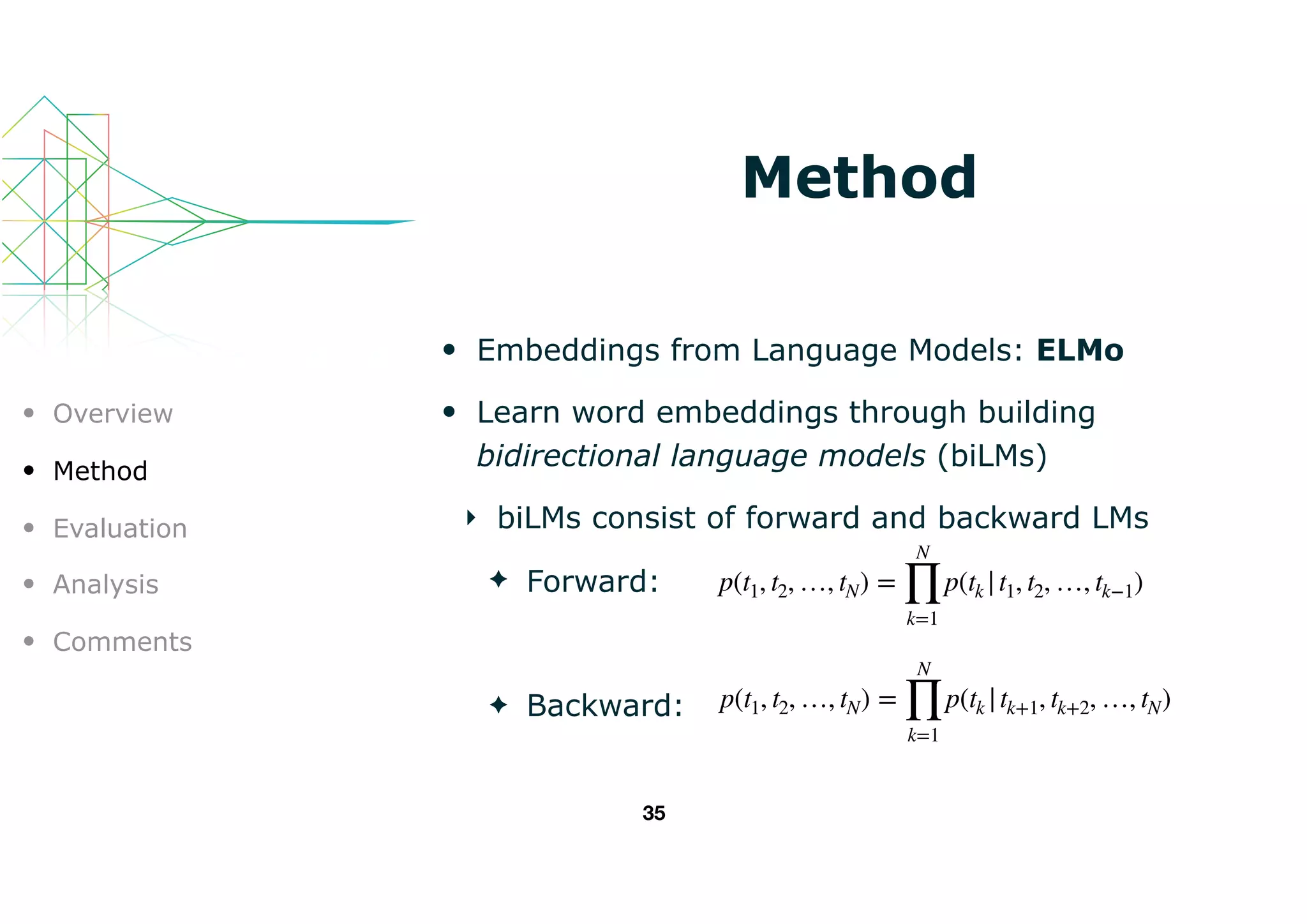
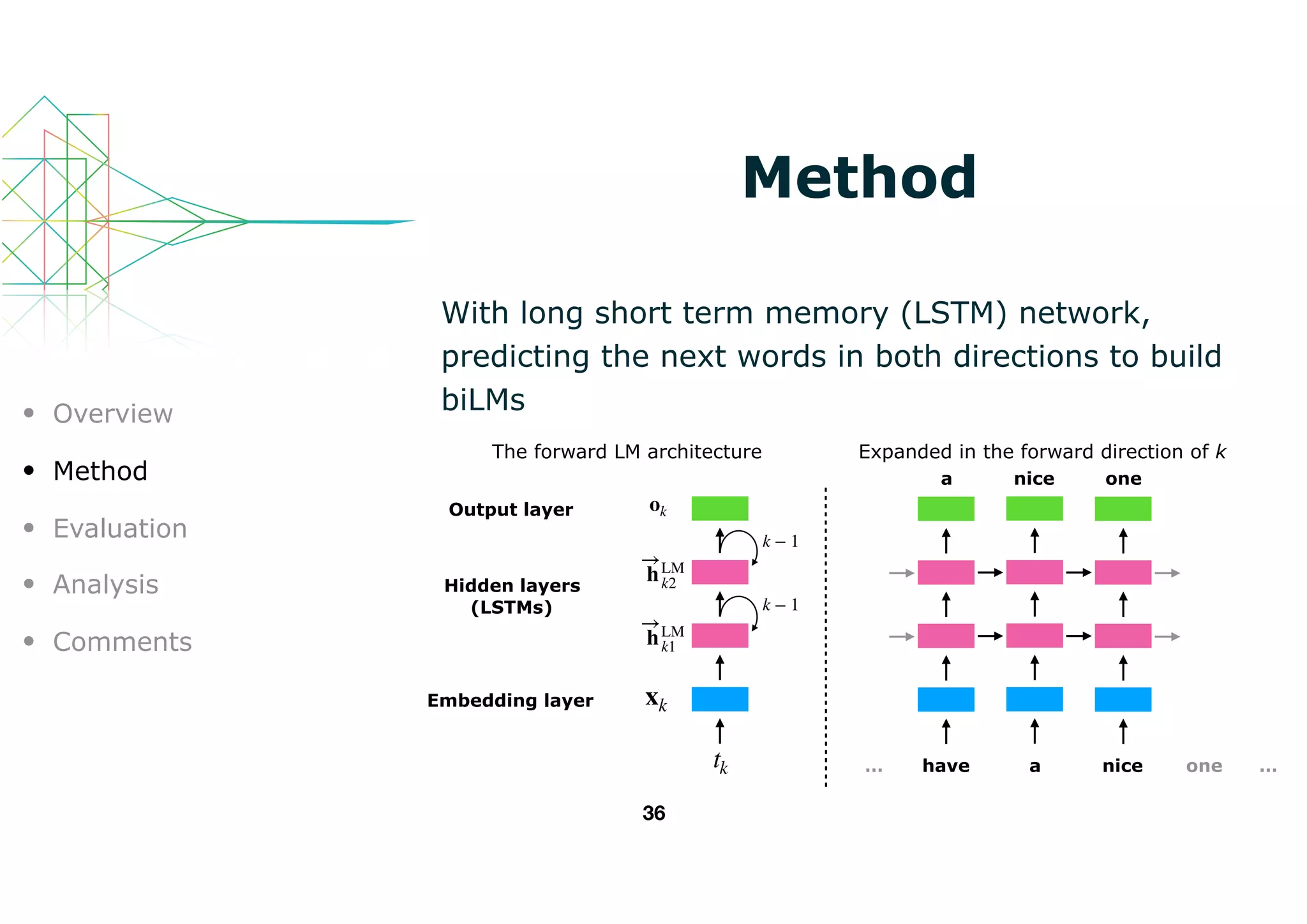
This document introduces ELMo, a new type of deep contextualized word representation designed to capture complex word usage characteristics and their variation across contexts. It discusses the method of learning embeddings through bidirectional language models and shows that ELMo enhances various NLP tasks by providing task-specific representations. The authors evaluate ELMo's effectiveness in improving performance in tasks like textual entailment, sentiment analysis, and more.


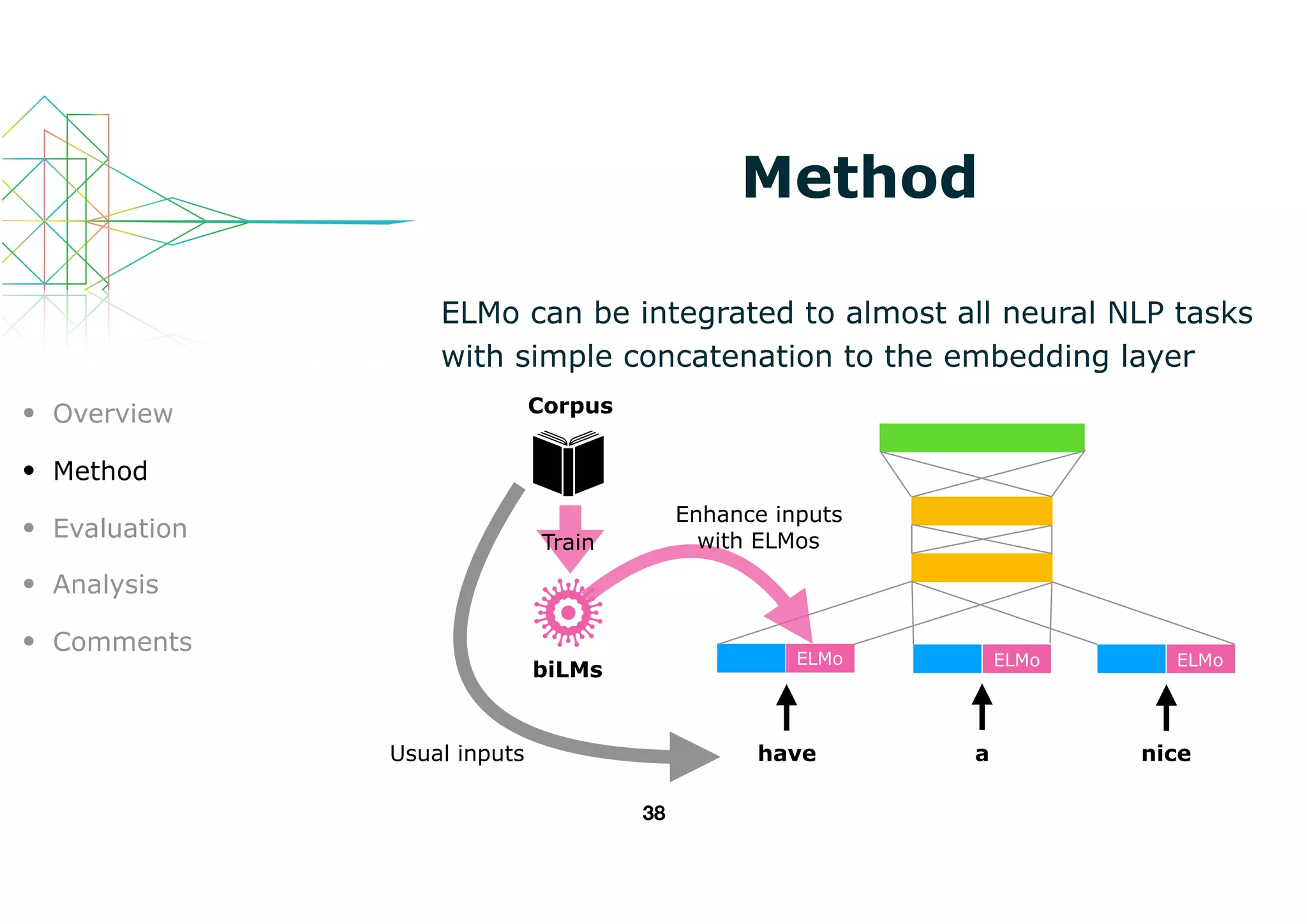
![Method
ELMo represents a word as a linear combination of
corresponding hidden layers (inc. its embedding)
37
tk
xk
ok
k − 1
k − 1
hLM
k1
ok
k + 1
k + 1
hLM
k2
hLM
k1
hLM
k2
Forward LM Backward LM
tk tk
stask
0
stask
1
stask
2
Concatenate
hidden layers
hLM
k1
hLM
k2
hLM
k0
([xk ; xk])
×
×
× [hLM
kj ; hLM
kj ]
{
ELMotask
k ×γtask
∑=
Unlike usual word embeddings, ELMo is
assigned to every token instead of a type
biLMs
ELMo is a task specific
representation. A down-stream
task learns weighting parameters](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/elmo2018-180622093026/75/A-Review-of-Deep-Contextualized-Word-Representations-Peters-2018-6-2048.jpg)