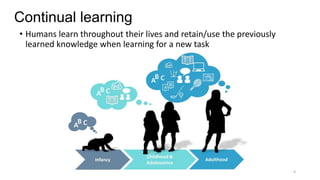
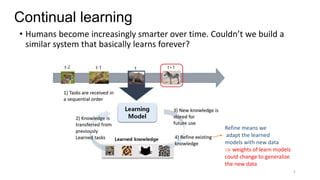
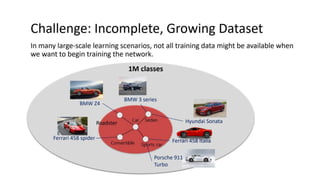
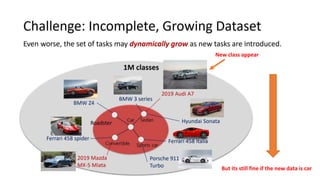
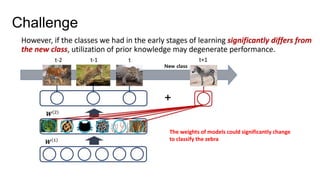
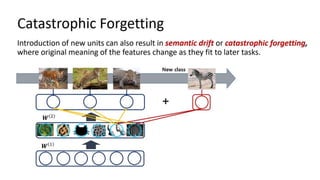
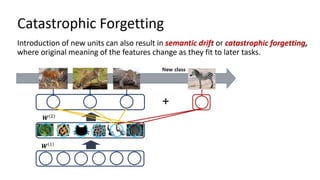
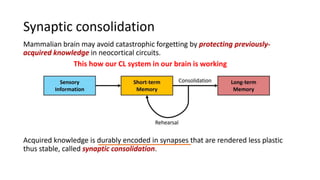
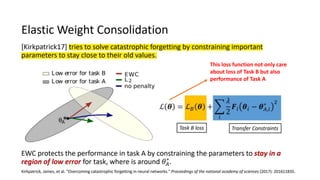
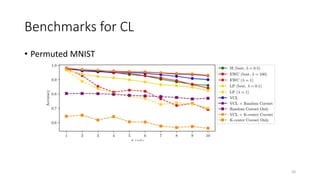
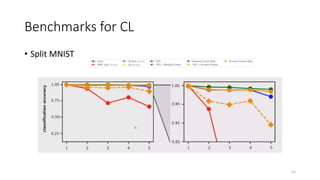
Continual learning involves building machine learning systems that can learn continuously over time from new data and tasks while retaining knowledge from previous learning. This mimics how humans learn throughout their lives. However, continual learning faces challenges like catastrophic forgetting where new learning interferes with past knowledge. Potential solutions involve balancing plasticity to learn new things with stability to retain old knowledge. The field is still new with experiments focused on simple tasks, but continual learning could enable increasingly intelligent systems that learn forever.