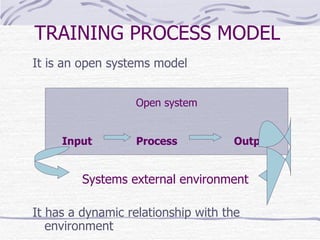
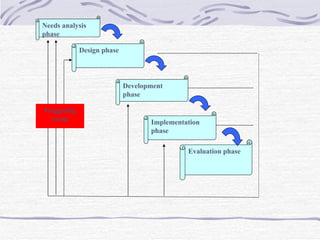
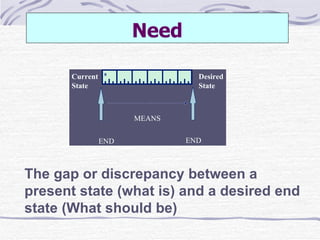
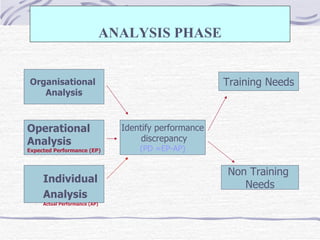
The document discusses training and development, including the definitions of learning, training, knowledge, skills, and attitudes. It describes the differences between training and development, and outlines the training process model. The training process model includes input, a process, and output. It also involves needs analysis, design, development, implementation, and evaluation phases. The needs analysis phase assesses needs at the organizational, task/operational, and individual levels to identify performance discrepancies and determine if training is the appropriate solution.