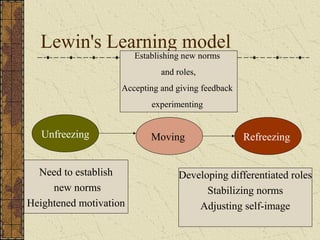
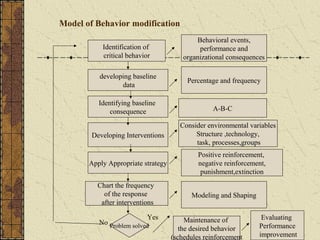
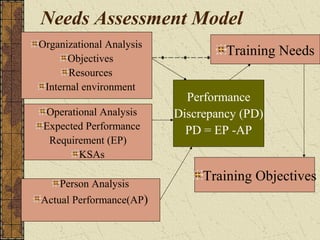
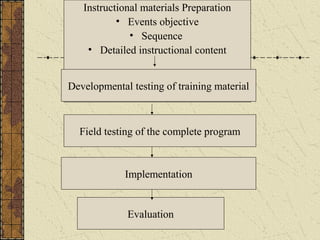
The document provides an overview of training and development. It defines training and discusses learning theories including social learning theory and Lewin's learning model. It also covers behavior modification models, characteristics of effective training practices, assessing training needs, and various training methods. Evaluation of training programs and factors affecting transfer of training are also summarized. Career development and stages are briefly discussed.