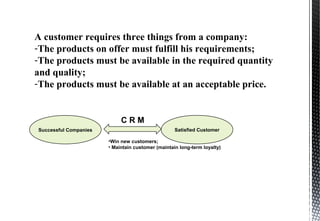
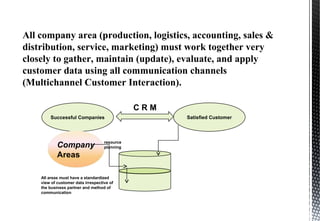
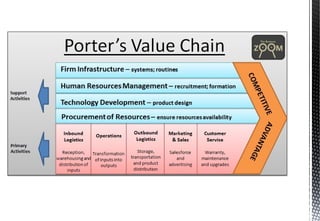
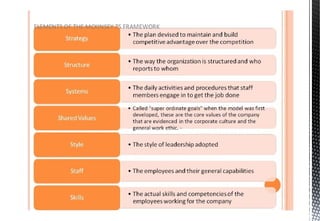
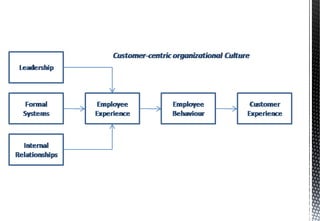
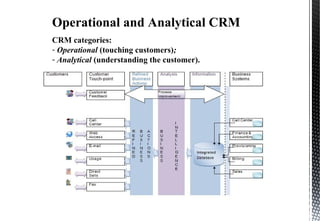
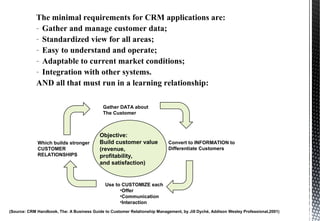
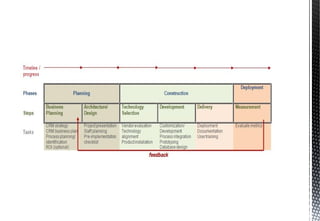
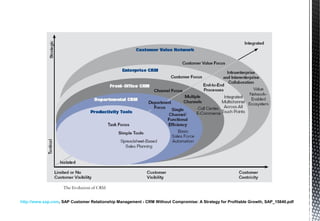
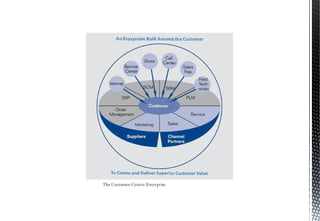
The document discusses customer relationship management (CRM) and its key aspects. It defines CRM as a business strategy and infrastructure that enables companies to increase customer value, loyalty, and retention by tracking and managing customer interactions. The document categorizes CRM into strategic, operational, analytical, and collaborative types and notes operational and analytical CRM focus on direct customer interactions and understanding customers respectively. It also outlines requirements for effective CRM software and discusses how CRM supports marketing, employee relationship management, and partner relationship management goals.