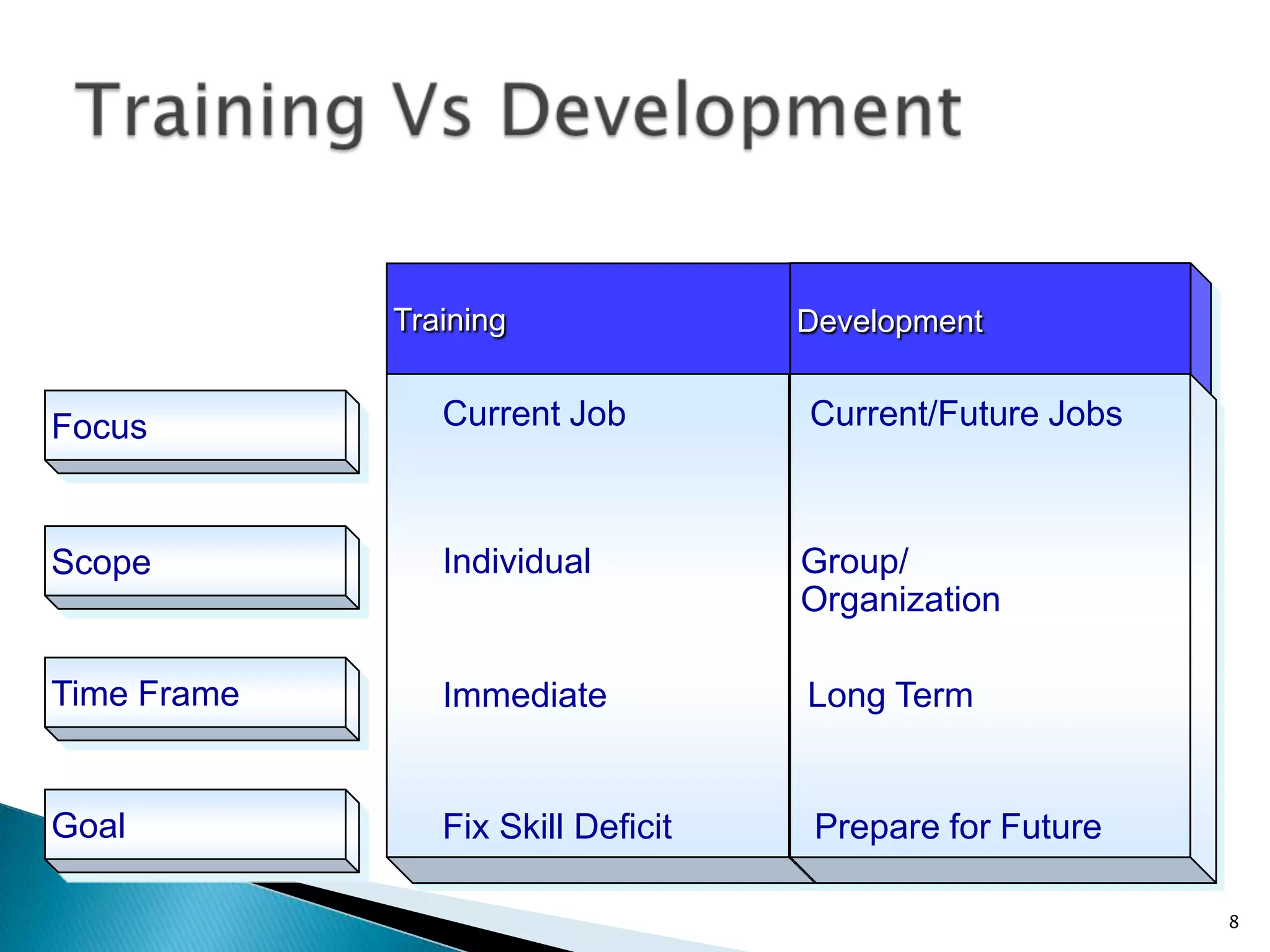
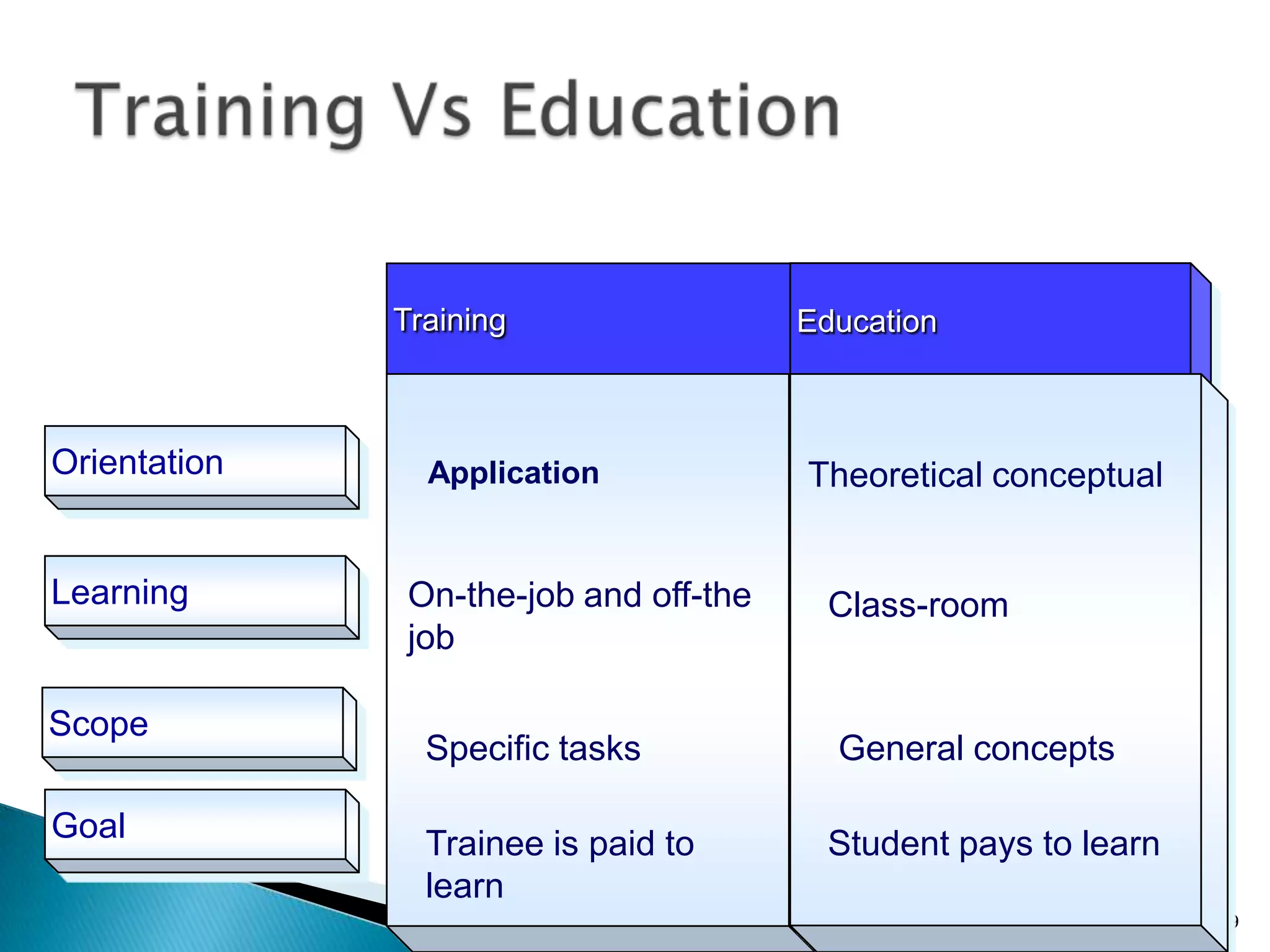
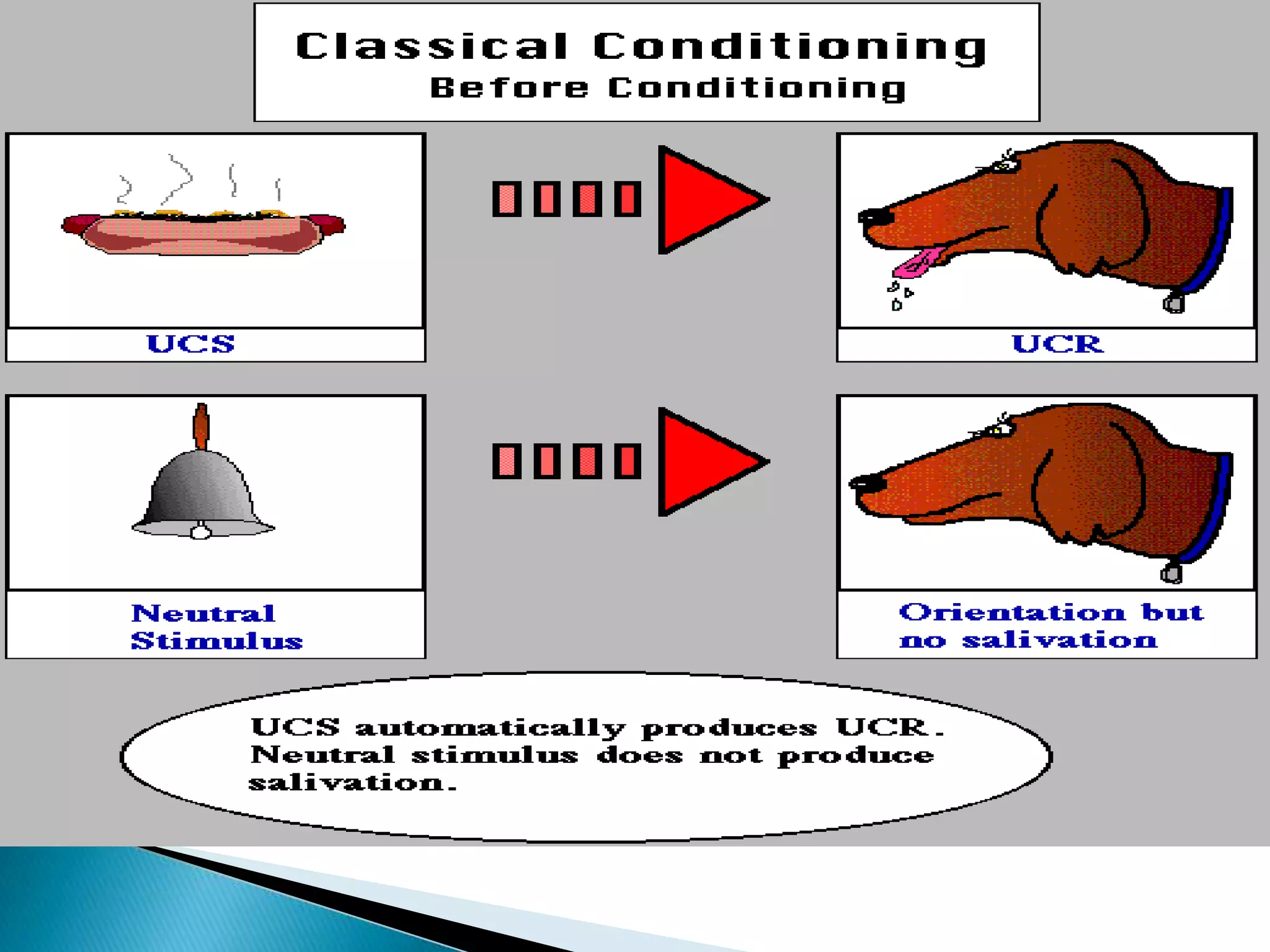
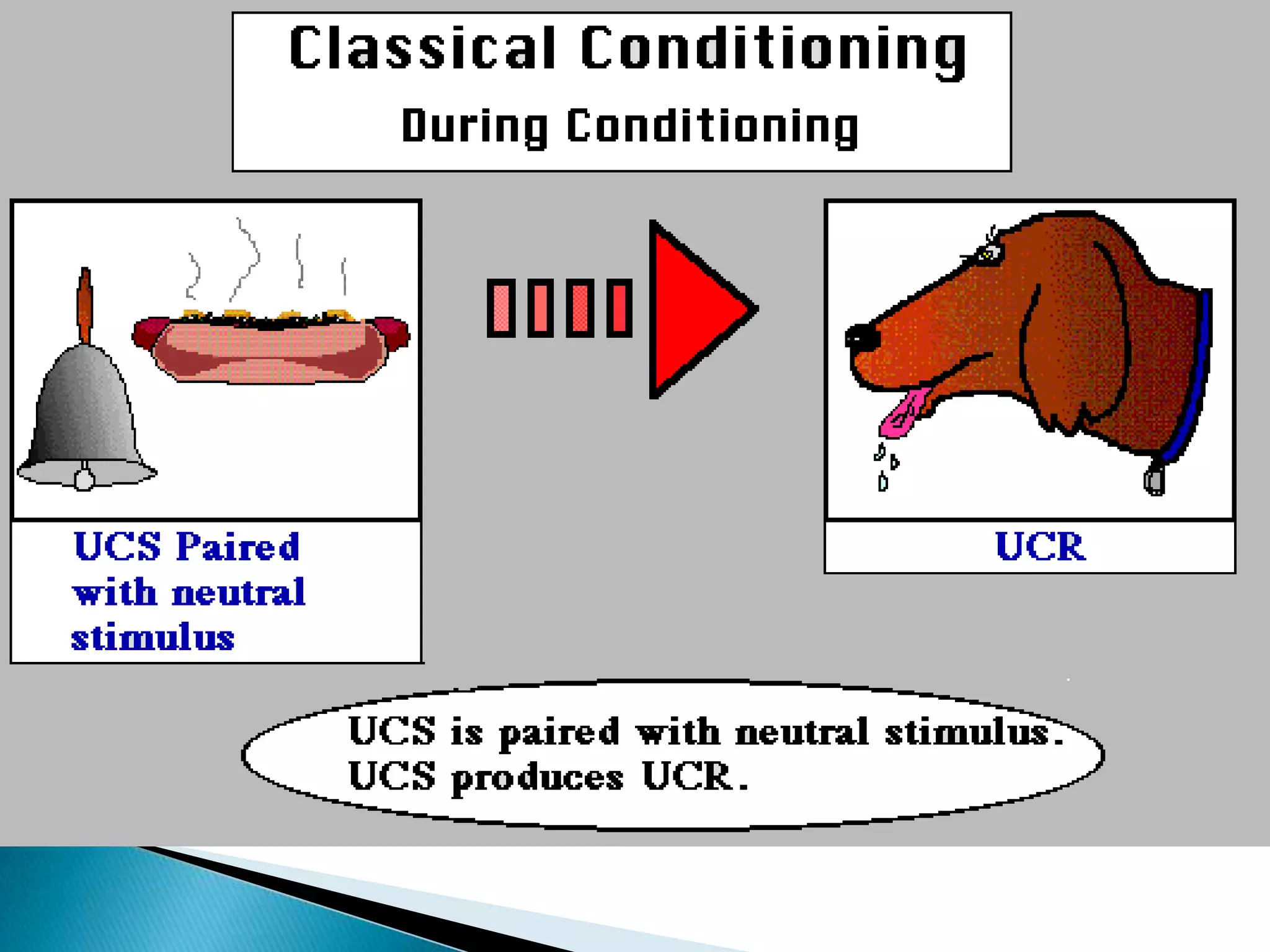
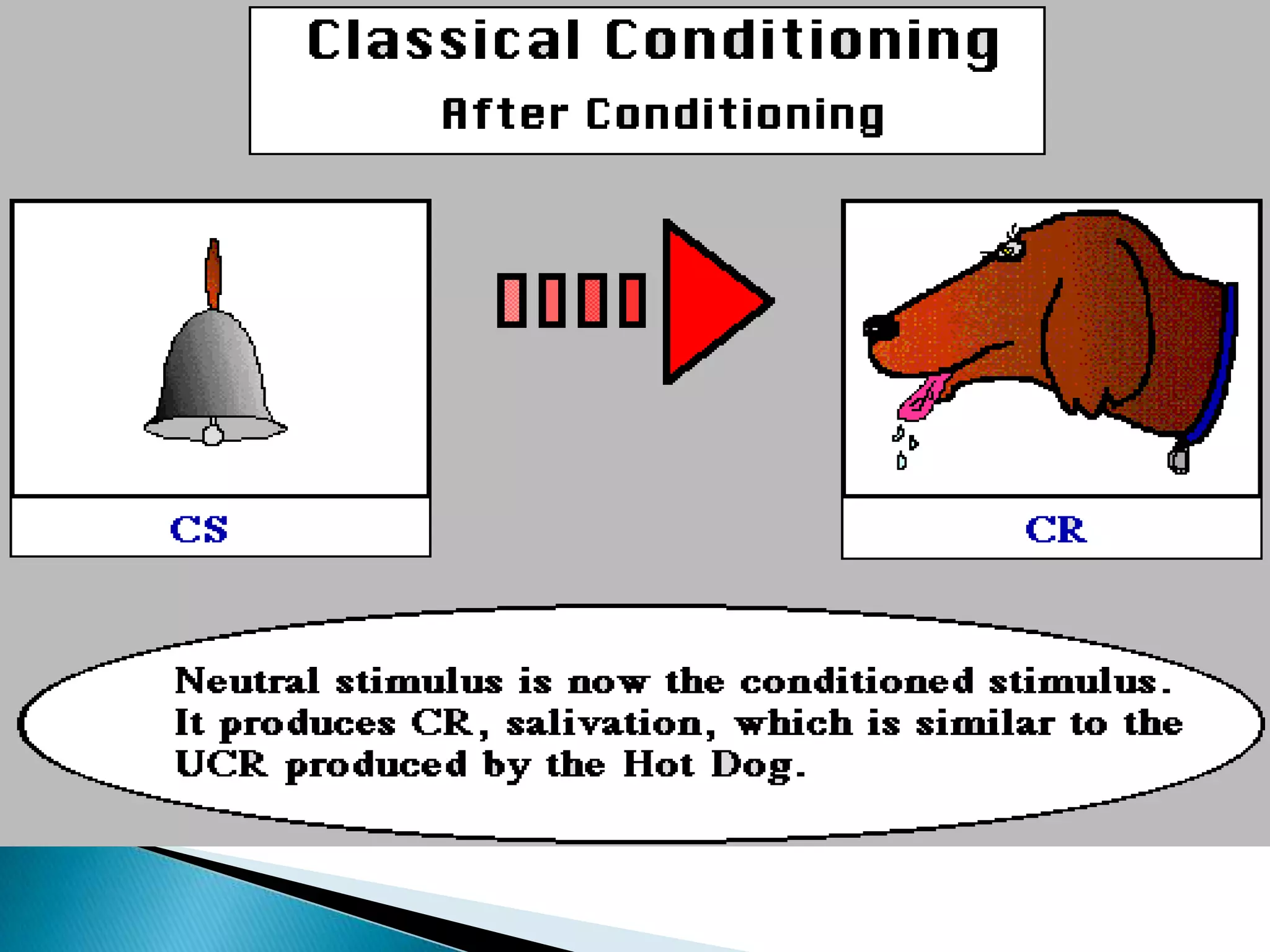
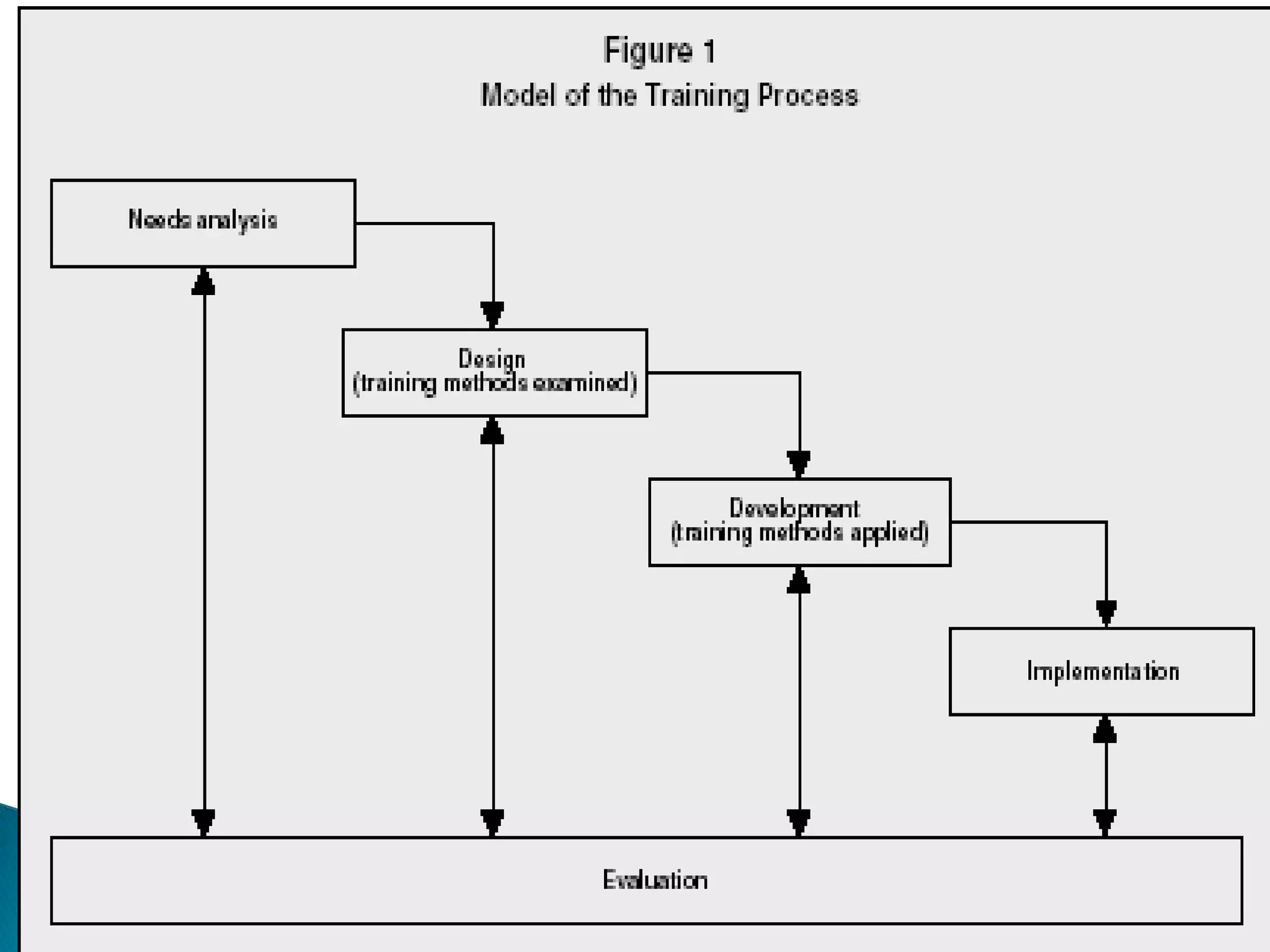
The document discusses the concepts of training, development, and education in organizations, explaining that training refers to facilitating employees' learning of job-related skills to achieve organizational goals, development aims to provide abilities needed in the future, and education involves general conceptual learning in a classroom setting. It also outlines the benefits of training for employees, supervisors, and businesses in terms of performance, costs, and profitability.