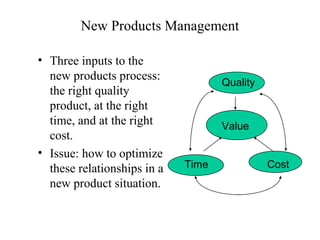
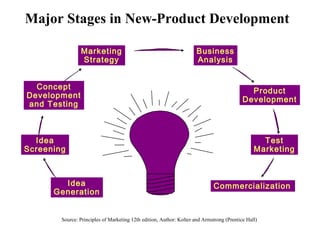
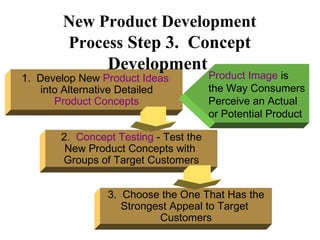
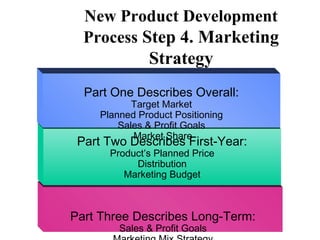
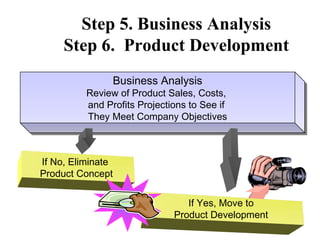
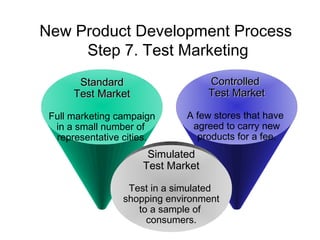
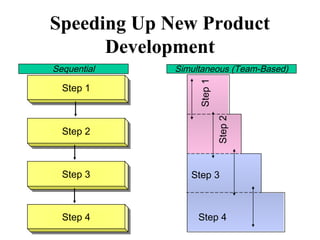
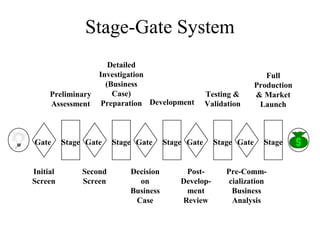
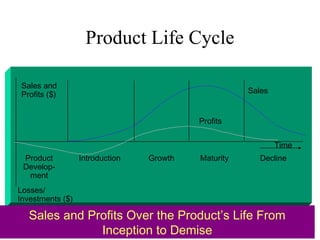
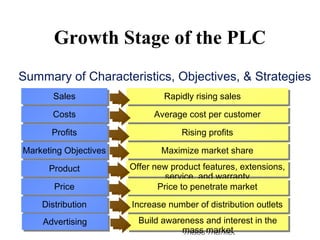
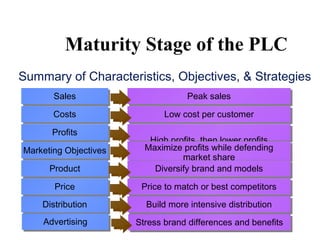
The document discusses the new product development process. It begins with defining products and identifying strategies for obtaining new product ideas. It then outlines the 8 major steps in the new product development process: 1) idea generation, 2) idea screening, 3) concept development and testing, 4) marketing strategy, 5) business analysis, 6) product development, 7) test marketing, and 8) commercialization. It also discusses challenges in new product development such as market uncertainty and reasons why new products often fail.