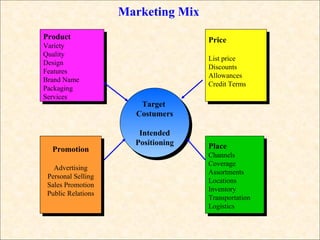
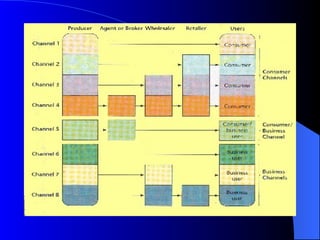
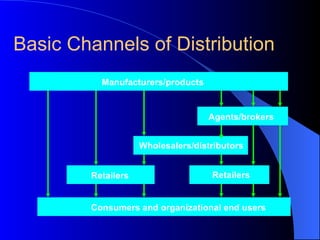
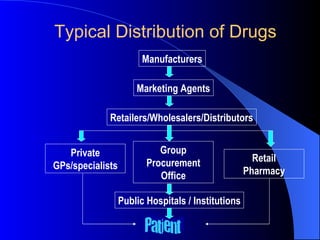
The document provides an overview of key marketing concepts including the marketing mix, target markets, market segmentation, the 4Ps of marketing (product, price, promotion, and place), and distribution channels. It defines these concepts and gives examples to illustrate how companies develop marketing strategies and get products into customers' hands.