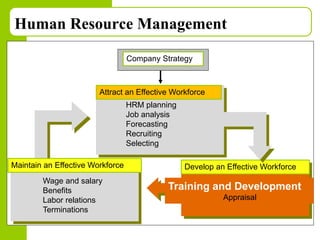
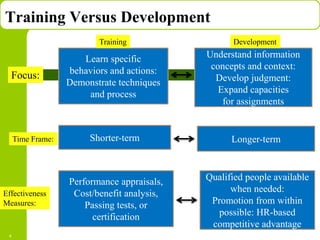
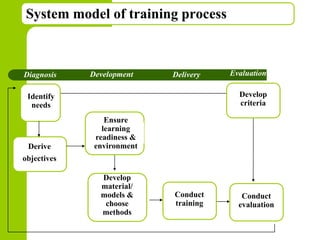
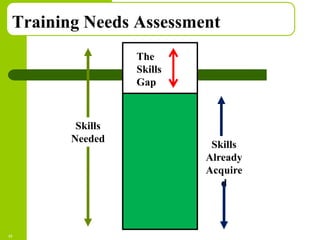
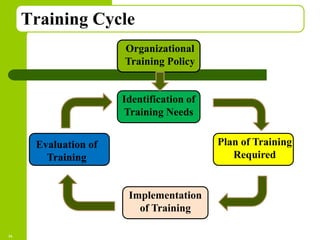
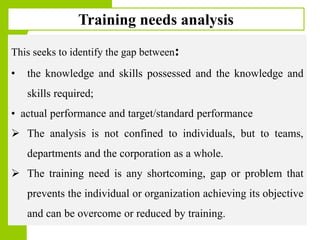
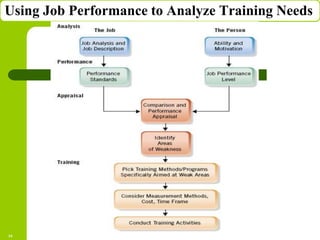
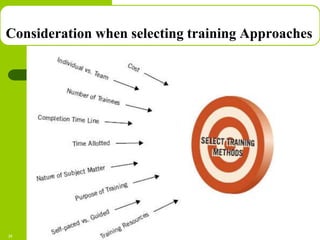
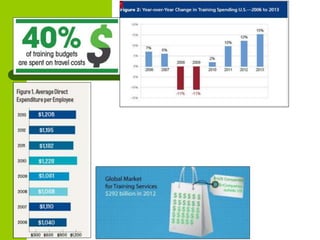
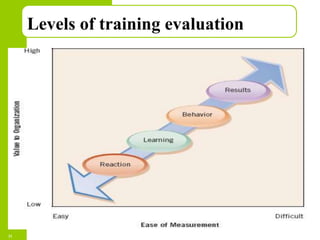
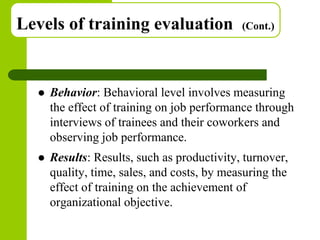
This document discusses training and development in organizations. It begins by defining training as developing skills for present jobs, while development focuses on long-term learning beyond the current job. Effective training and development leads to benefits like increased productivity, quality and motivation. The document then outlines the training process, including needs assessment, planning, implementation, and evaluation. It provides examples of different training methods and the importance of evaluating training to measure its impact.