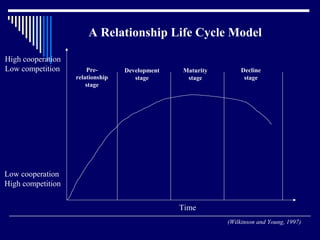
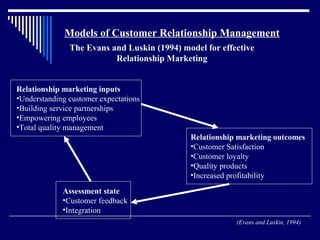
CRM involves developing long-term mutually beneficial relationships with customers through open communication and customized products and services. It is based on trust and providing superior value compared to competitors. Customer relationships progress through different stages from basic interactions to long-term partnerships. Global salespeople play a key role in building and promoting customer relationships by understanding customer needs, providing quality service, and enhancing loyalty over time. The goal of CRM is to turn prospects into loyal, long-term partners through ongoing value creation.