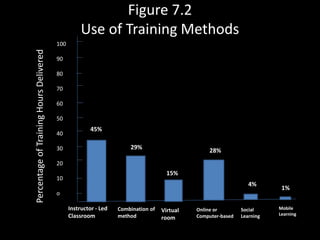
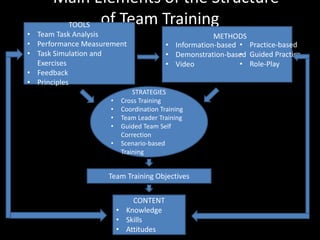
This document discusses traditional training methods that require an instructor and face-to-face interaction. It describes various presentation methods like lectures and audiovisual techniques where trainees are passive recipients of information. It also covers hands-on methods like on-the-job training, simulations, case studies, and role playing where trainees are actively involved. Finally, it discusses alternative methods like self-directed learning, apprenticeships, team training, action learning, and Six Sigma training.