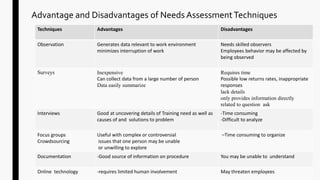
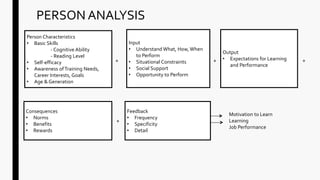
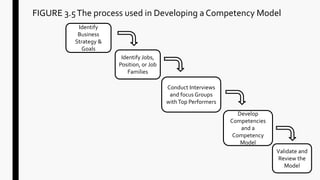
This chapter discusses needs assessment for training programs. It identifies the objectives of needs assessment as determining if training is necessary by analyzing the organization, tasks, and individuals. The chapter explains that needs assessment involves organizational analysis, person analysis, and task analysis. It discusses why needs assessment is important to ensure training addresses real needs and problems. Key methods of needs assessment include observation, surveys, interviews, focus groups, and documentation analysis. The chapter also outlines the needs assessment process and considerations.