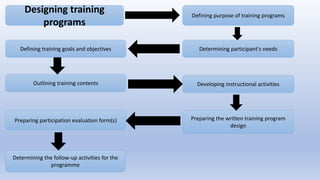
The document outlines the key factors, strategies, and challenges in designing effective training programs, emphasizing the importance of careful planning to ensure successful learning outcomes. It discusses the ADDIE model, which includes stages such as analysis, design, development, implementation, and evaluation, as well as essential steps like defining training objectives and assessing participant needs. The document also highlights the need for various training methods and the challenges faced by training managers in creating programs that cater to diverse learning styles and organizational goals.