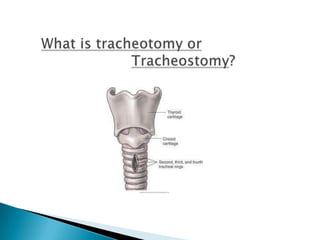
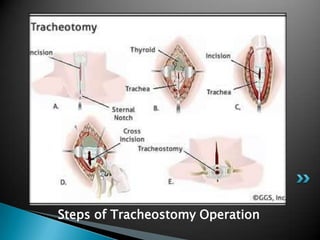
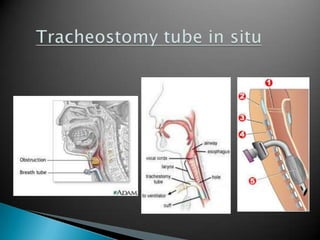
Dr. Maleka Afroz discusses tracheostomy, listing its indications such as bypassing airway obstruction from larynx cancer or for tracheobronchial toiletting in acute laryngotrachealbronchitis. Tracheostomy may also be used to protect the tracheobronchial area in unconscious patients, for patients on ventilators in the ICU, or for those with respiratory insufficiency from COPD. It can be done as a temporary procedure prior to head/neck surgery or permanently prior to total laryngectomy. The document outlines the different types of tracheostomy as emergency, elective or permanent and reviews causes for airway obstruction. Steps for the tracheostomy operation are