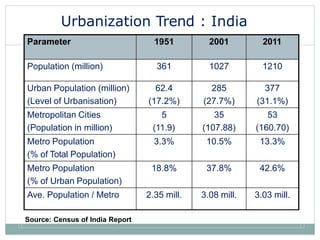
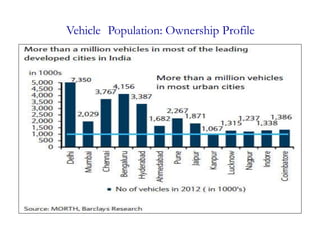
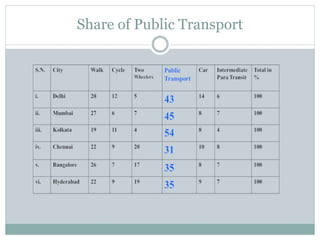
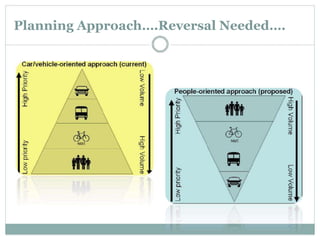
This document discusses the importance and requirements of urban mass transportation systems, highlighting factors affecting travel demand, types of mass transit such as road and rail-based, and advantages including environmental and economic impacts. It emphasizes the growing demand for public transport in Indian cities due to urbanization and population growth, and addresses necessary integrations for efficient public transit systems. Challenges such as high costs, safety concerns, and service reliability are also noted.