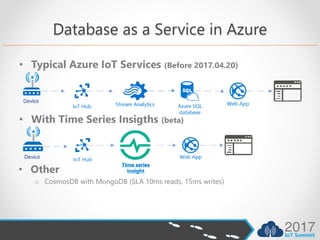
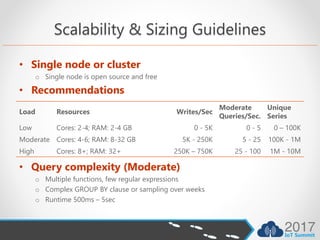
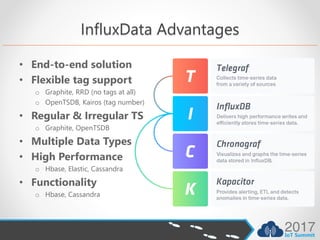
This document discusses choosing the right time series database for IoT data. It compares InfluxDB to SQL Server and other databases.
Some key points made:
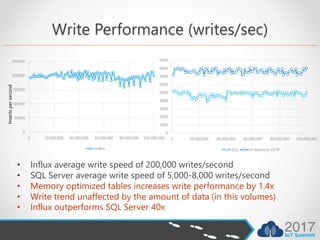
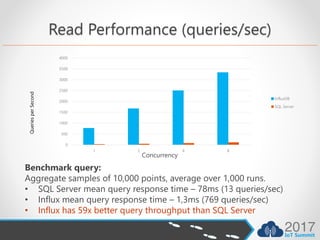
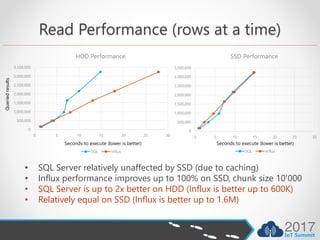
- InfluxDB outperforms SQL Server for writes by 40x and queries by 59x for time series data due to its optimized design.
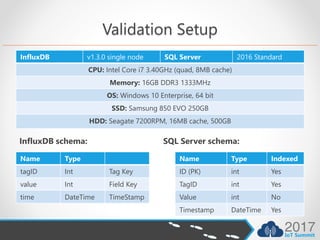
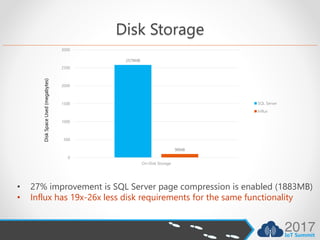
- InfluxDB uses 19x-26x less disk storage than SQL Server for the same data.
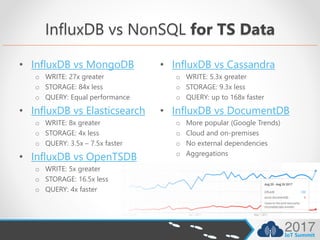
- InfluxDB also outperforms MongoDB, Elasticsearch, OpenTSDB, and Cassandra for time series workloads.
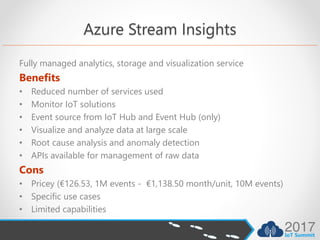
- Azure Stream Insights is a managed service but has limited capabilities and can be pricey for high volumes of data.
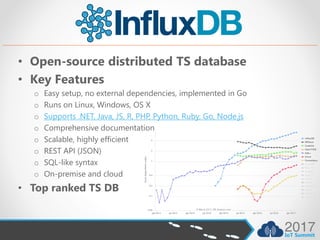
- InfluxDB is open source, has no dependencies, and