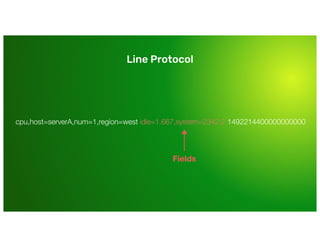
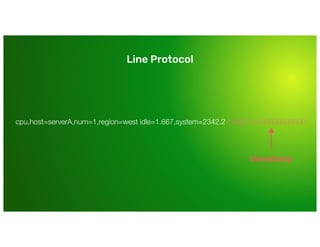
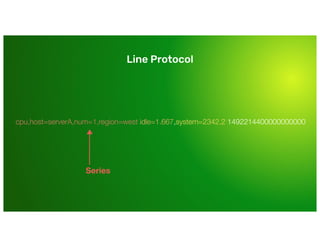
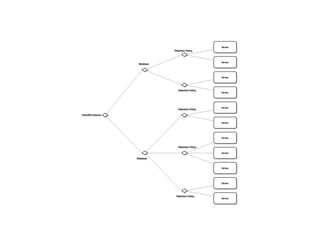
The document is a training presentation on InfluxDB and time-series data aimed at engineering managers. It covers concepts such as the InfluxDB data model, schema design, and querying data using various languages. Participants will learn how to manage and effectively utilize time-series data within the InfluxDB platform.








![© InfluxData. All rights reserved.
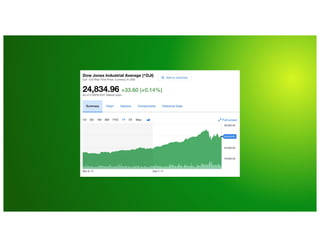
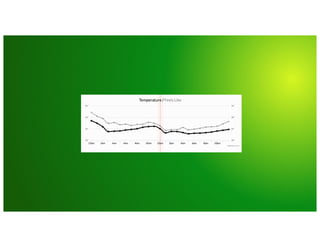
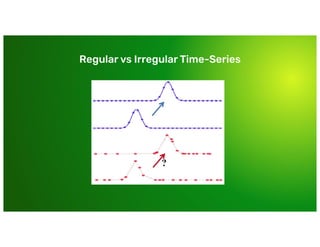
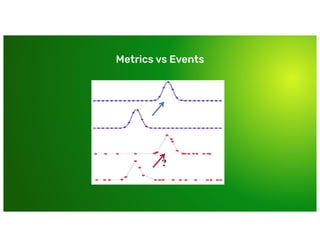
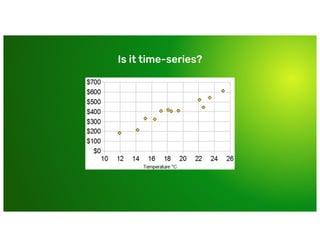
Why couldn’t I just use [...]
© InfluxData. All rights reserved.
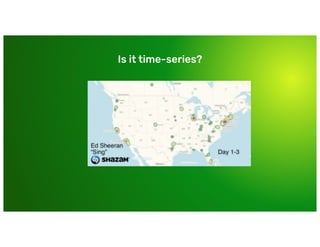
Why couldn’t I just use [...]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/day2-b-9-40am-influxdbconceptsandarchitecturebymichaeldesa-191007034007/85/InfluxDB-101-Concepts-and-Architecture-Michael-DeSa-InfluxData-15-320.jpg)