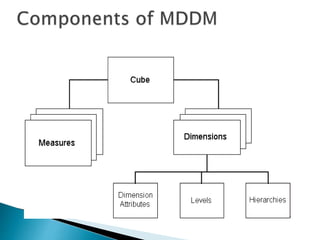
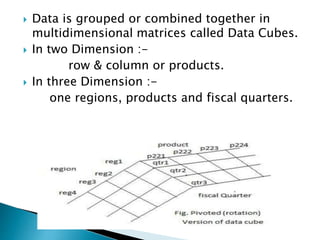
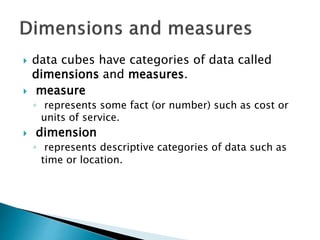
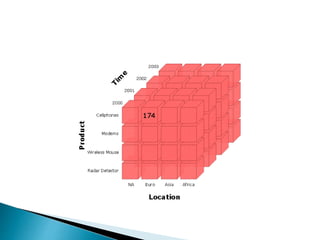
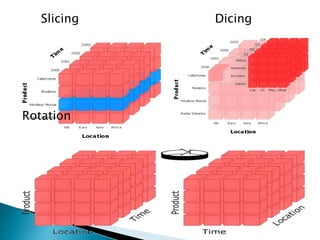
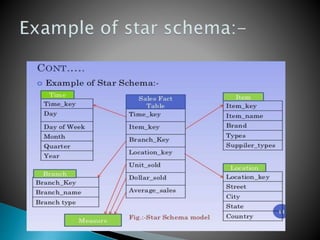
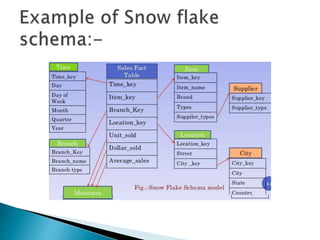
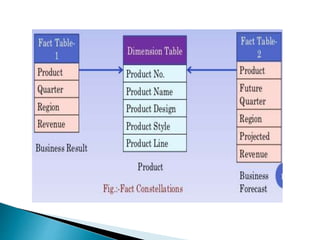
The document discusses multidimensional databases and data warehousing. It describes multidimensional databases as optimized for data warehousing and online analytical processing to enable interactive analysis of large amounts of data for decision making. It discusses key concepts like data cubes, dimensions, measures, and common data warehouse schemas including star schema, snowflake schema, and fact constellations.