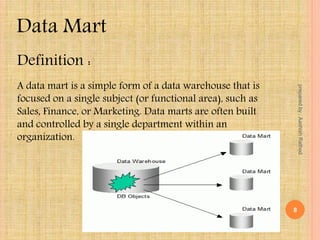
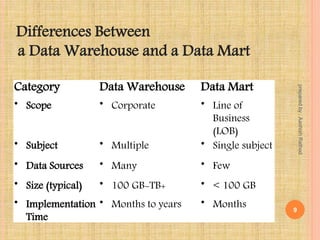
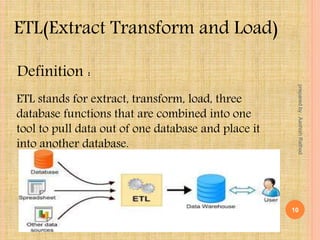
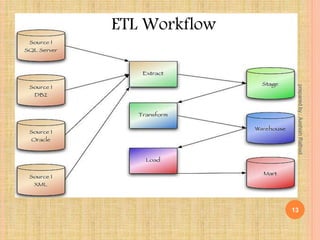
This document defines key concepts in data warehousing including data warehouses, data marts, and ETL (extract, transform, load). It states that a data warehouse is a non-volatile collection of integrated data from multiple sources used to support management decision making. A data mart contains a single subject area of data. ETL is the process of extracting data from source systems, transforming it, and loading it into a data warehouse or data mart.