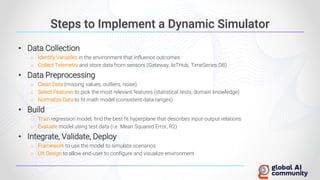
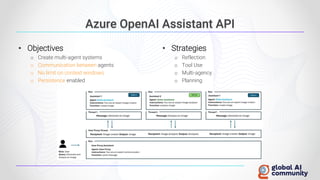
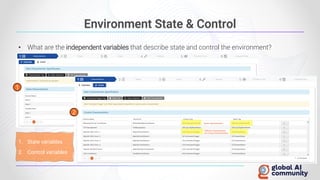
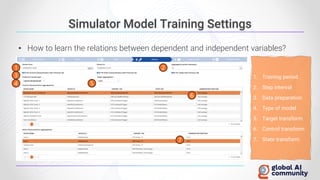
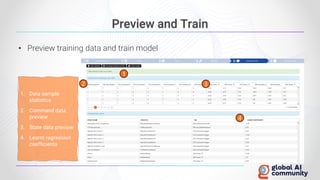
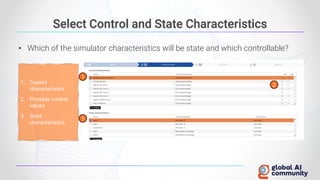
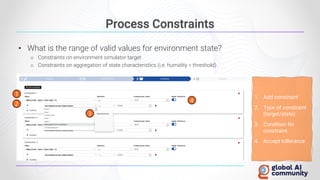
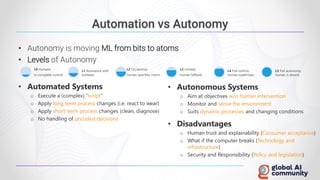
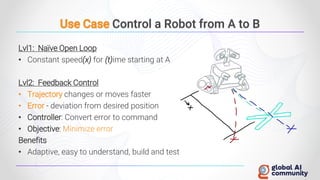
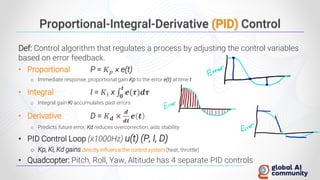
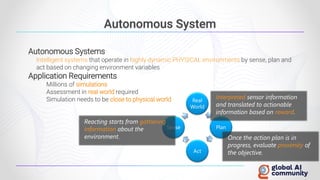
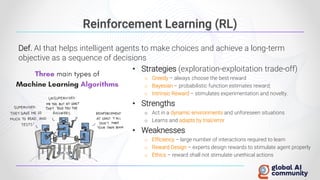
The document discusses advancements in autonomous systems and control frameworks, highlighting techniques like reinforcement learning and PID control. It introduces various projects such as Microsoft's Project Malmo and Project Bonsai, while also emphasizing the importance of simulation in developing these technologies. Key components, methodologies, and use cases are presented to illustrate the efficacy and challenges of implementing autonomous systems in dynamic environments.












![Gymnasium Installation (Windows)
• Install Python (supported v.3.8 - 3.11)
o Add Python to PATH; Windows works but not officially supported
• Install Gymnasium
• Install MuJoCo (Multi-Joint dynamics with Contact)
o Developed by Emo Todorov (University of Washington)
o Acquired by Google DeepMind; Feely available from 2021
• Dependencies for environment families
• Test Gymnasium
o Create environment instance
pip install gymnasium
pip install “gymnasium[mujoco]”
pip install mujoco](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/autonomoussystemsforoptimizationandcontrol-240914194523-d1d19362/85/Autonomous-Systems-for-Optimization-and-Control-18-320.jpg)






![Simulate Non-Linear Relations
Support Vector Machine (SVM)
• Supervised ML algorithm for classification
• Precondition
Number of samples (points) > Number of features
• Support Vectors – points in N-dimensional space
• Kernel Trick – determine point relations in higher space
o i.e. Polynomial Kernel 2D [𝒙𝟏, 𝒙𝟐] -> 3D [𝒙𝟏, 𝒙𝟐, 𝒙𝟏
𝟐
+ 𝒙𝟐
𝟐
], 5D [𝒙𝟏
𝟐
, 𝒙𝟐
𝟐
, 𝒙𝟏 × 𝒙𝟐 , 𝒙𝟏 , 𝒙𝟐]
Support Vector Regression (SVR)
• Identify regression hyperplane in a higher dimension
• Hyperplane in ϵ margin where most points fit
• Python:](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/autonomoussystemsforoptimizationandcontrol-240914194523-d1d19362/85/Autonomous-Systems-for-Optimization-and-Control-25-320.jpg)
![Simulate Multiple Outcomes
Example: Predictors [diet, exercise, medication] -> Outcomes [blood pressure, cholesterol, BMI]
Option 1: Multiple SVR Models
• SVR model for each outcome
• Precondition: outcomes are independent
Option 2: Multivariative Multiple Regression
• Predictors (Xi): multiple independent input variables
• Outcomes (Yi): multiple dependent variables to be predicted
• Coefficients (β), Error (ϵi)
• Precondition: linear relations
• Python:](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/autonomoussystemsforoptimizationandcontrol-240914194523-d1d19362/85/Autonomous-Systems-for-Optimization-and-Control-26-320.jpg)