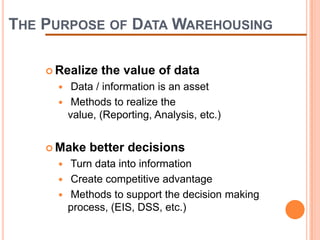
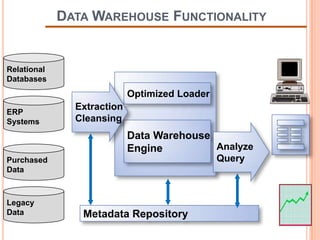
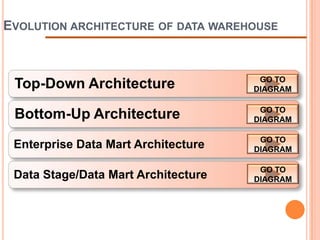
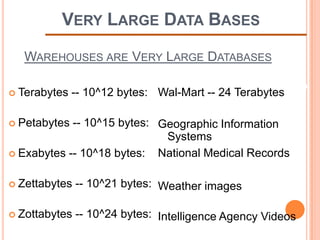
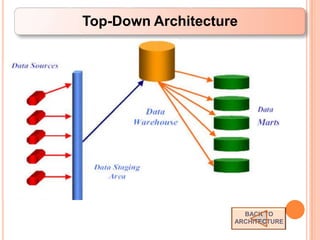
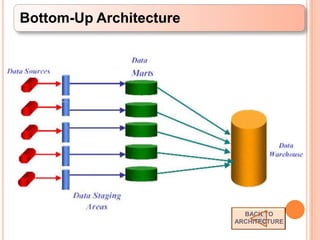
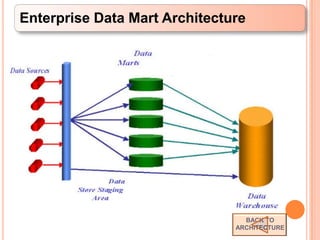
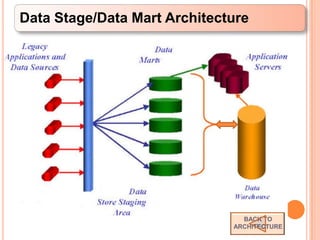
This document defines a data warehouse as a collection of corporate information derived from operational systems and external sources to support business decisions rather than operations. It discusses the purpose of data warehousing to realize the value of data and make better decisions. Key components like staging areas, data marts, and operational data stores are described. The document also outlines evolution of data warehouse architectures and best practices for implementation.