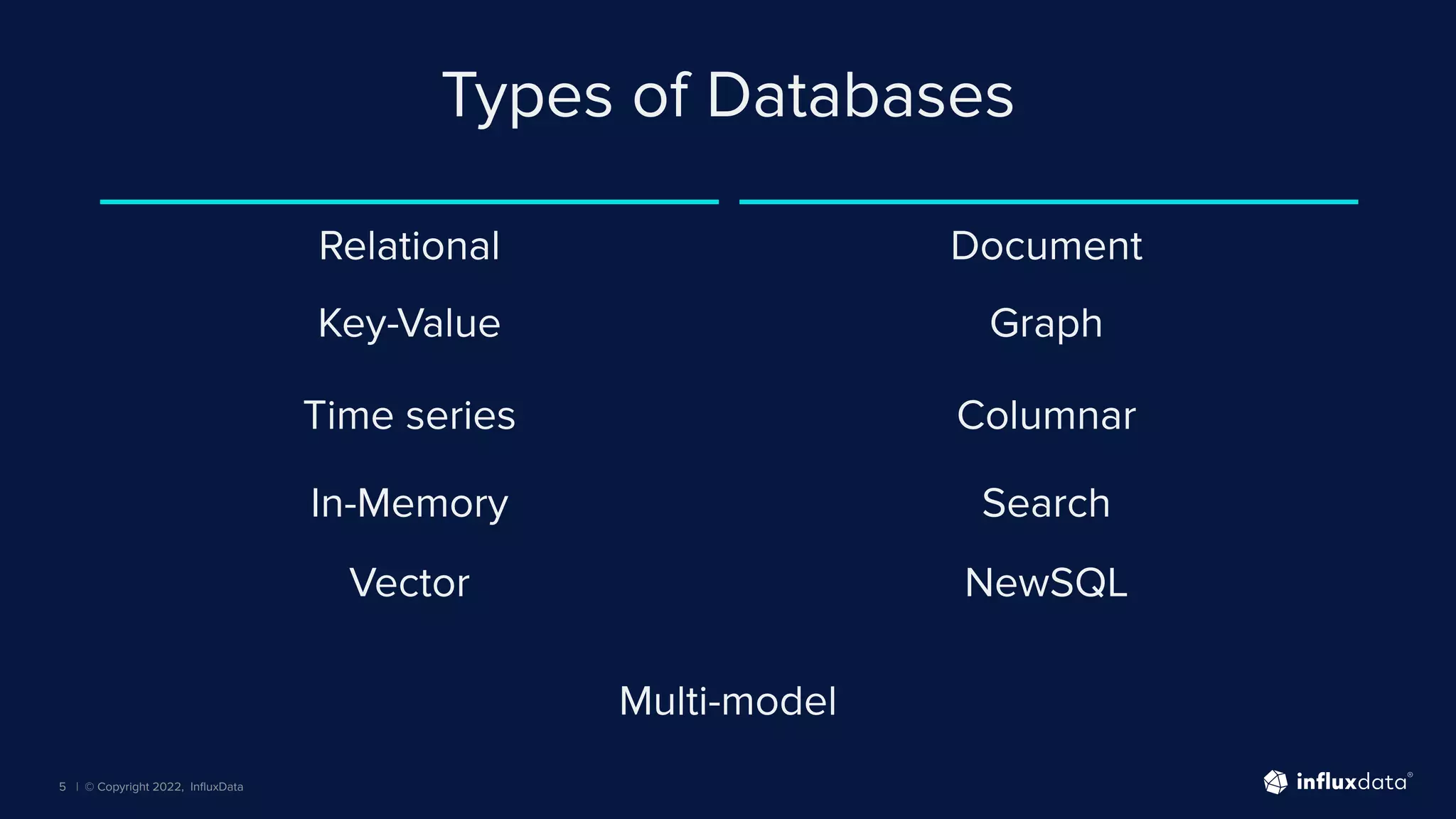
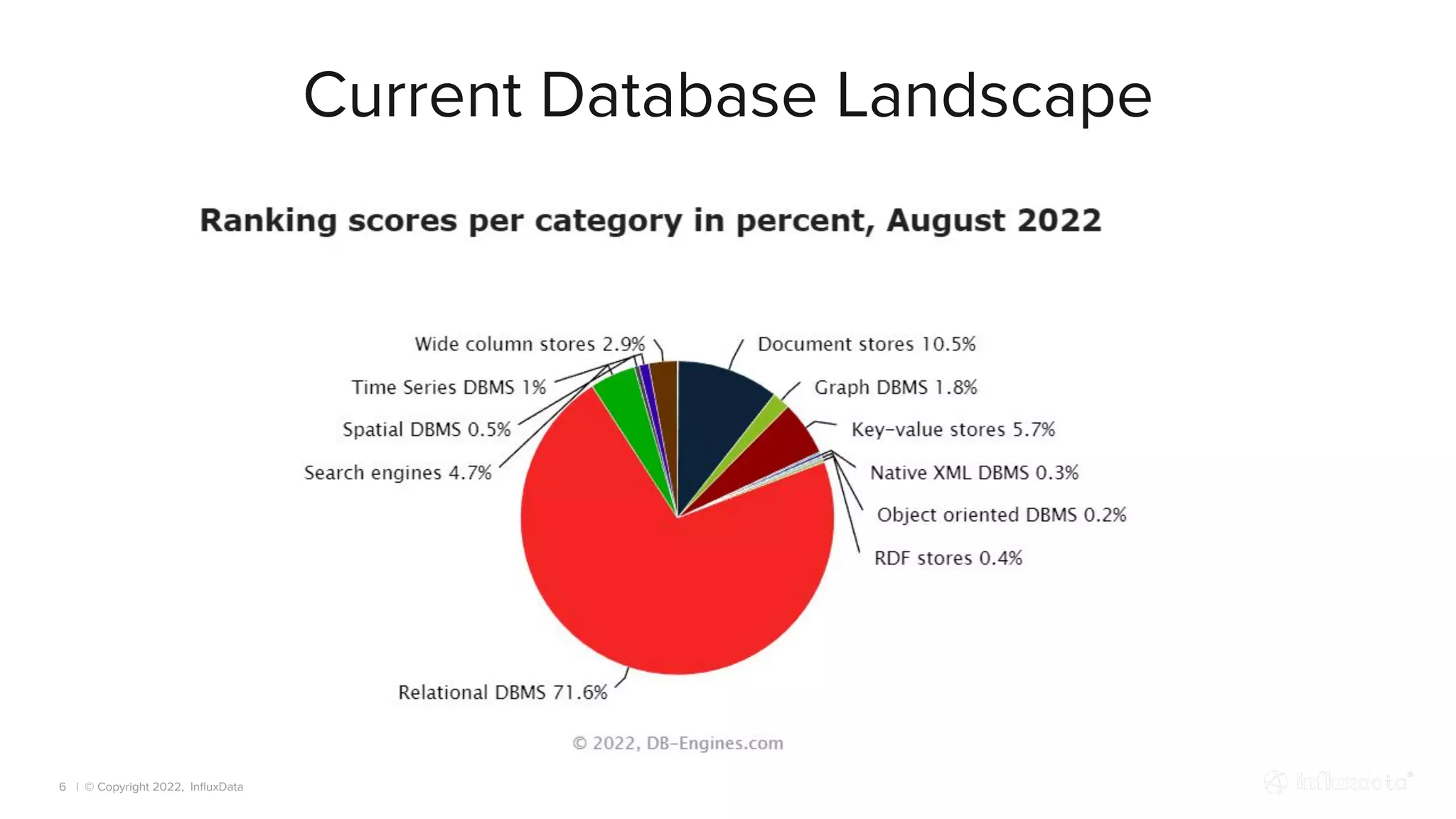
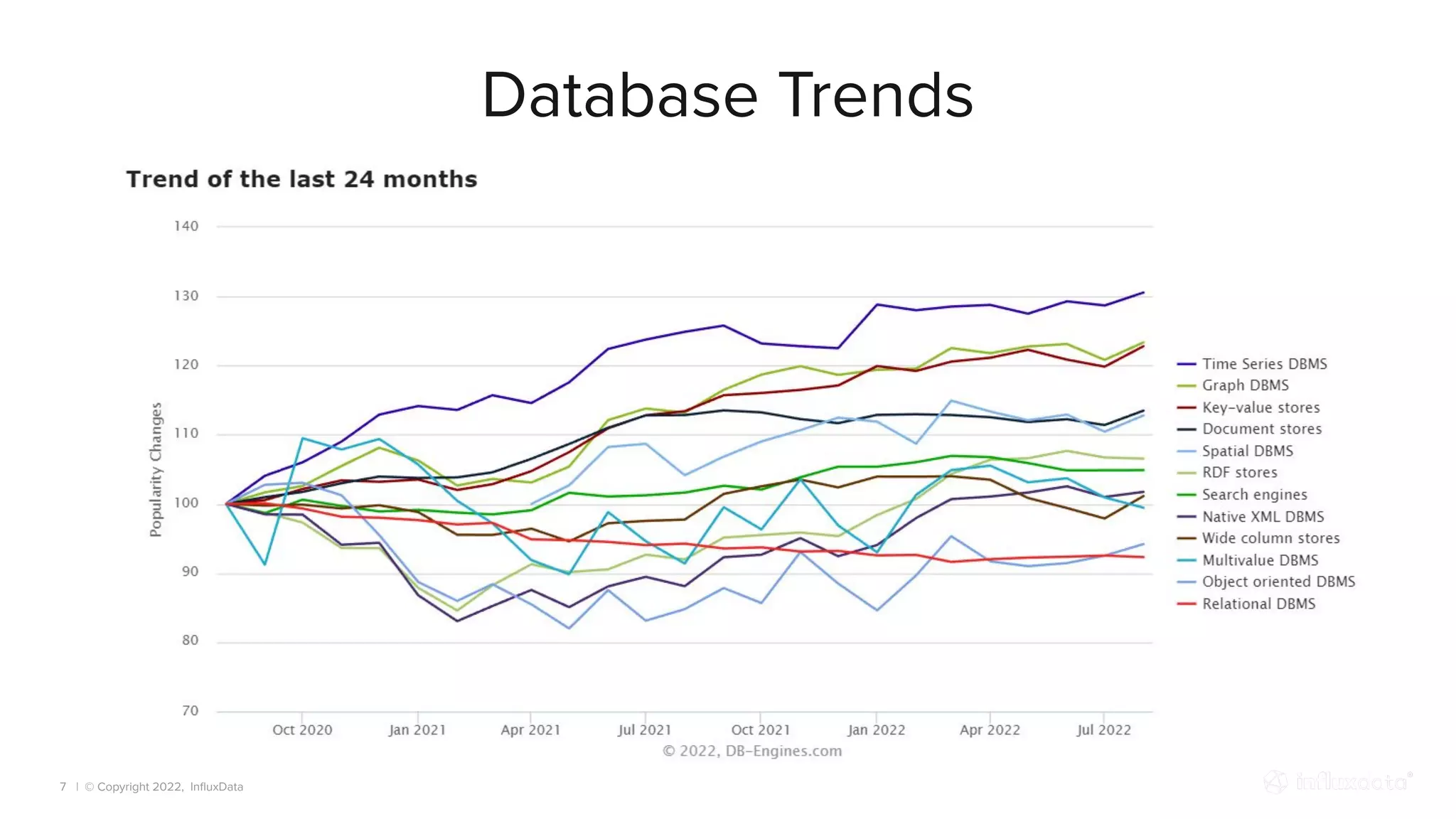
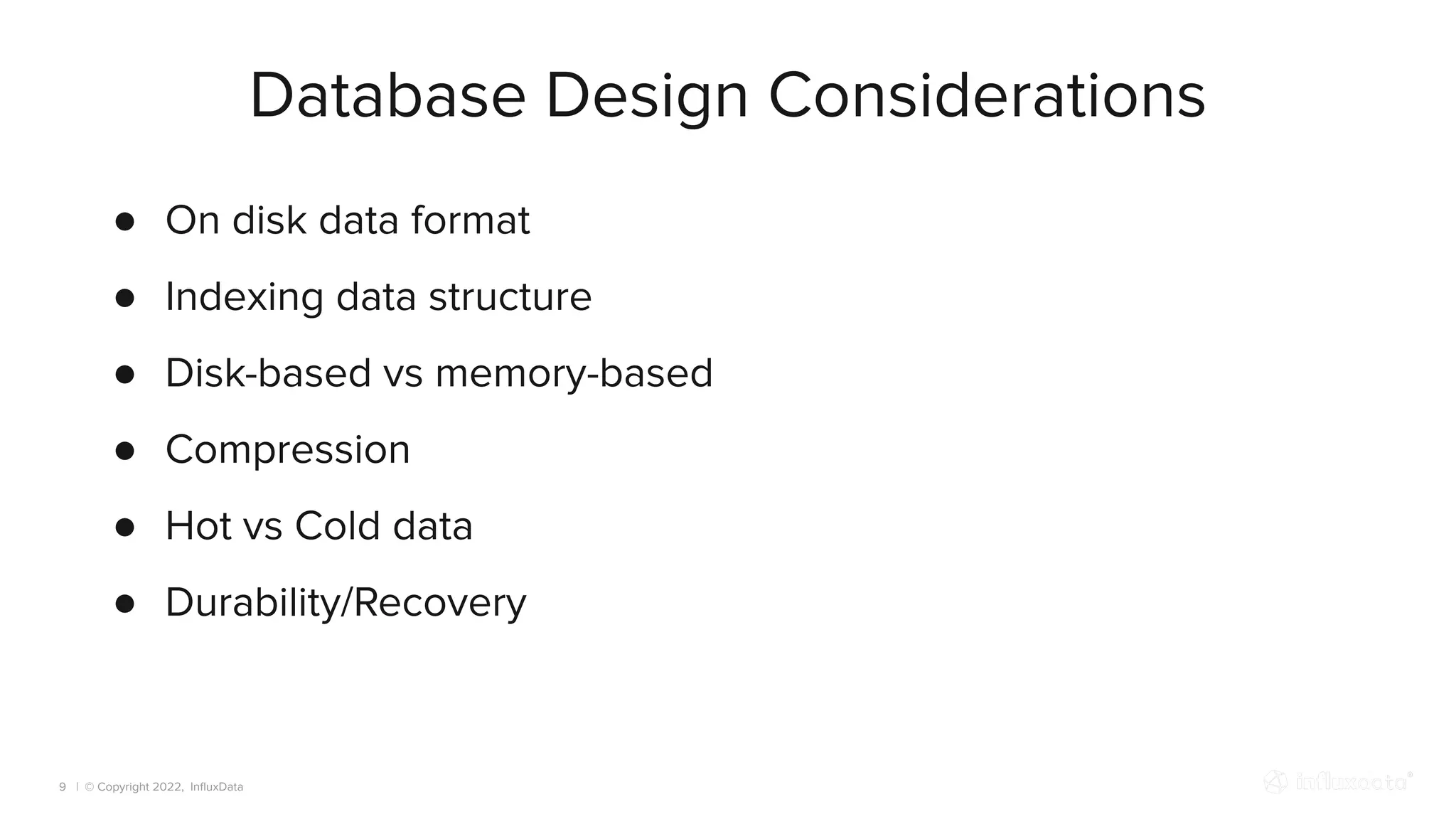
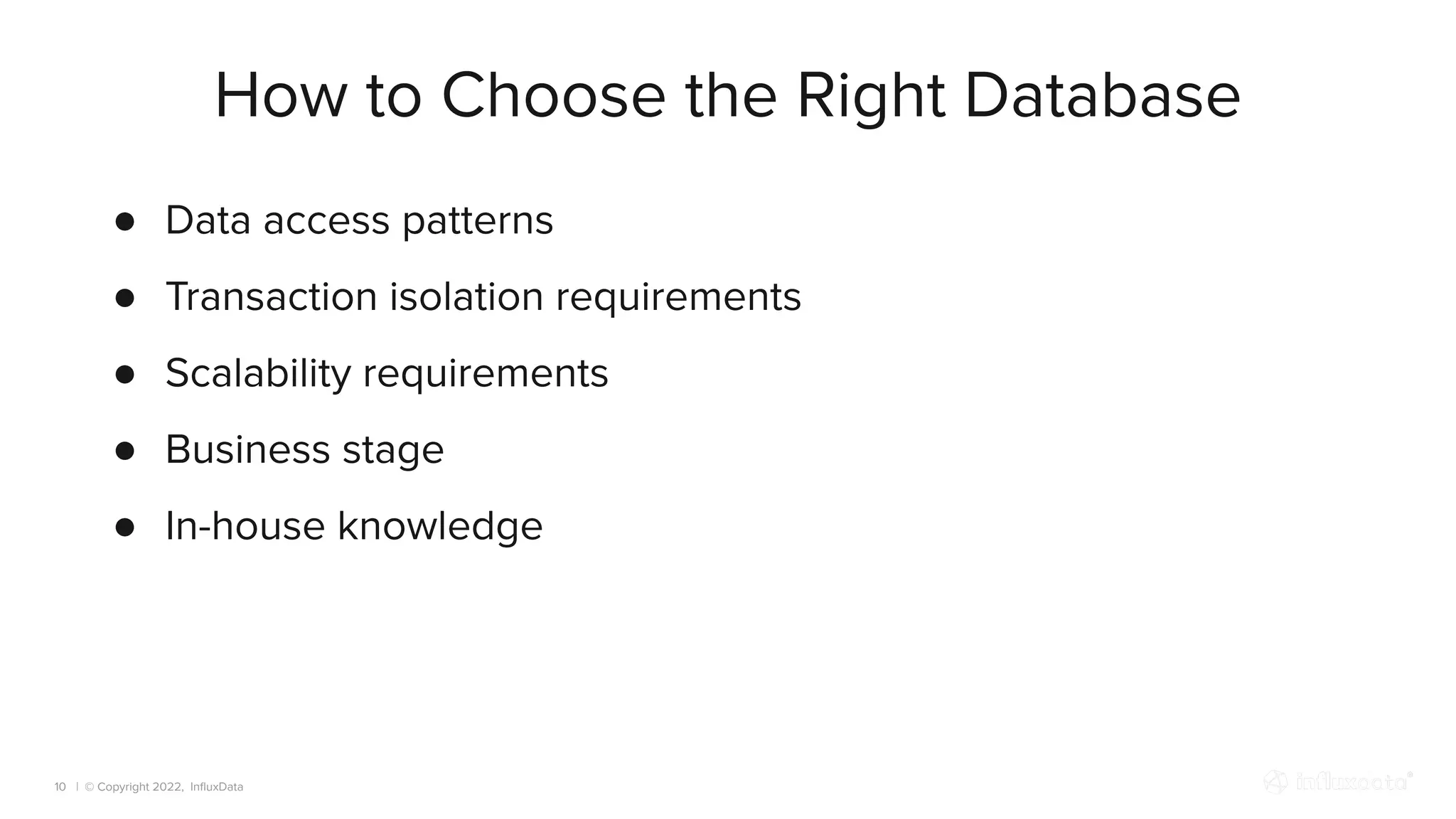
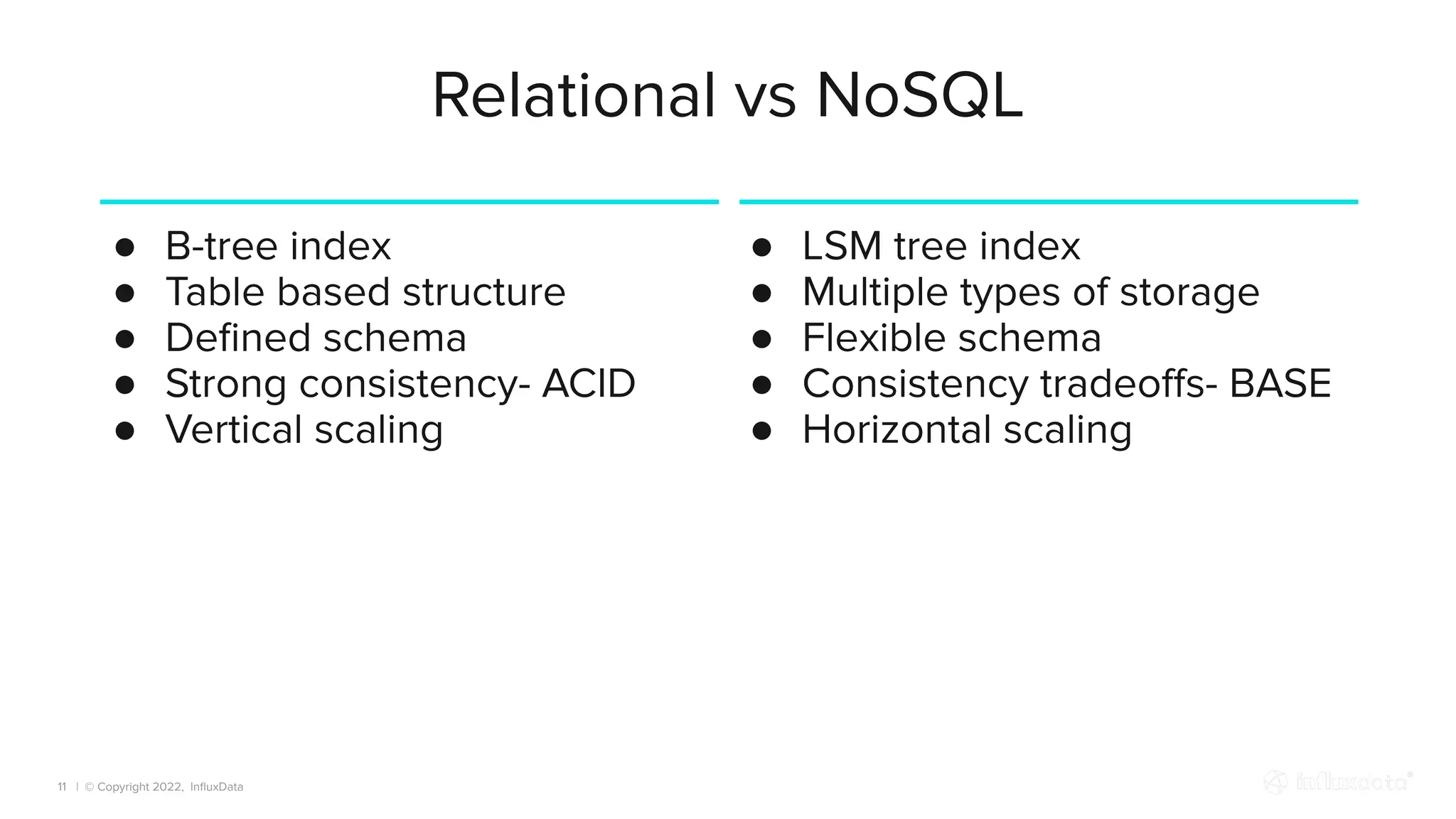
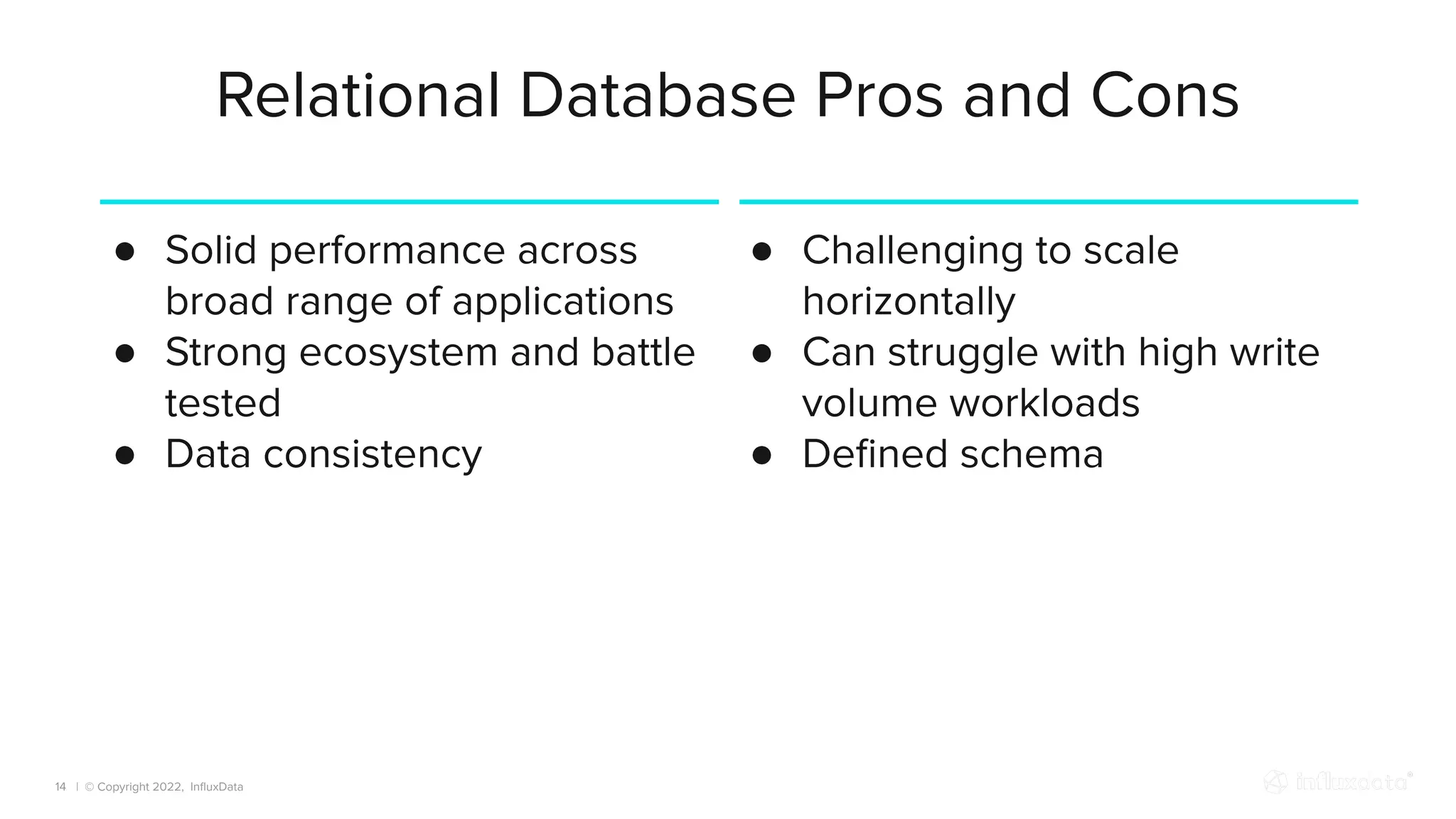
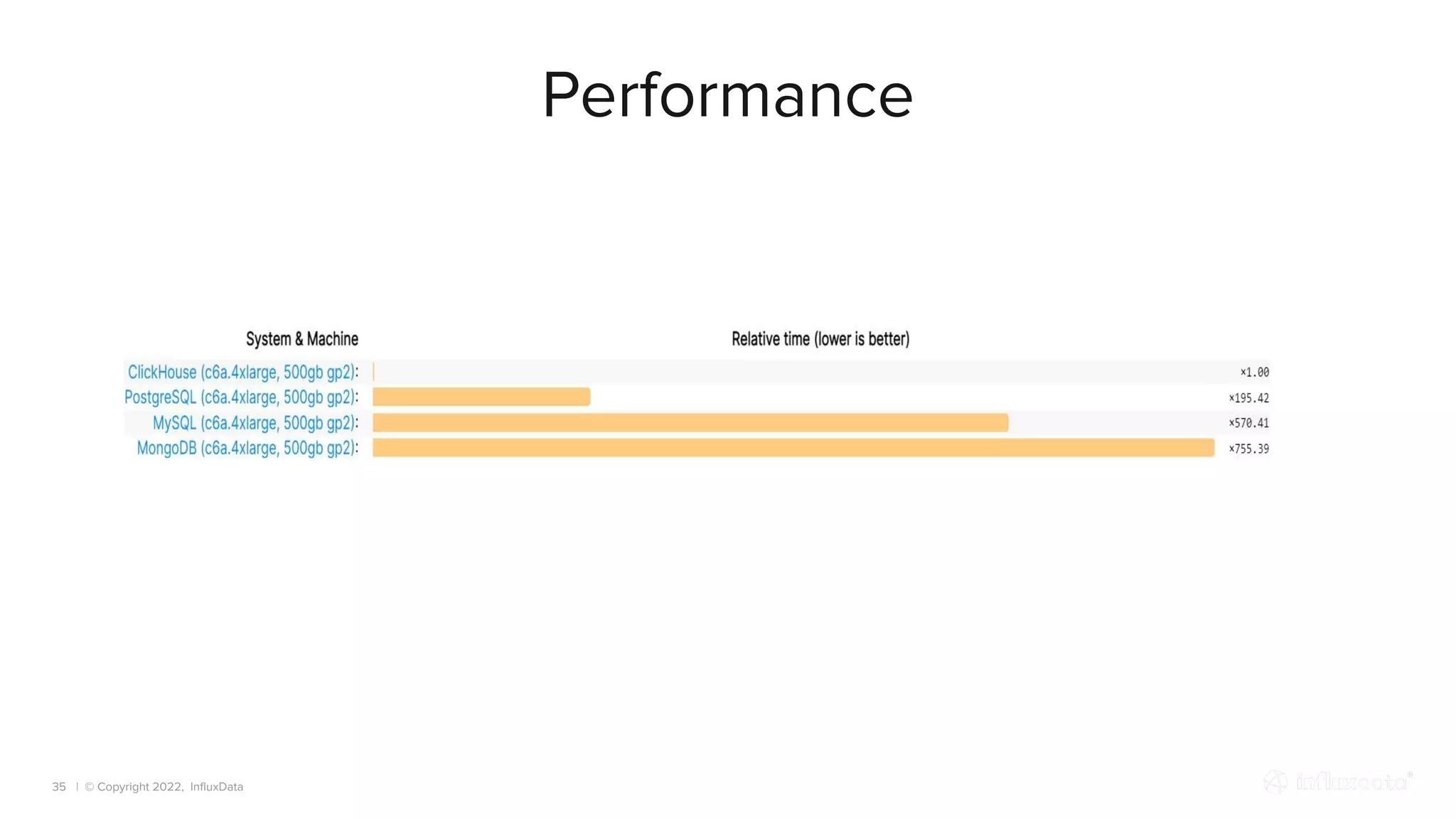
The document provides an overview of the various types of databases, including relational, NoSQL, time series, and graph databases, detailing their pros, cons, and suitable use cases. It highlights the current database landscape and trends, emphasizing considerations for choosing the right database based on factors such as data access patterns and transaction requirements. Additionally, it discusses future trends in database technology, such as multi-model databases and advancements in machine learning indexing.