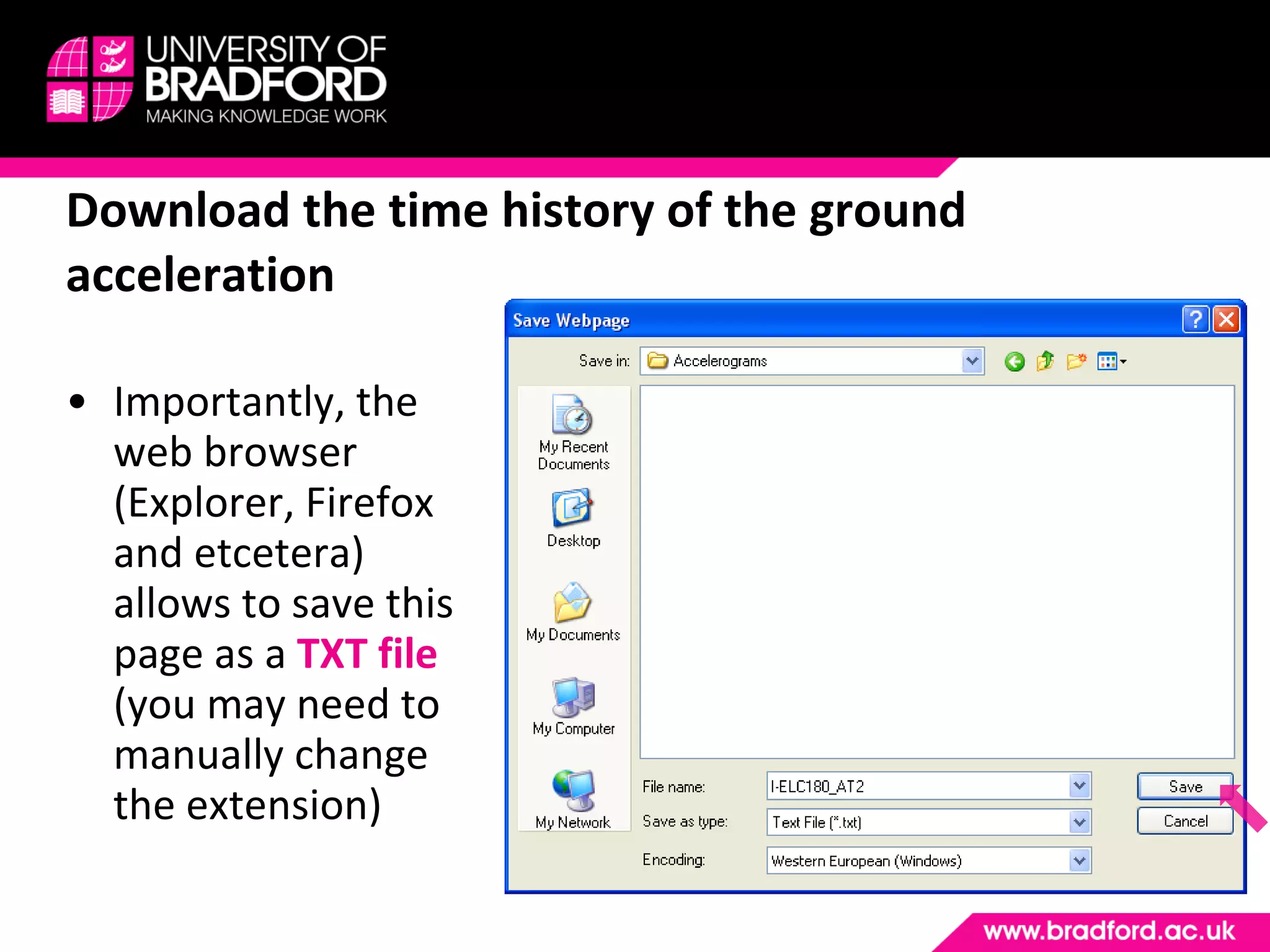
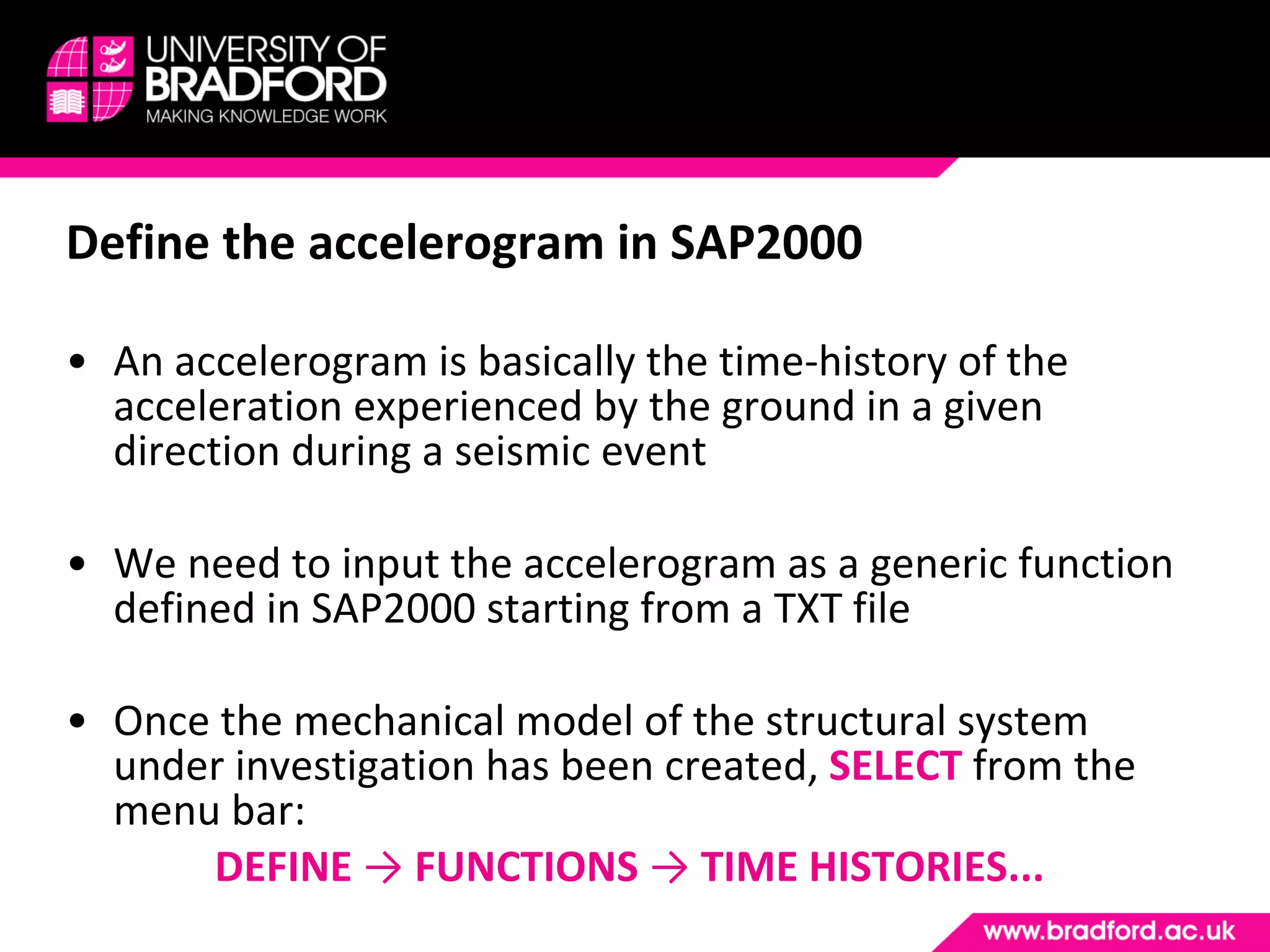
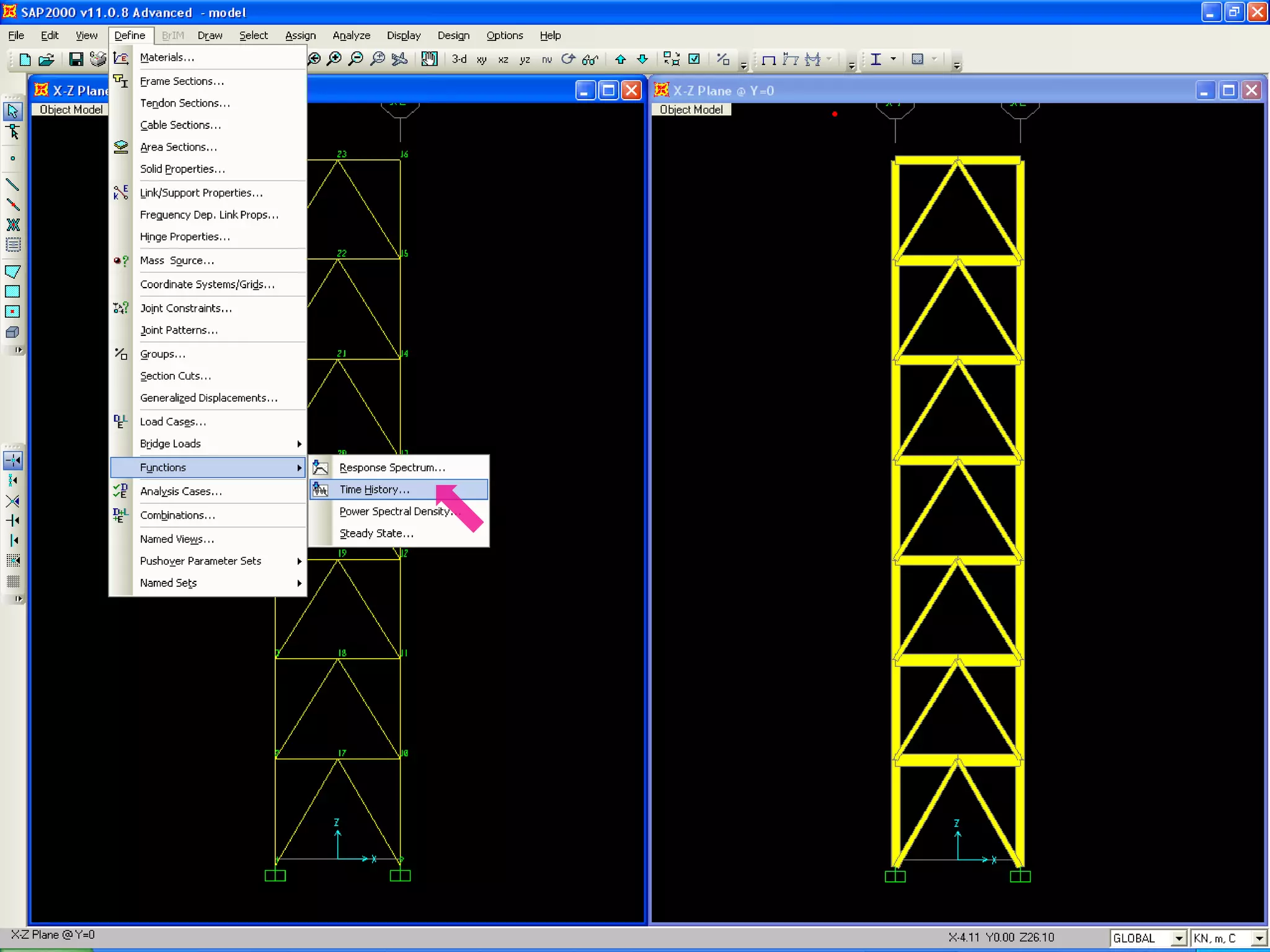
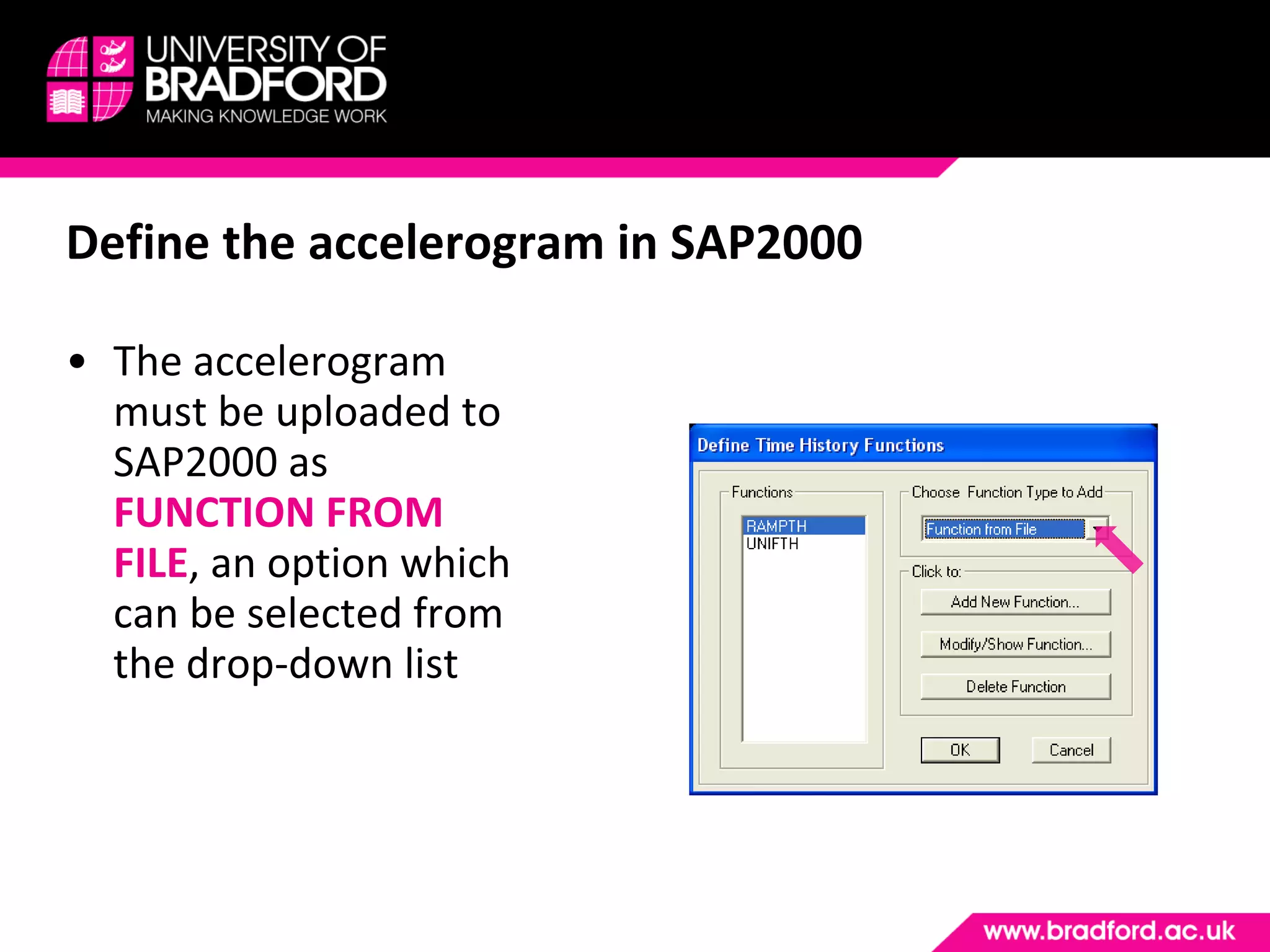
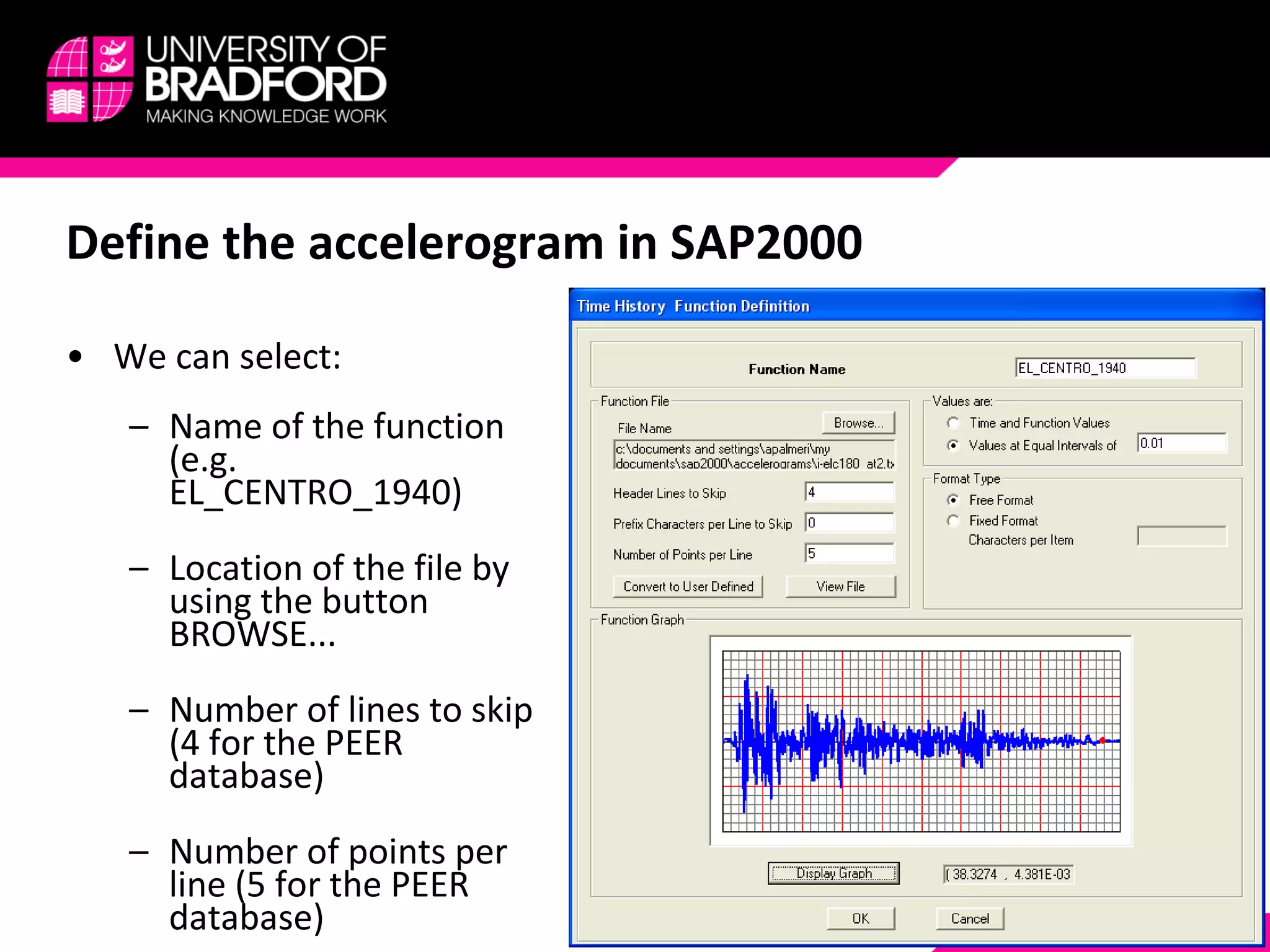
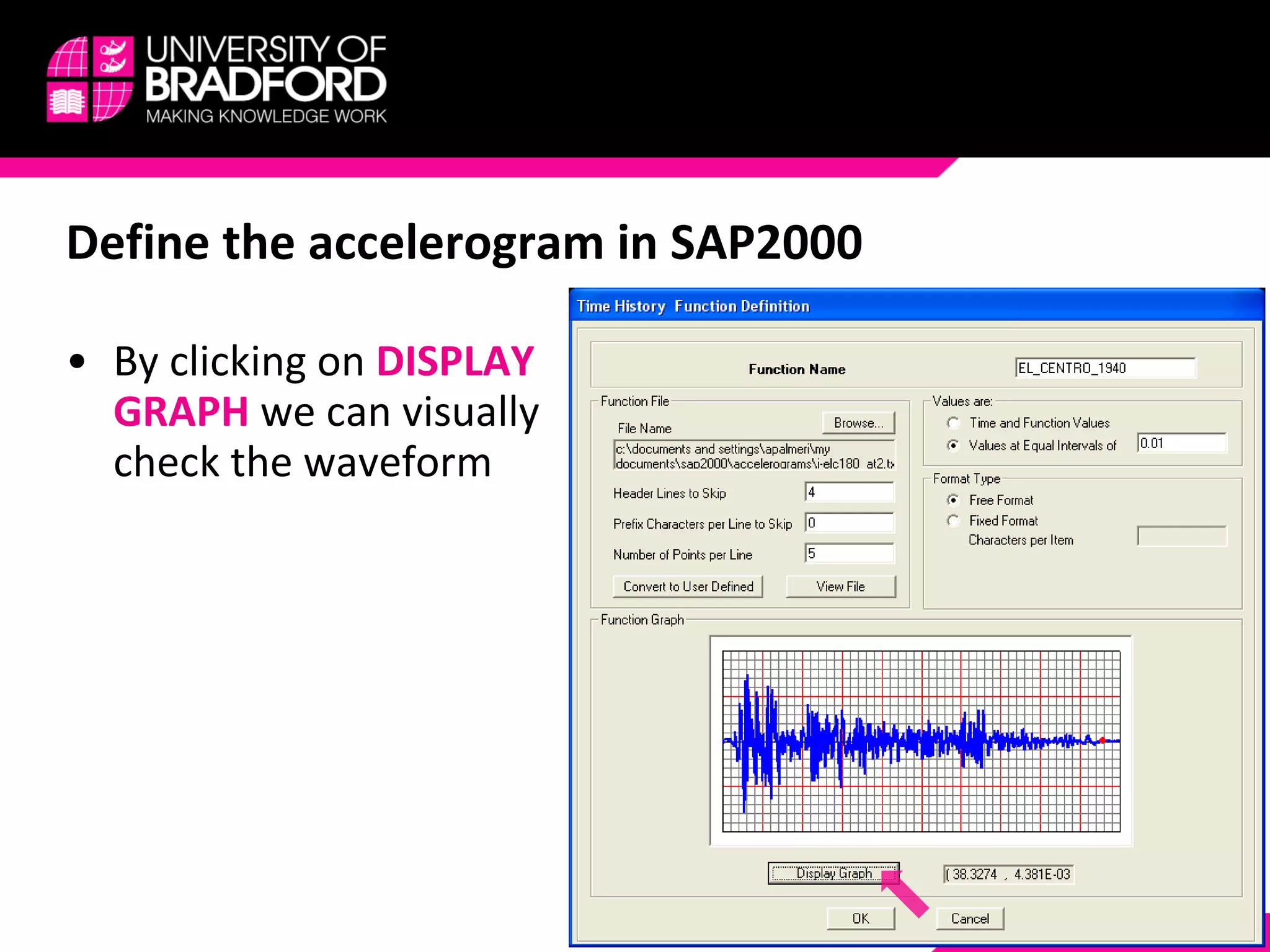
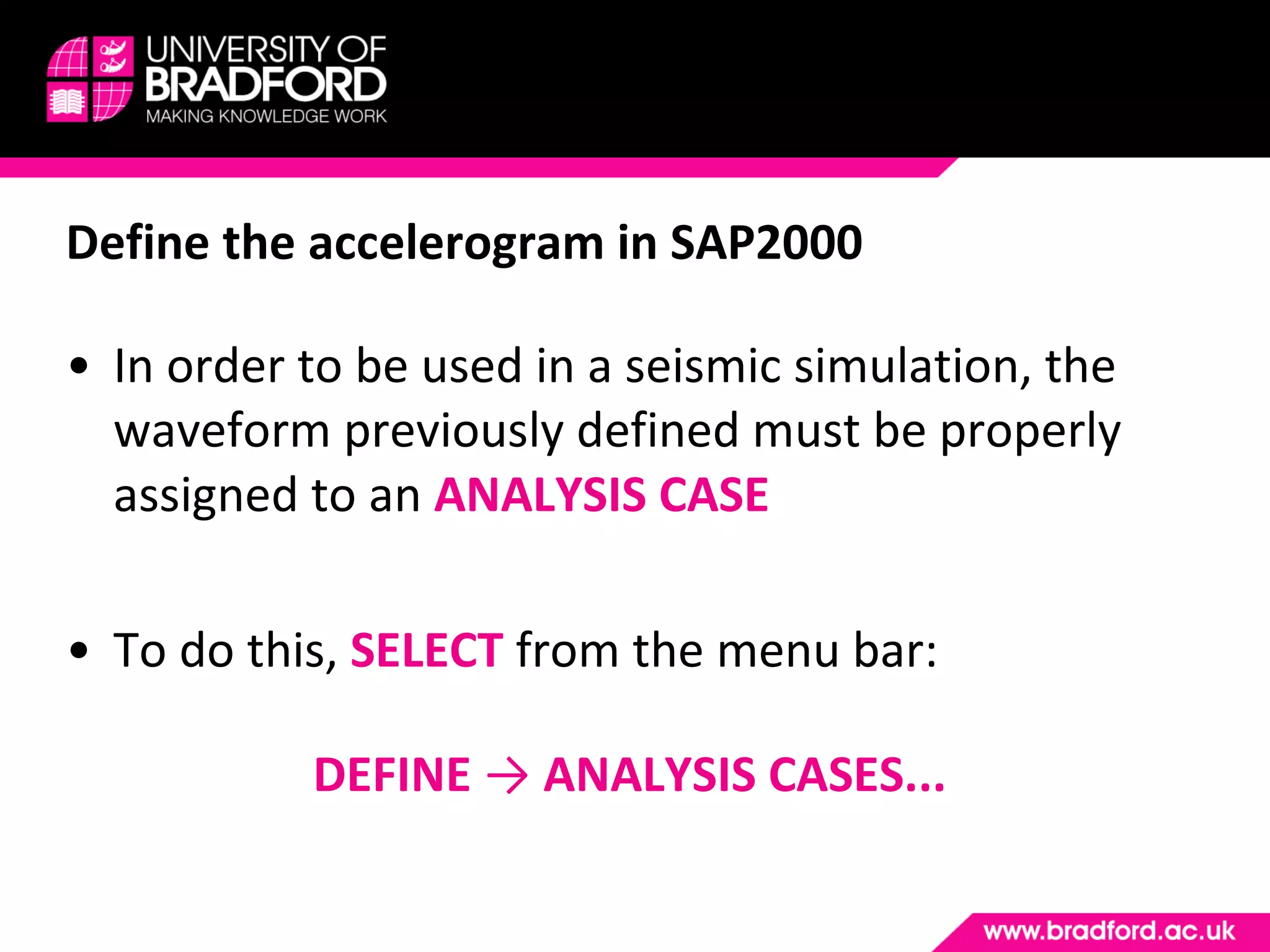
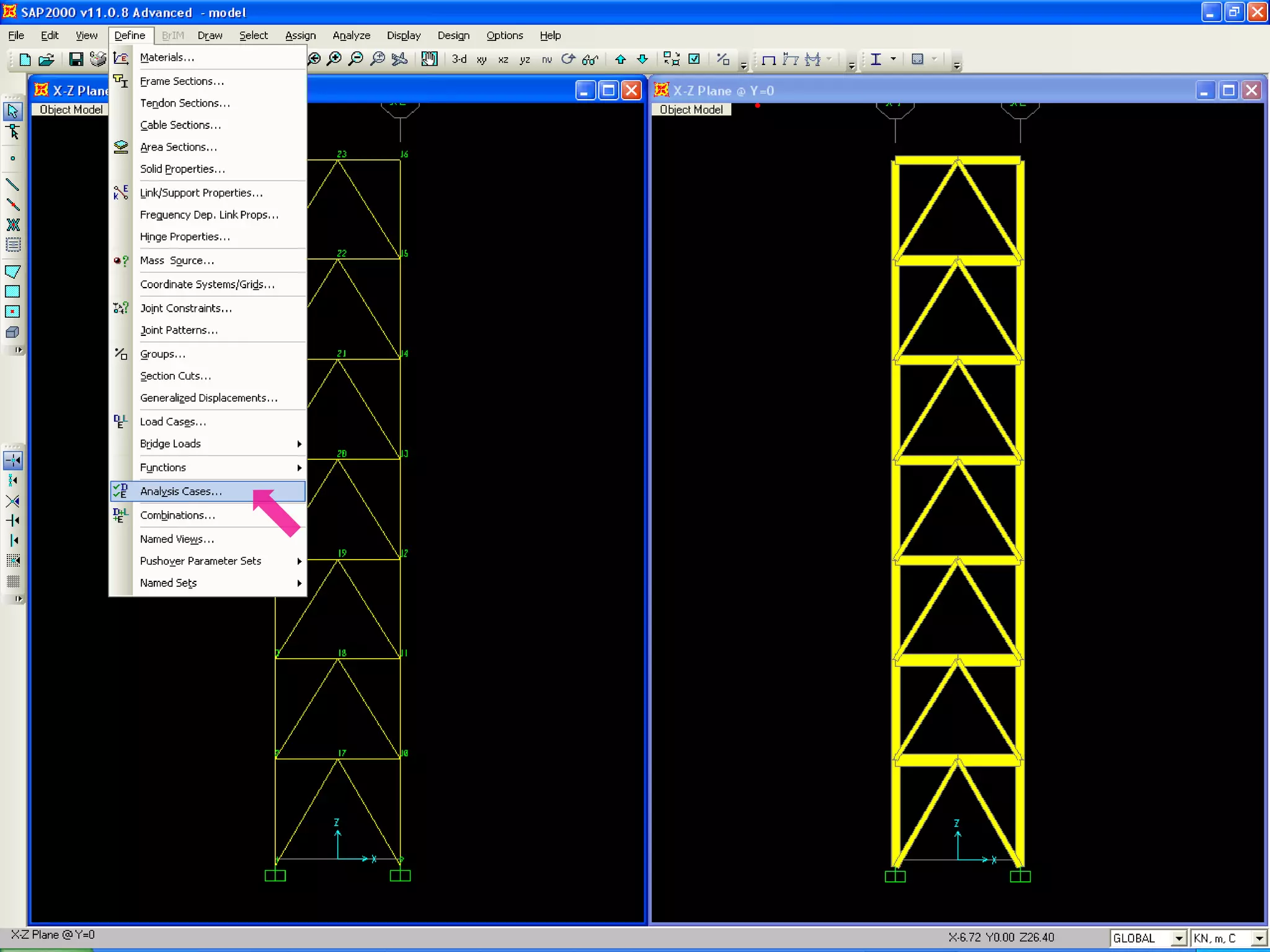
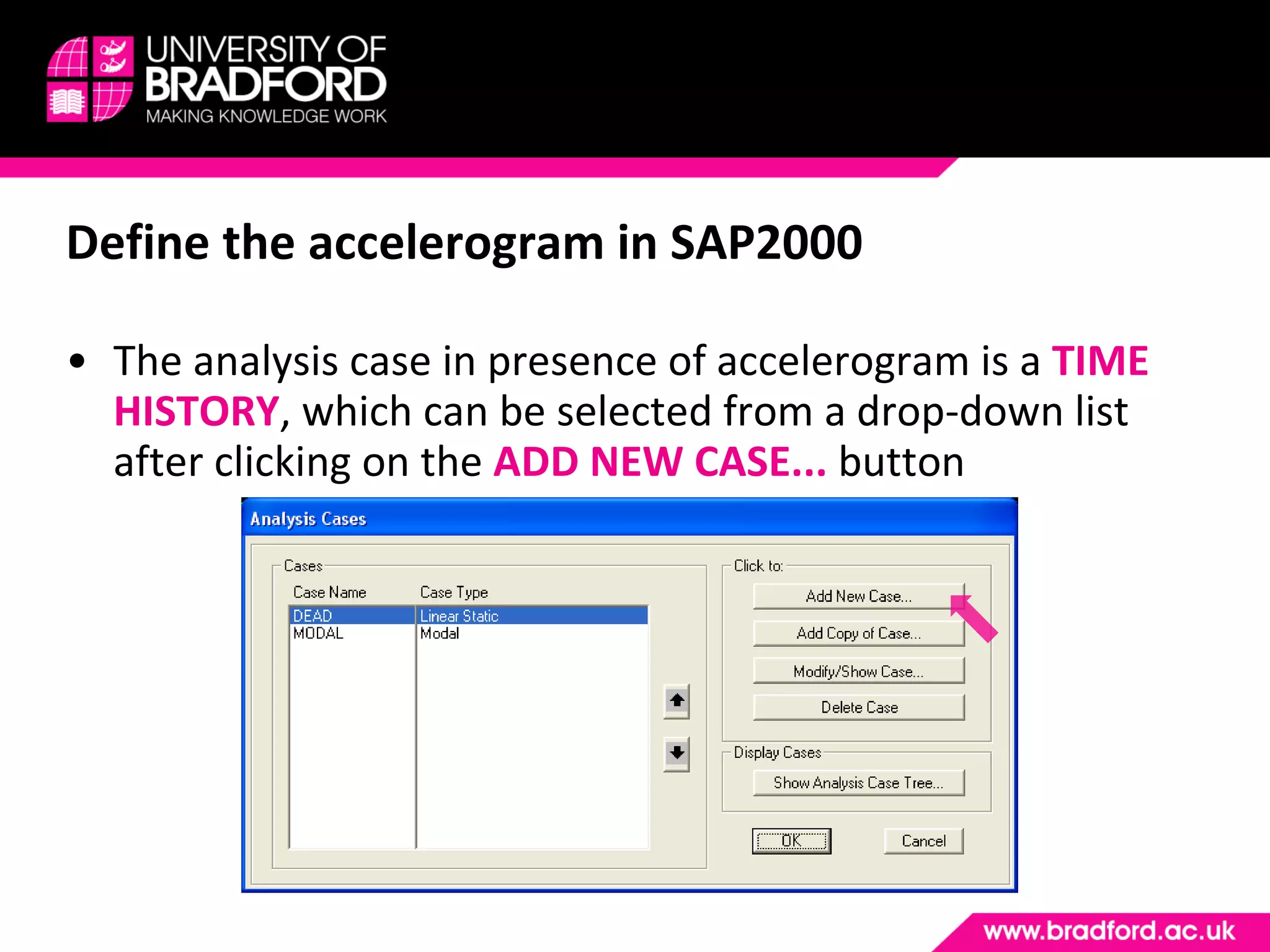
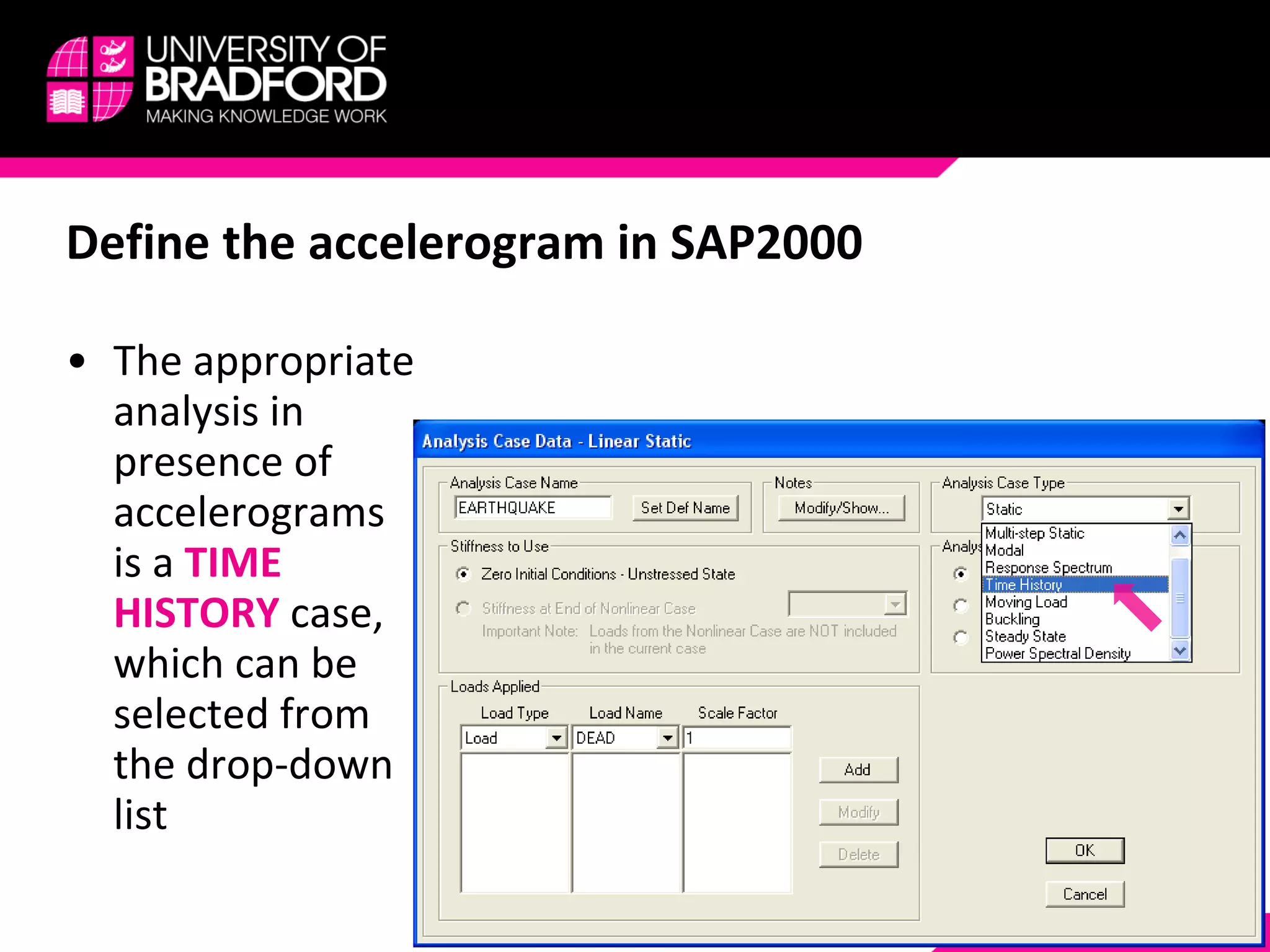
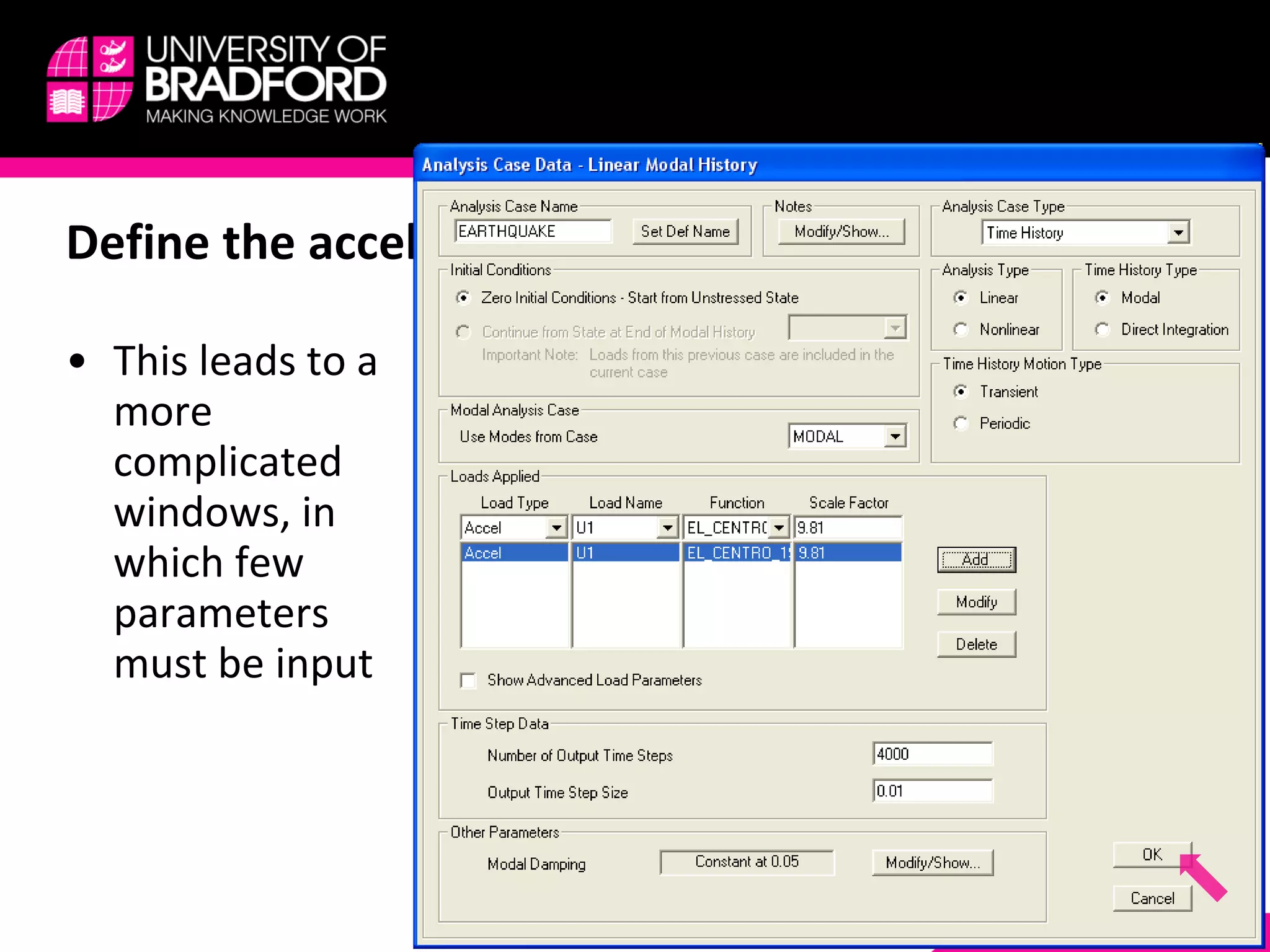
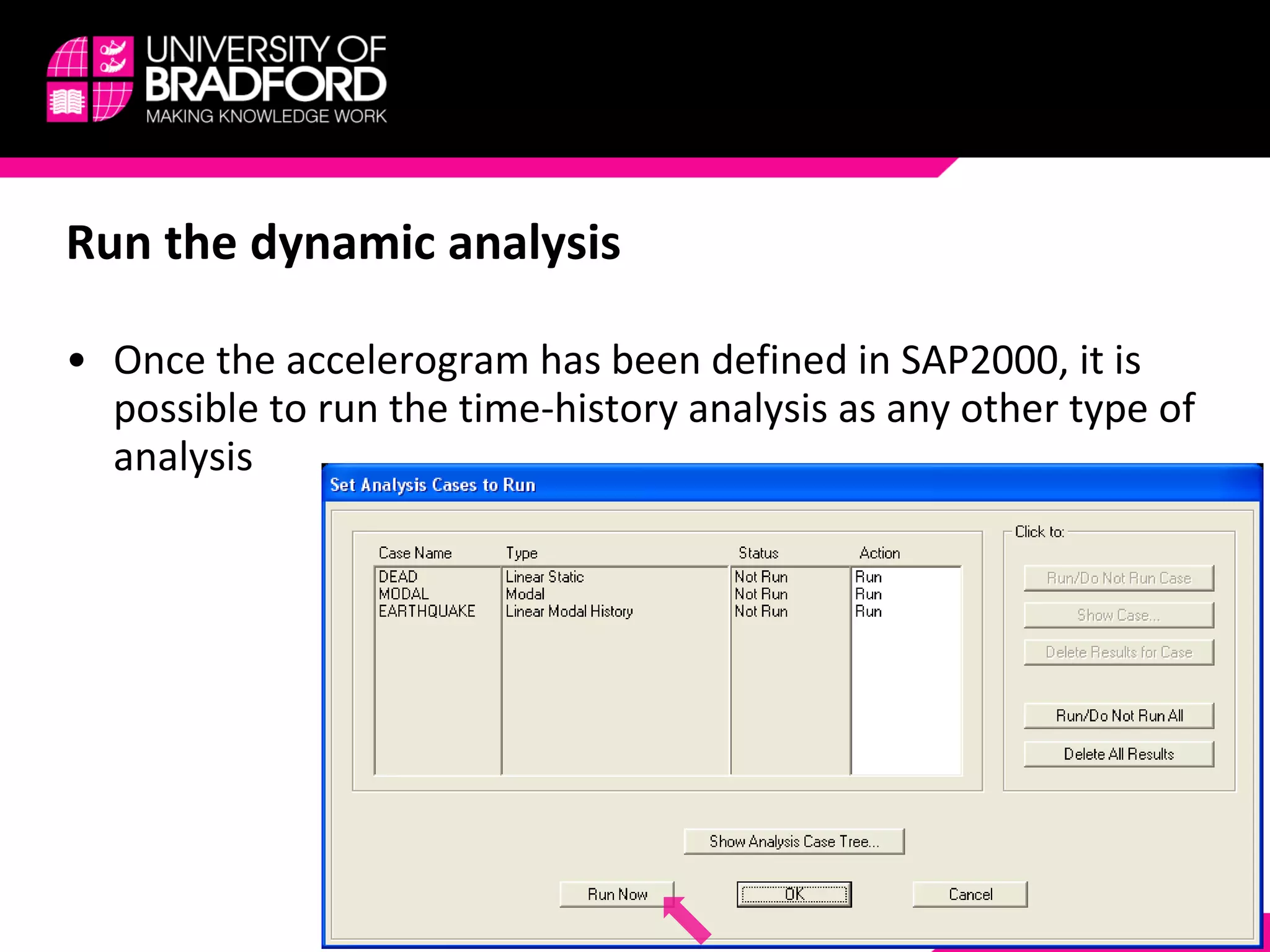
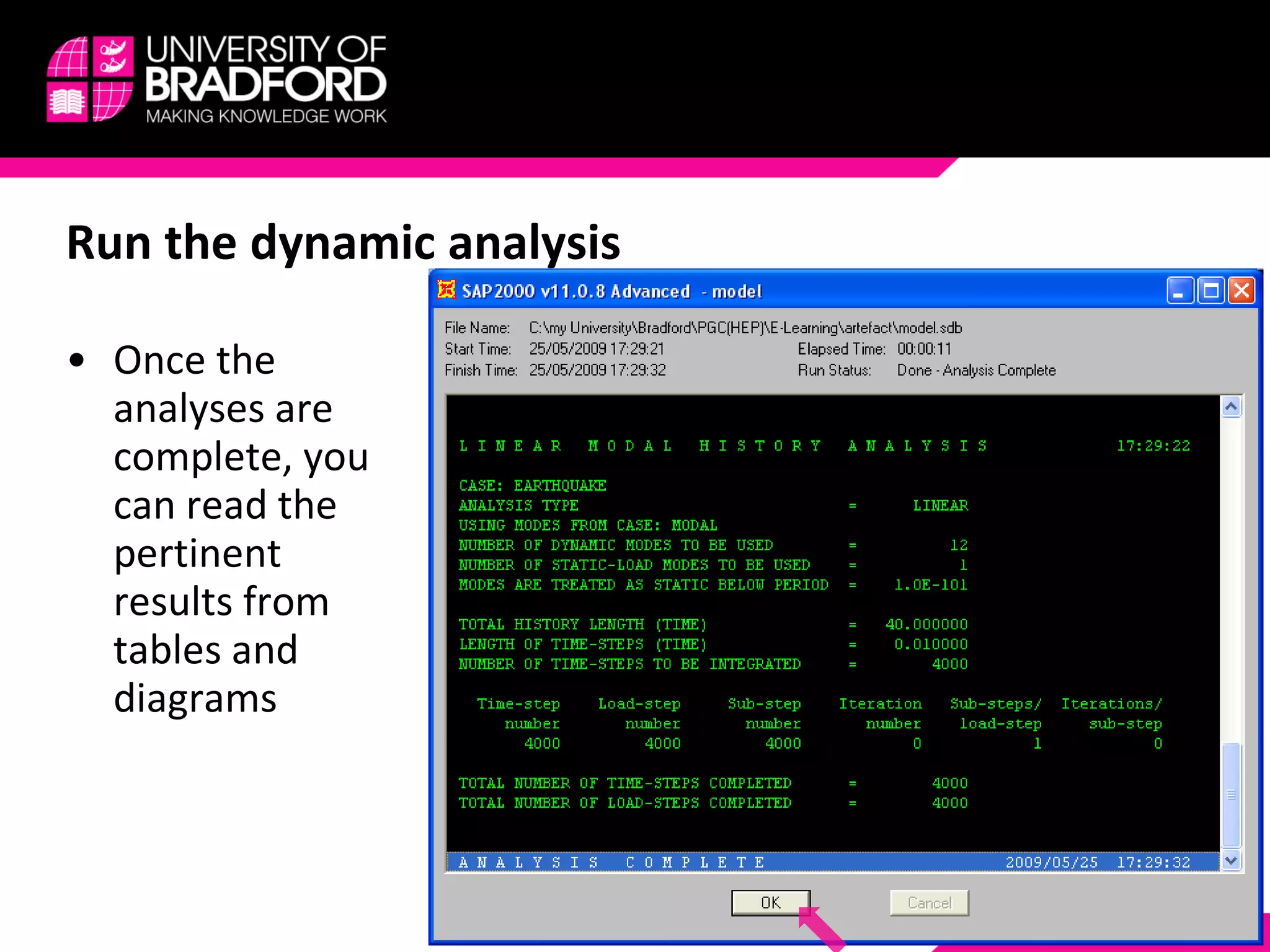
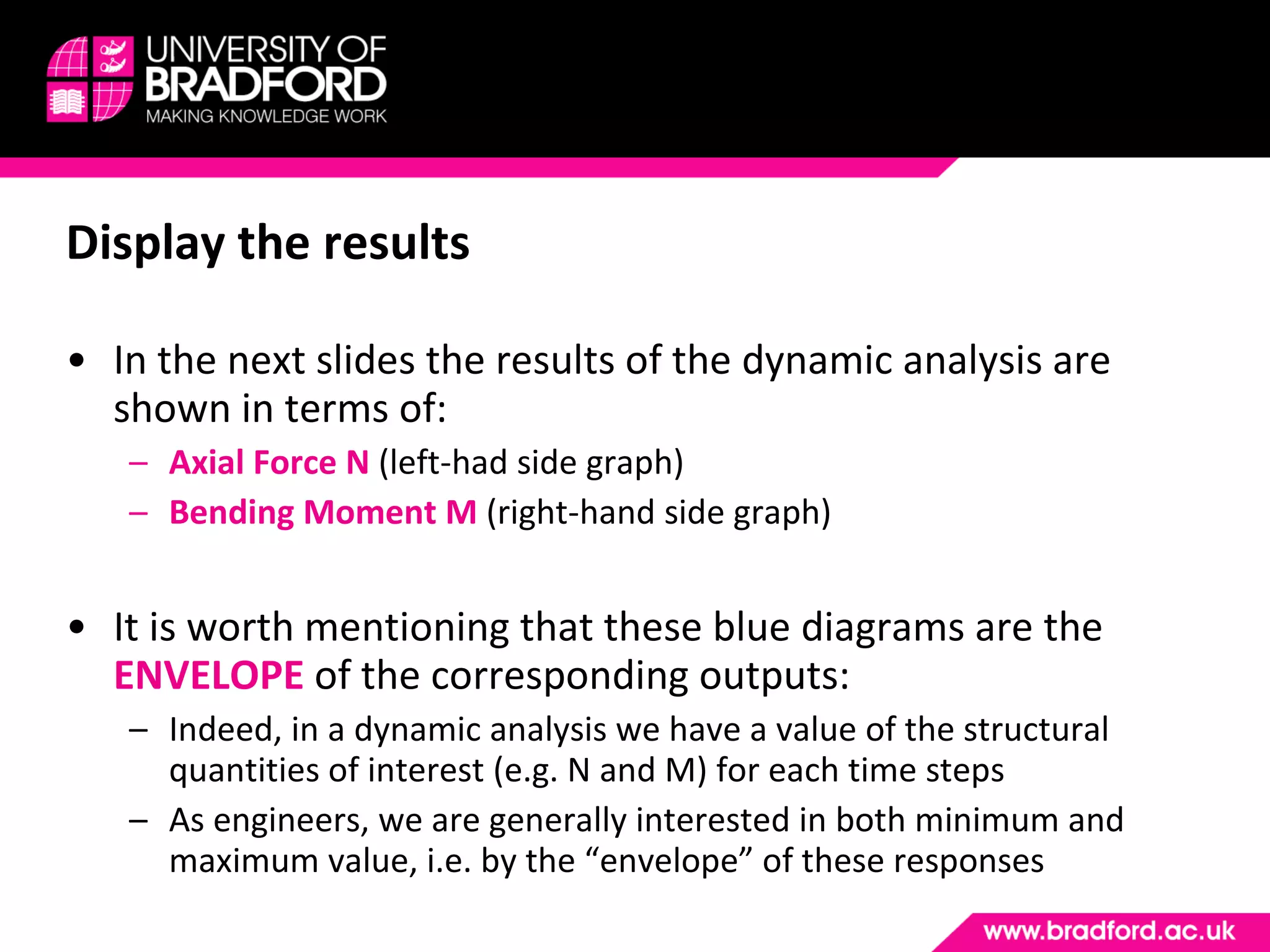
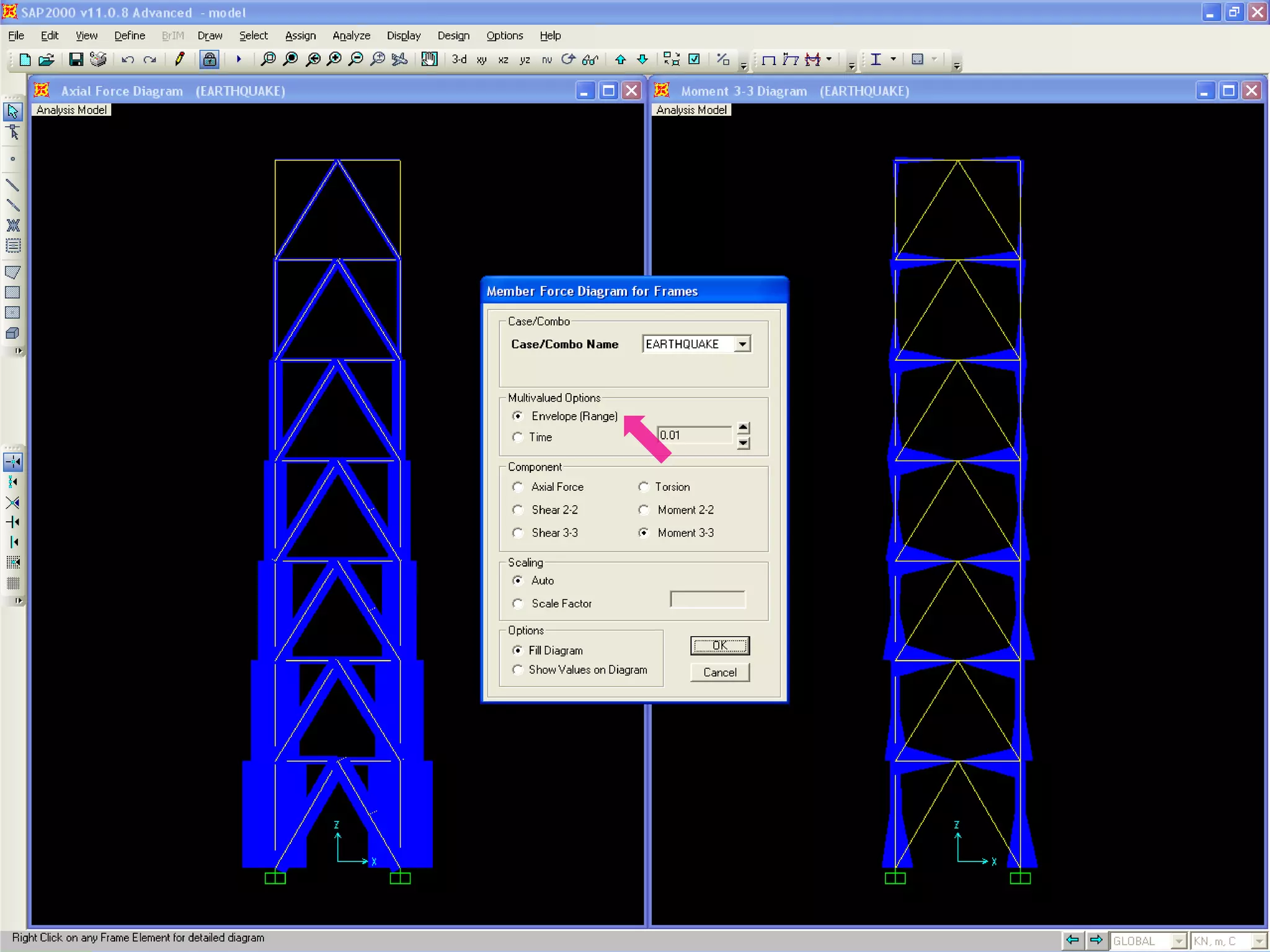
The document provides a step-by-step guide for conducting a time-history seismic analysis using SAP2000 software. It details how to:
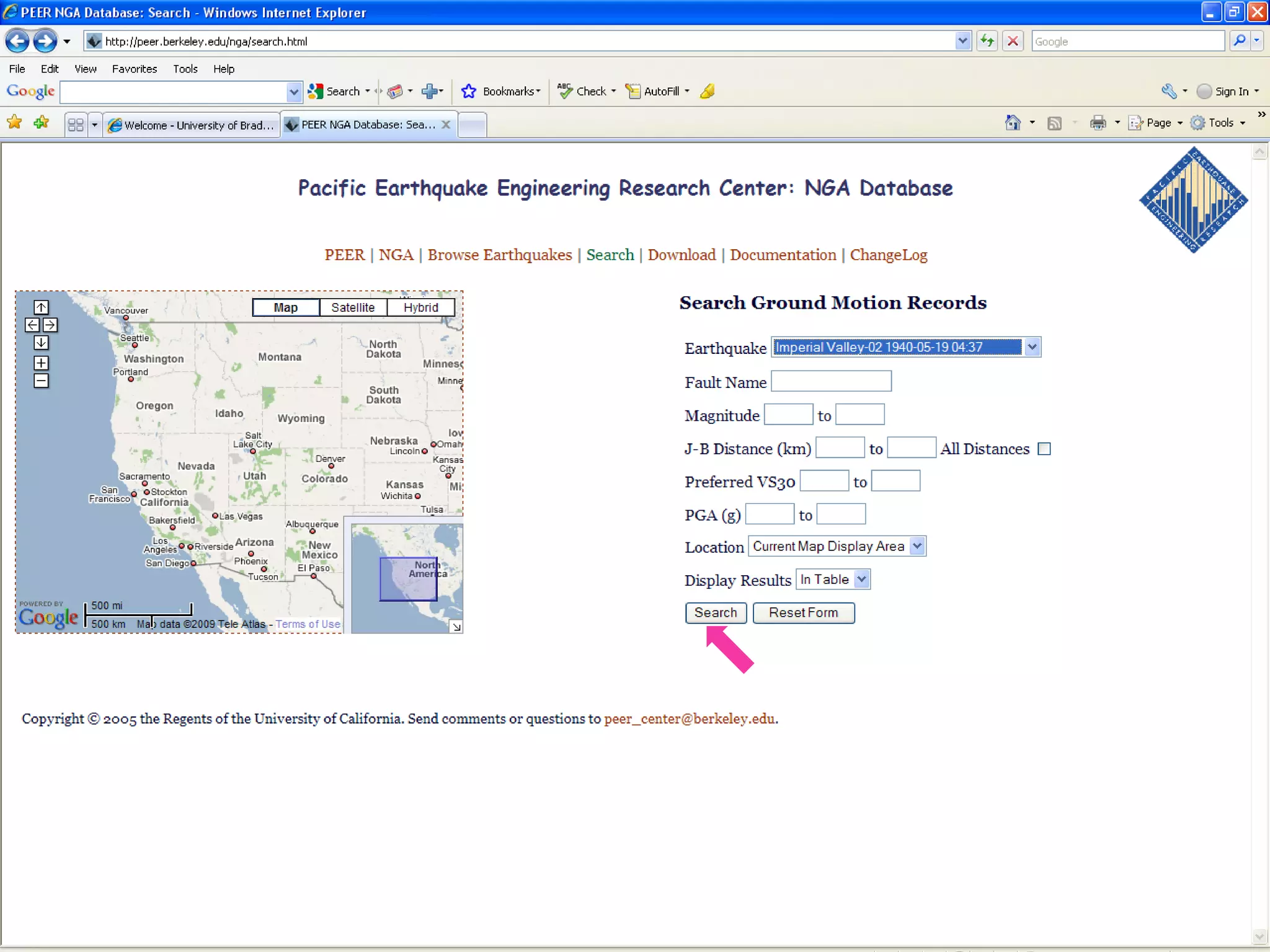
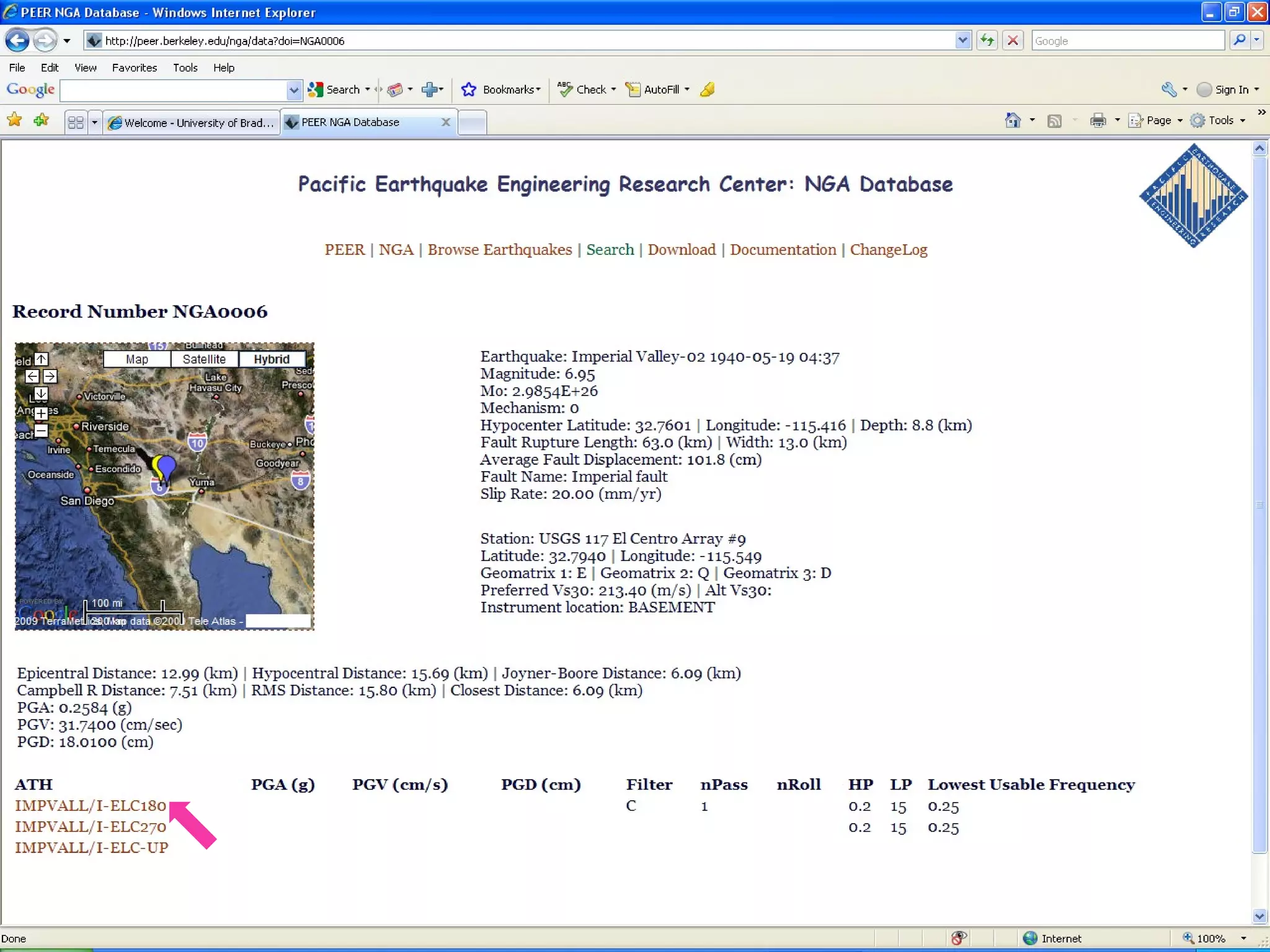
1) Download recorded earthquake accelerograms from the PEER database, such as one from the 1940 Imperial Valley earthquake.
2) Upload the selected accelerogram file into SAP2000 and define it as a time history function.
3) Assign the accelerogram to a time history analysis case and run the dynamic analysis.
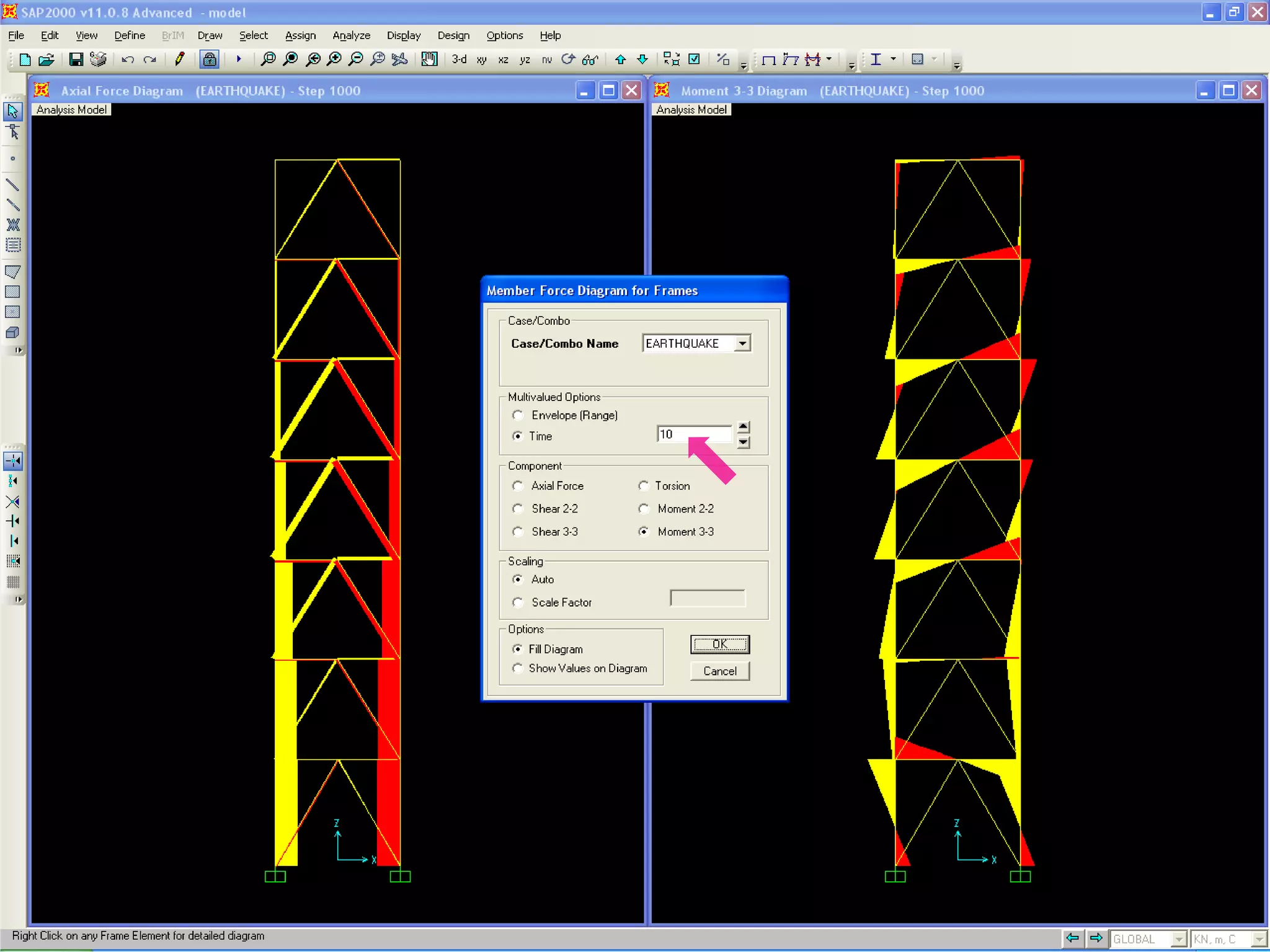
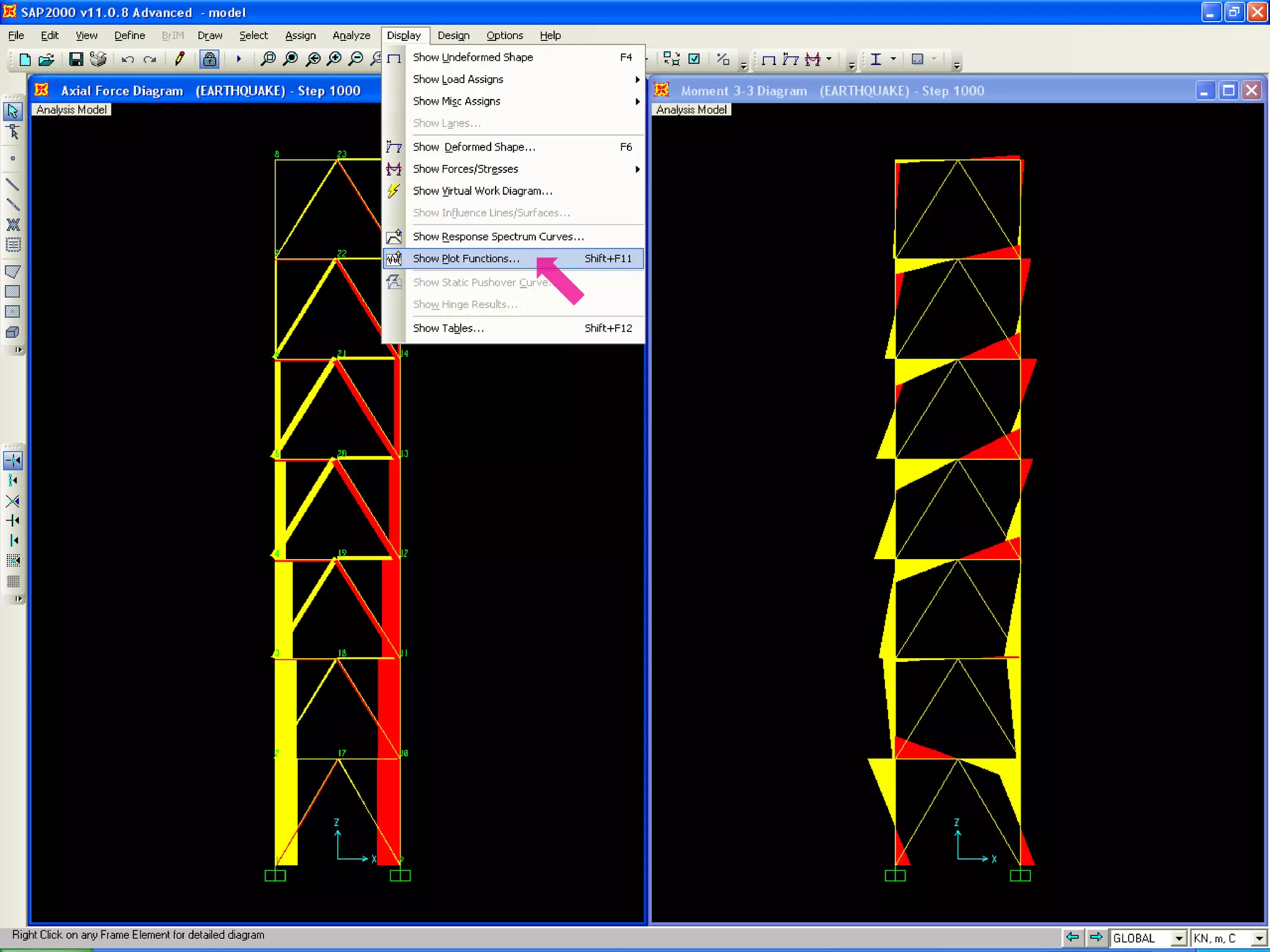
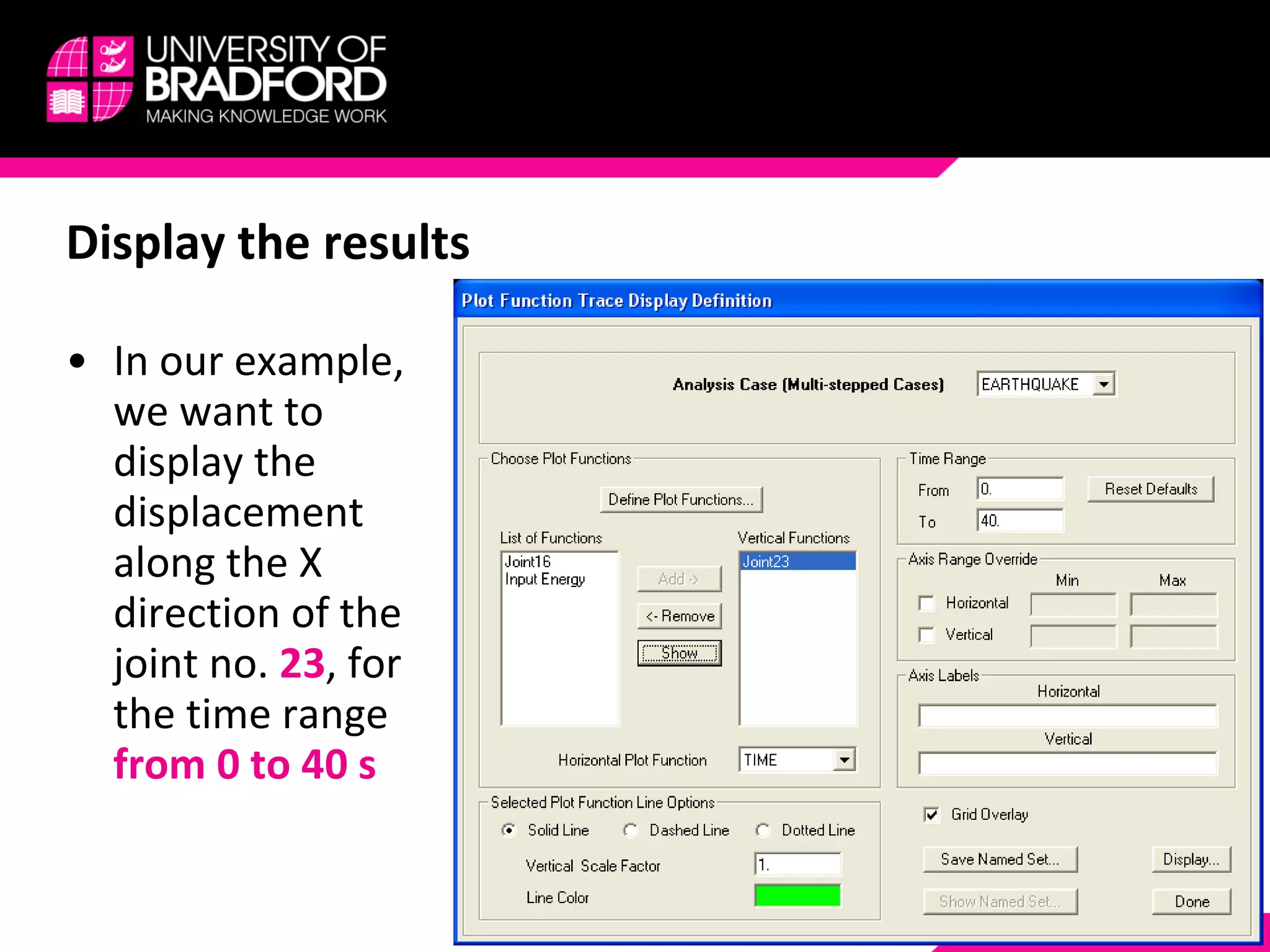
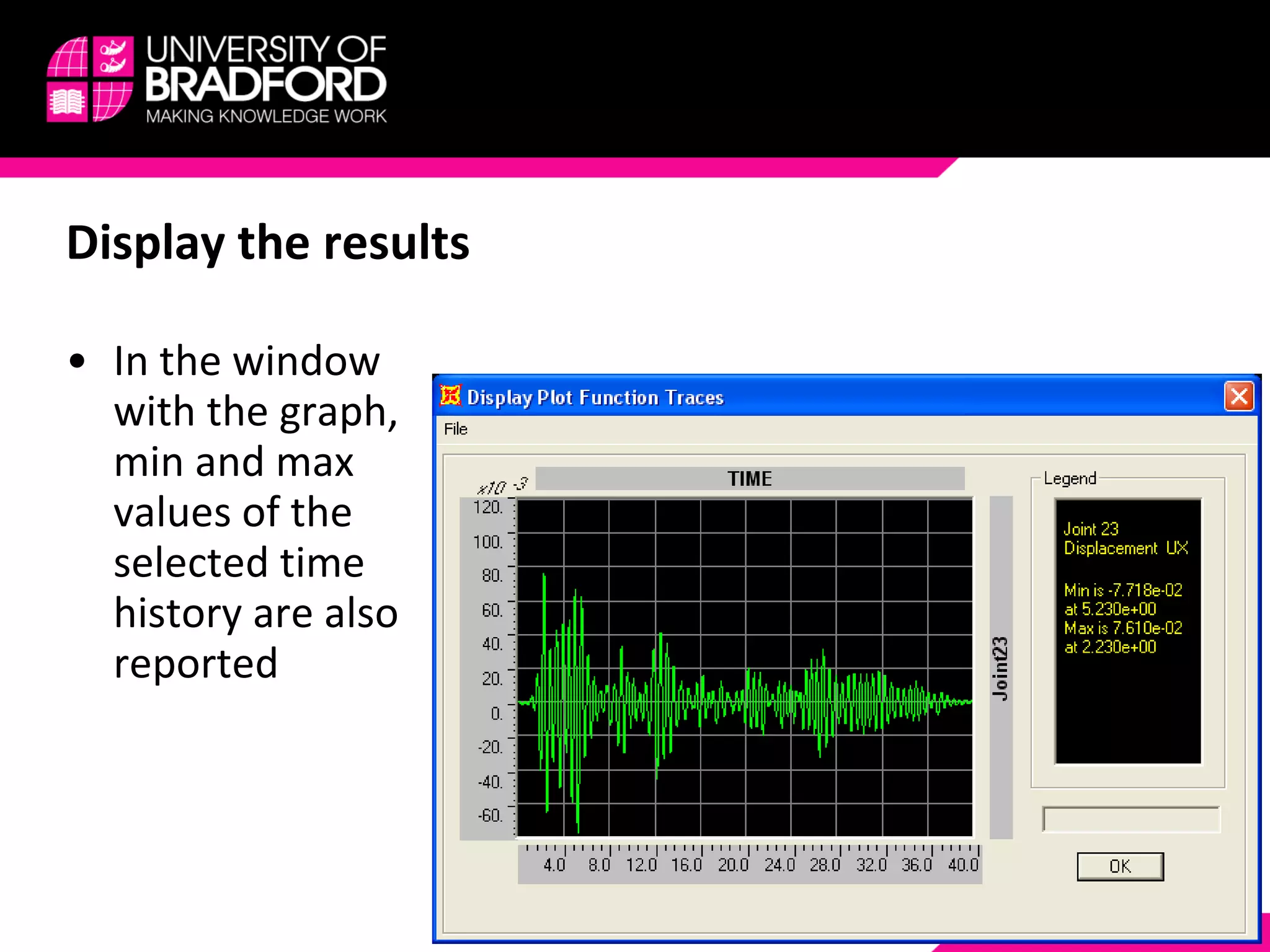
4) View and analyze results like envelopes of axial forces, moments, and time histories of displacements.