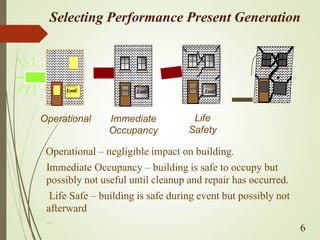
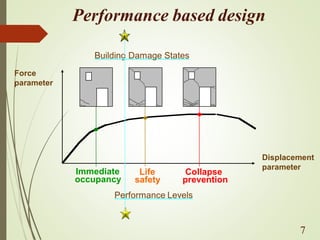
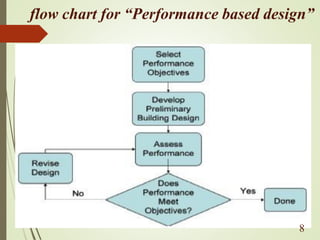
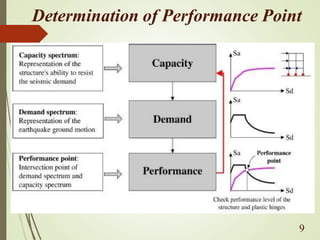
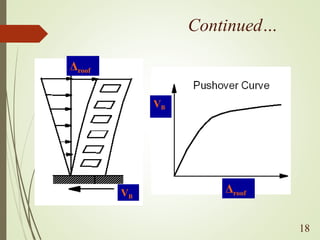
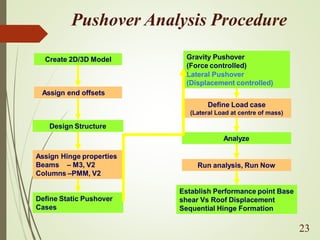
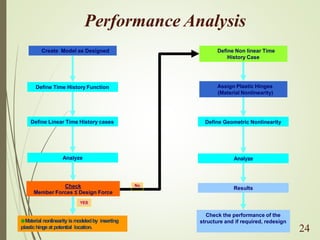
The document discusses performance-based seismic design, emphasizing its role in ensuring buildings can withstand earthquakes with predictable outcomes. It outlines various performance objectives ranging from operational stability to collapse prevention, and contrasts this approach with traditional design methods. Key analysis methods include pushover and time history analyses, which help assess building performance under seismic loads.