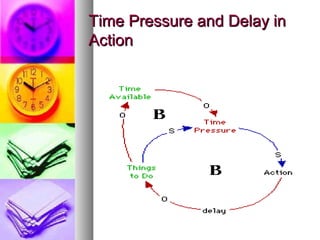
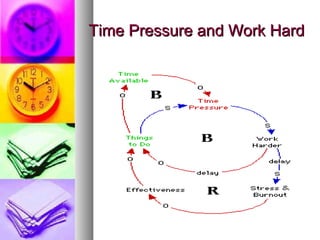
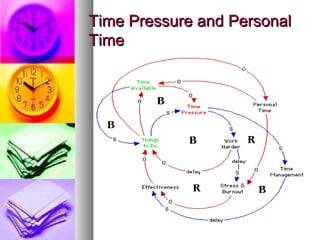
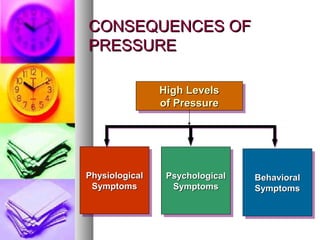
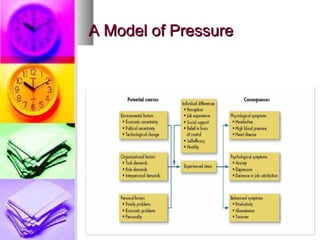
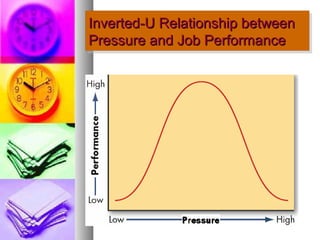
The document discusses time and pressure management, defining time as a valuable resource essential for success and pressure as a condition involving uncertainty and demand. It emphasizes effective time management through habits, planning, and making the best use of available time while addressing various factors that contribute to pressure. Strategies for both individual and organizational approaches to manage pressure are provided, highlighting the importance of communication, support systems, and personal well-being.