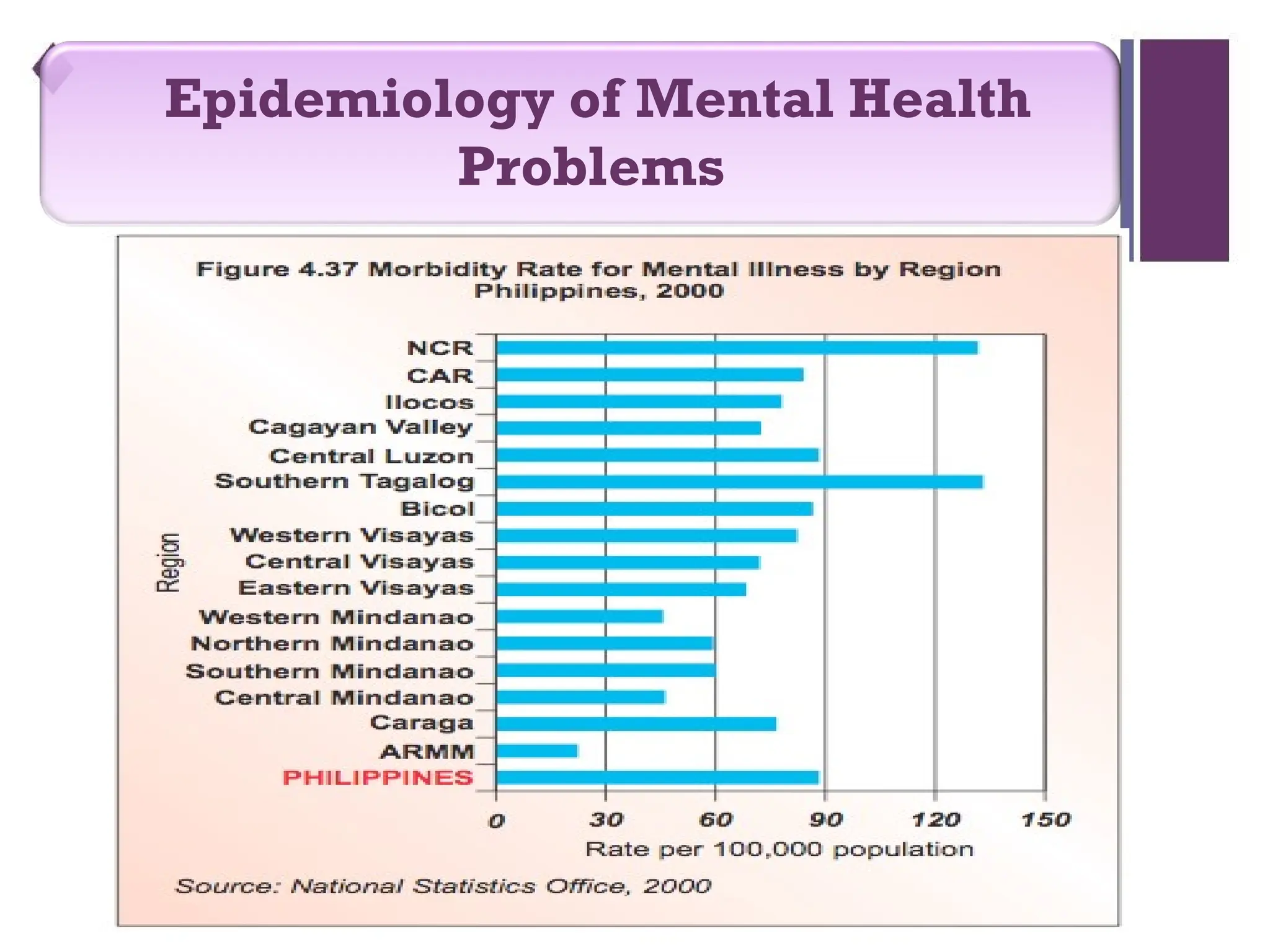
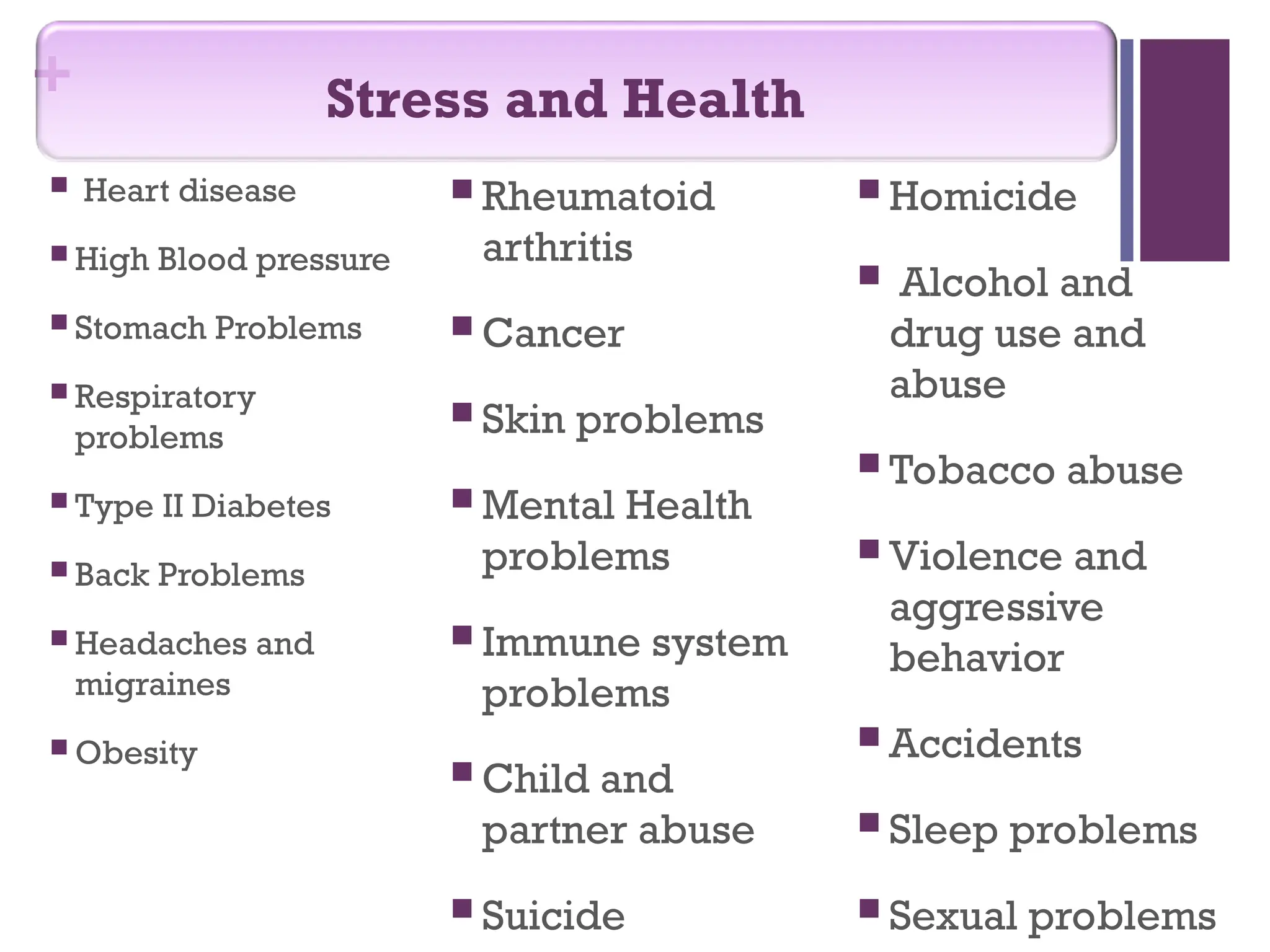
The document discusses the magnitude of mental health problems and the importance of stress management and promoting mental health in the workplace. It identifies various factors contributing to mental health issues, different types of stress, and their impact on health and productivity while outlining strategies for stress management. Additionally, it emphasizes the benefits of promoting mental well-being through social support, positive thinking, and healthy coping mechanisms.