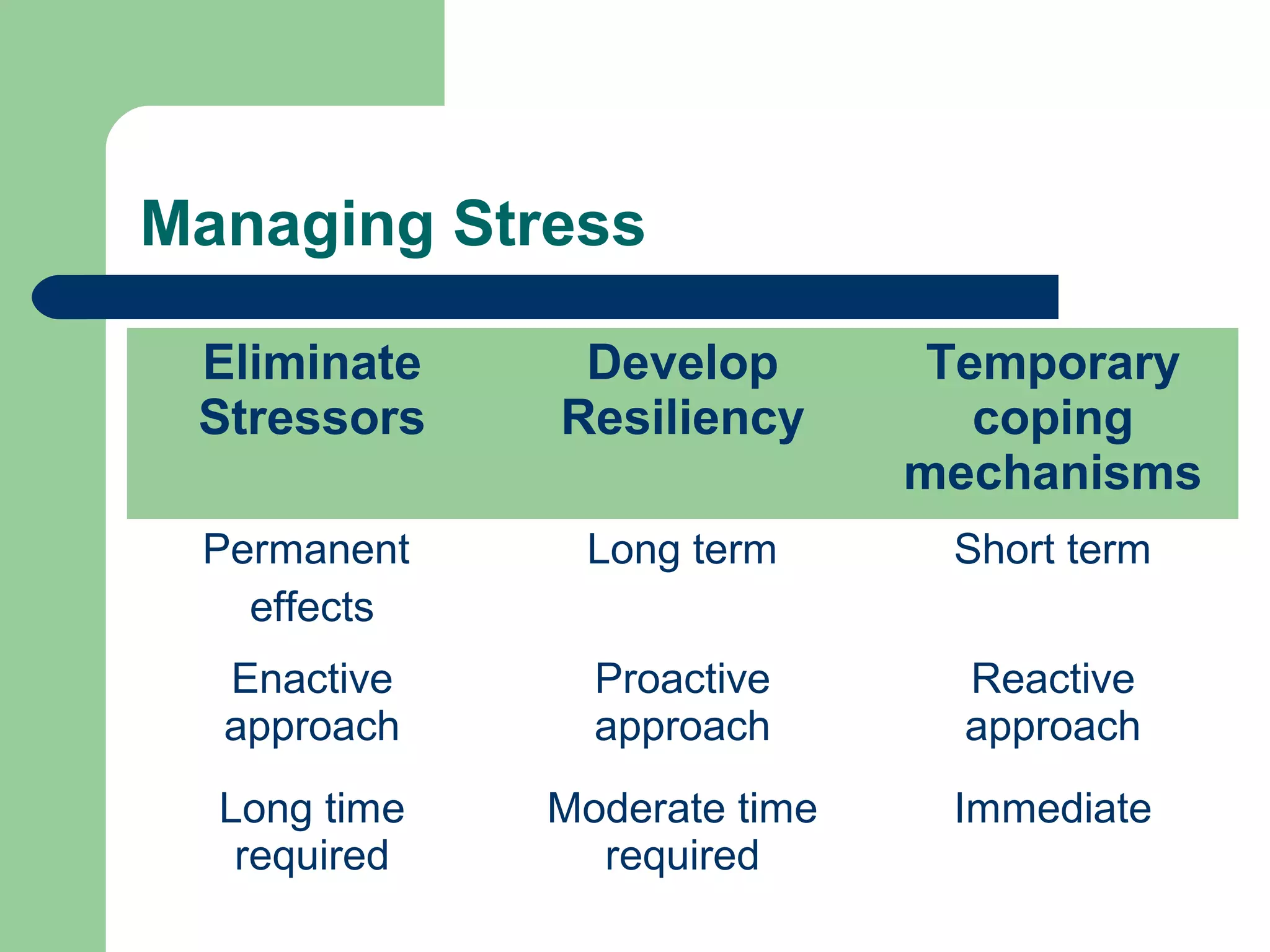
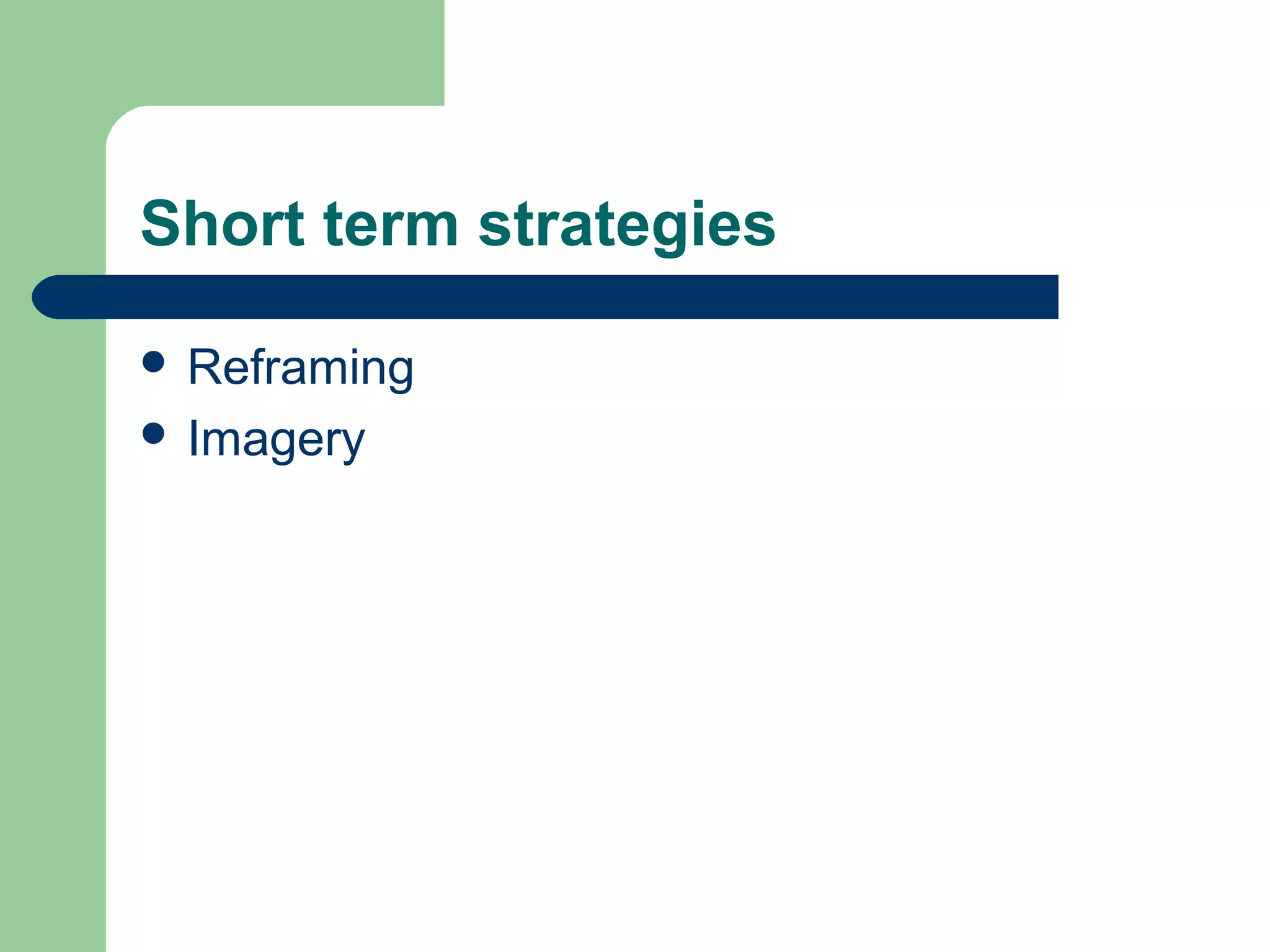
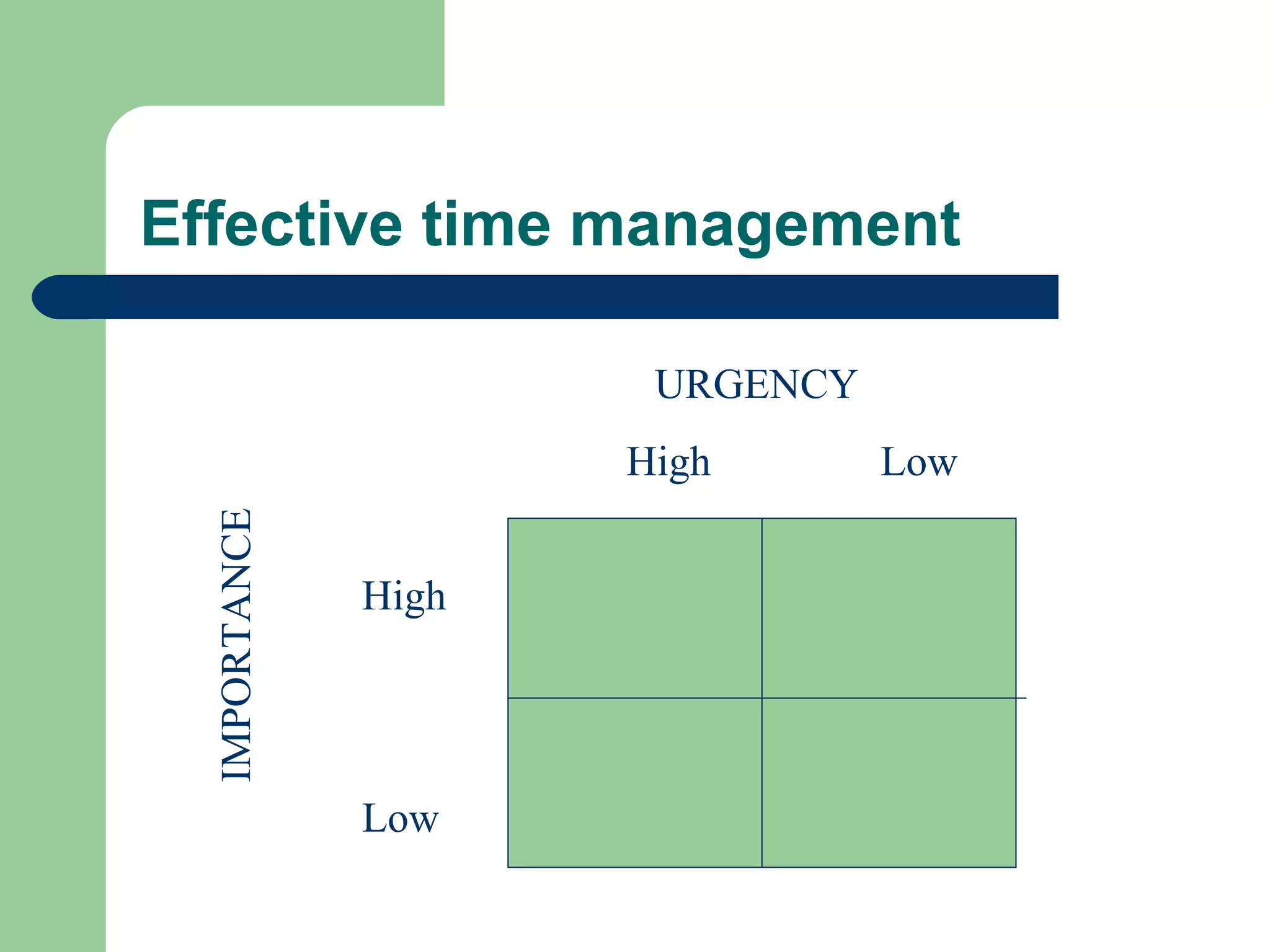
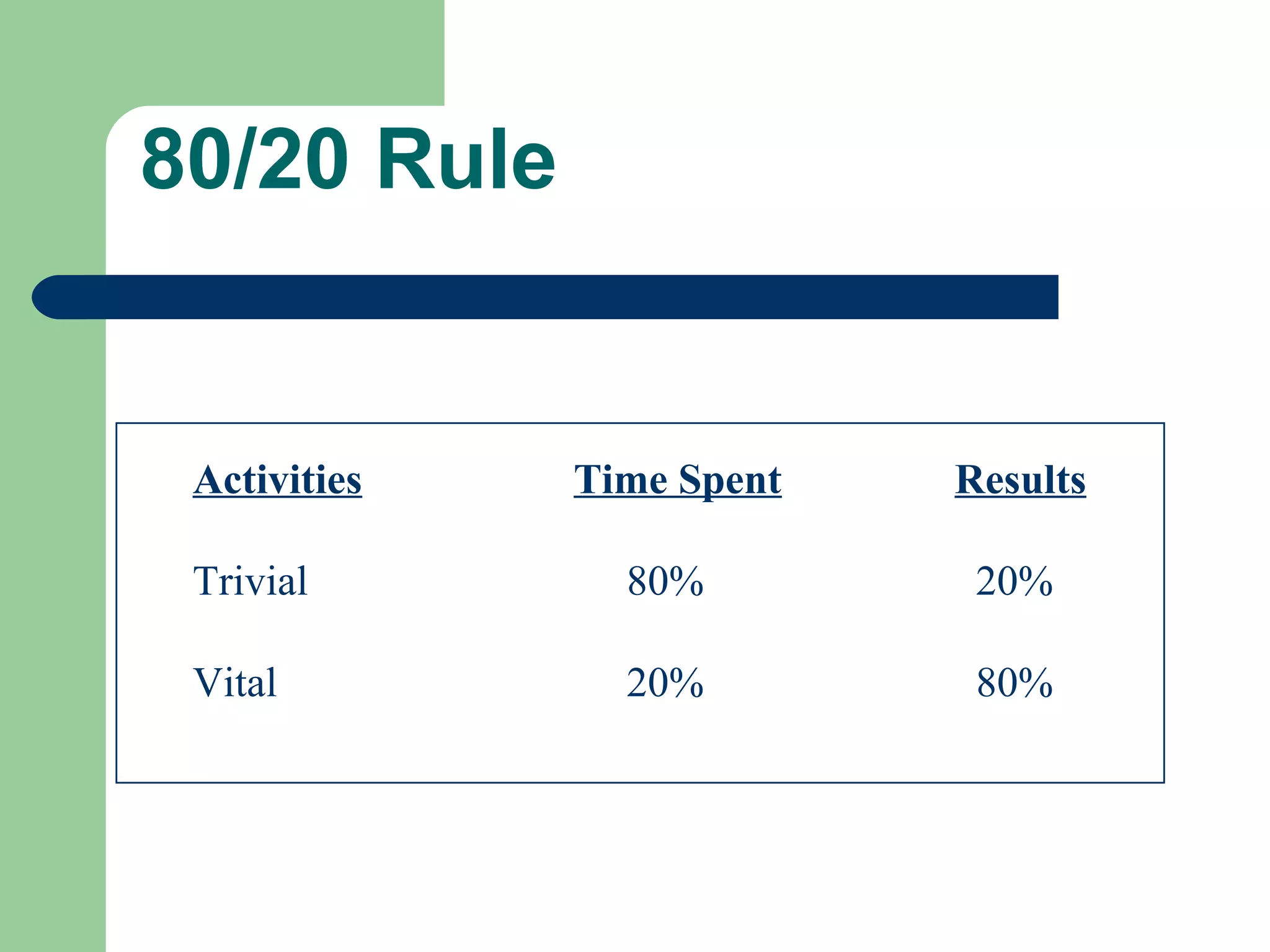
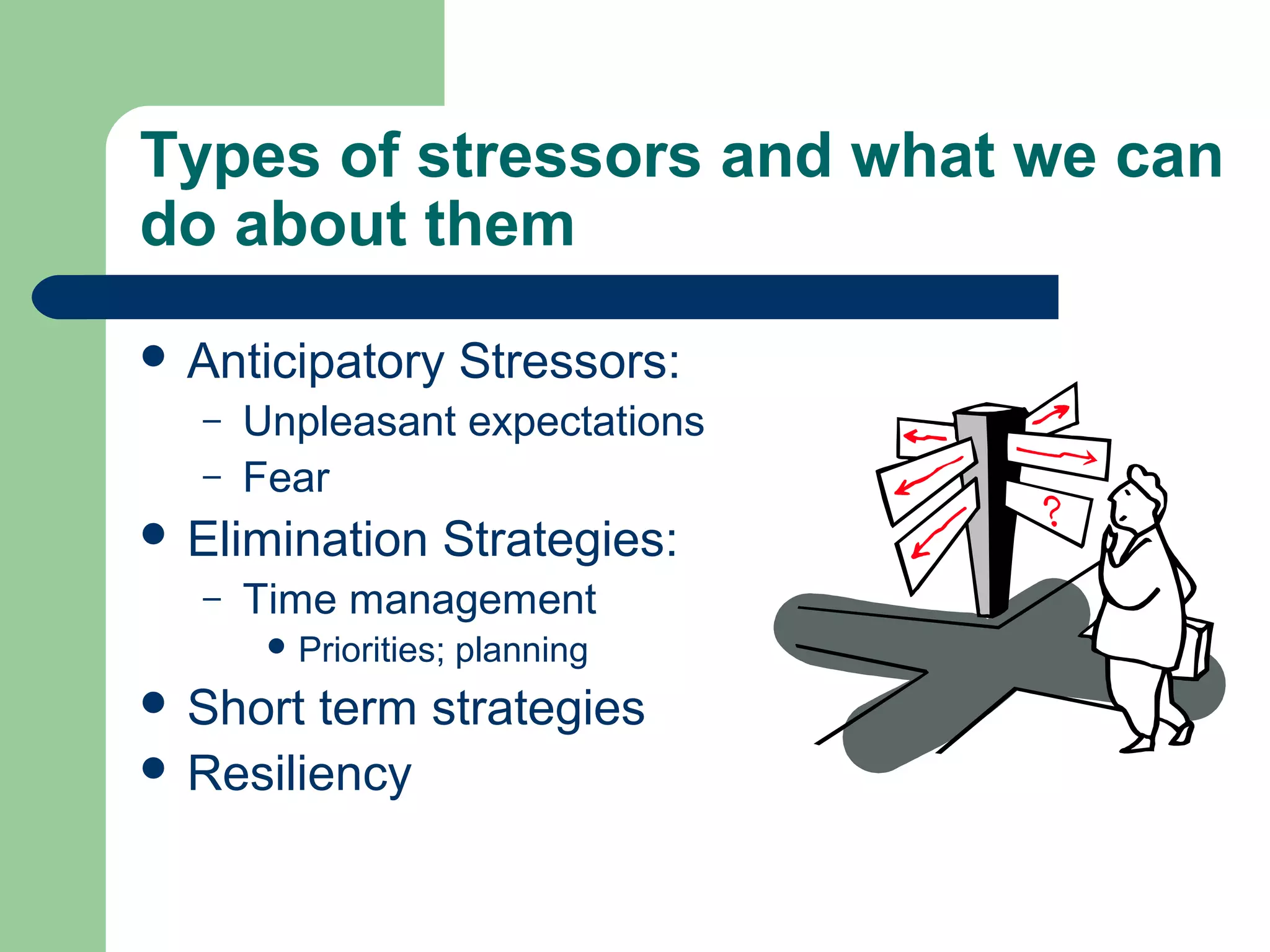
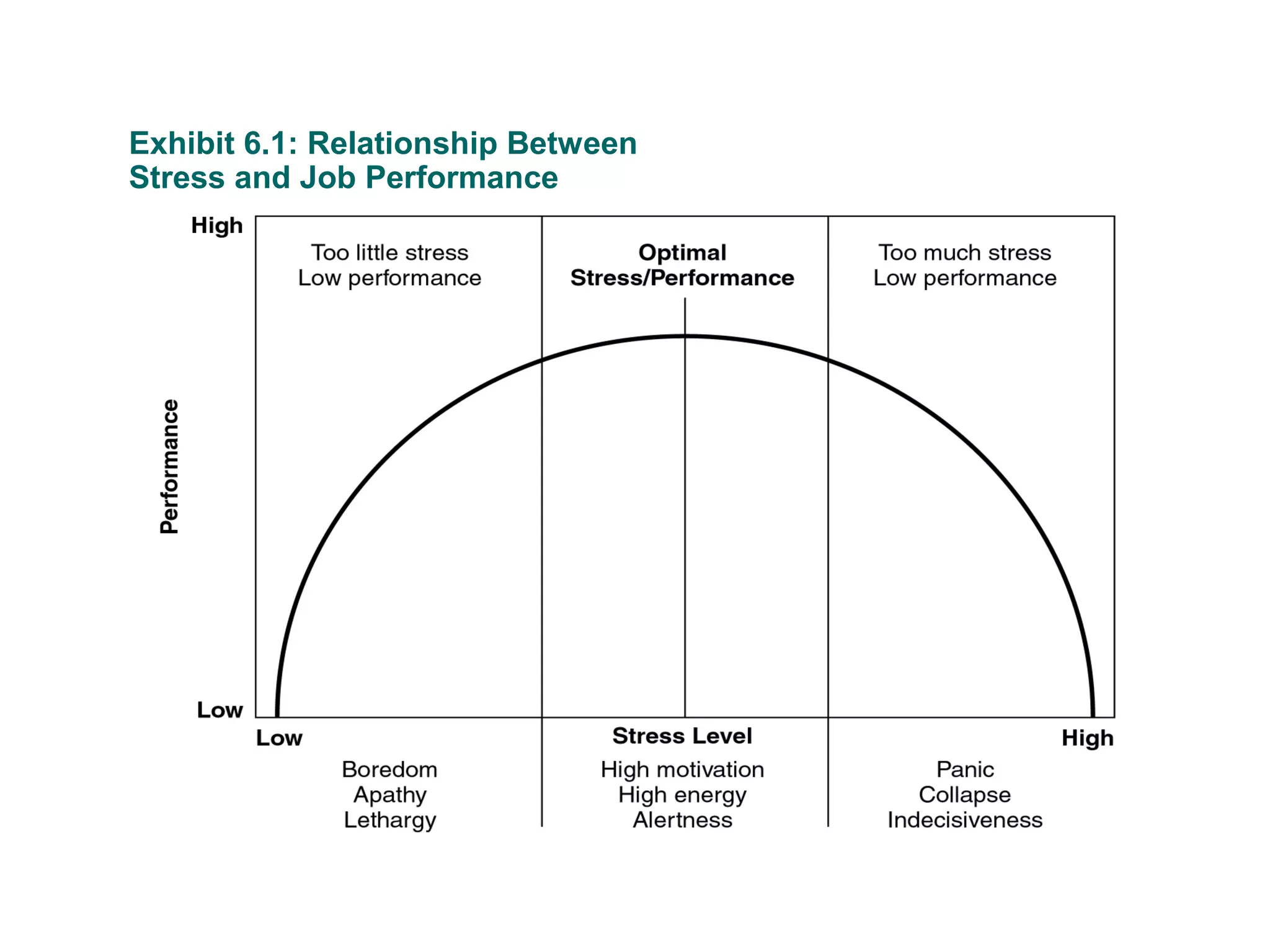
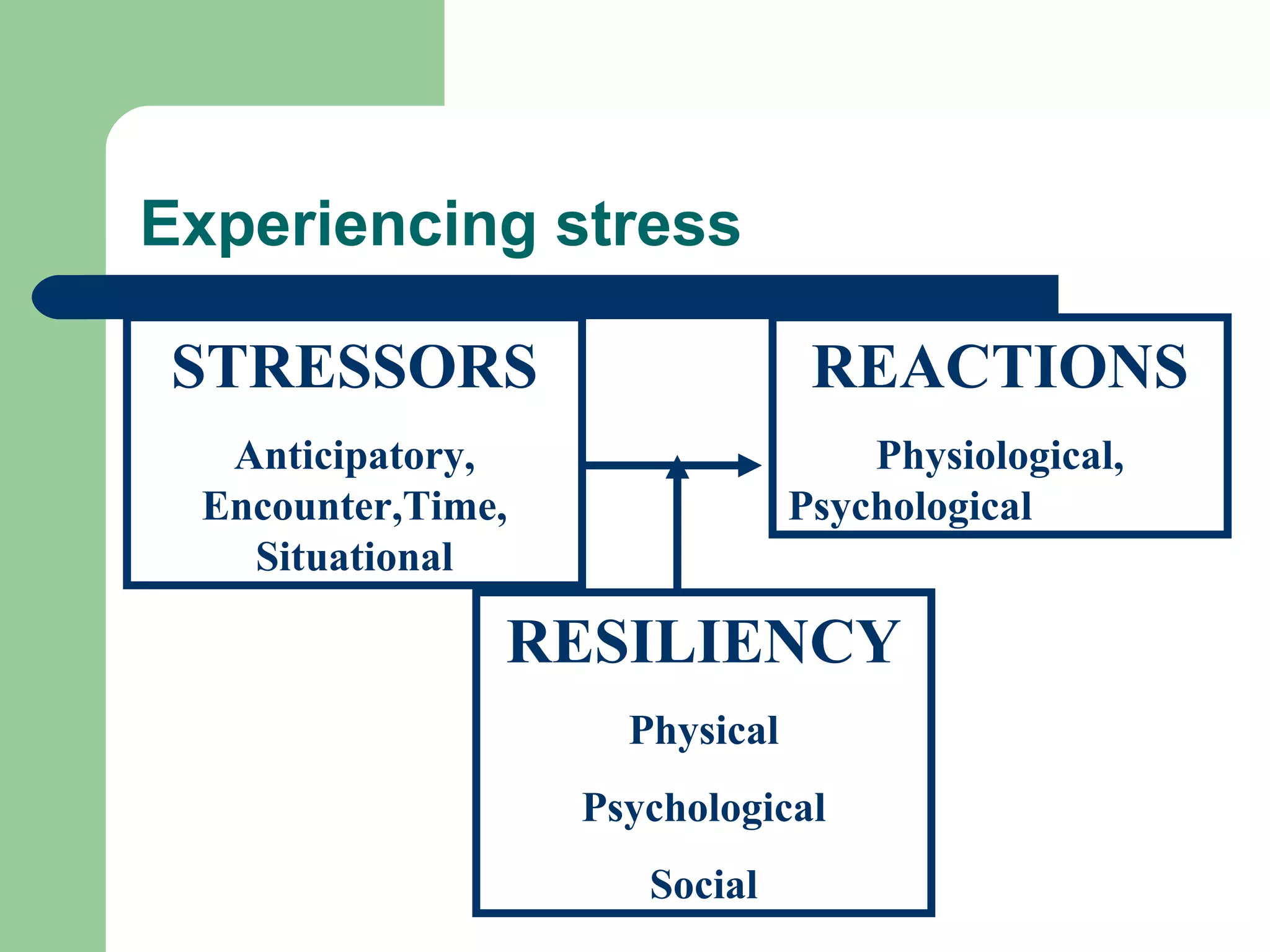
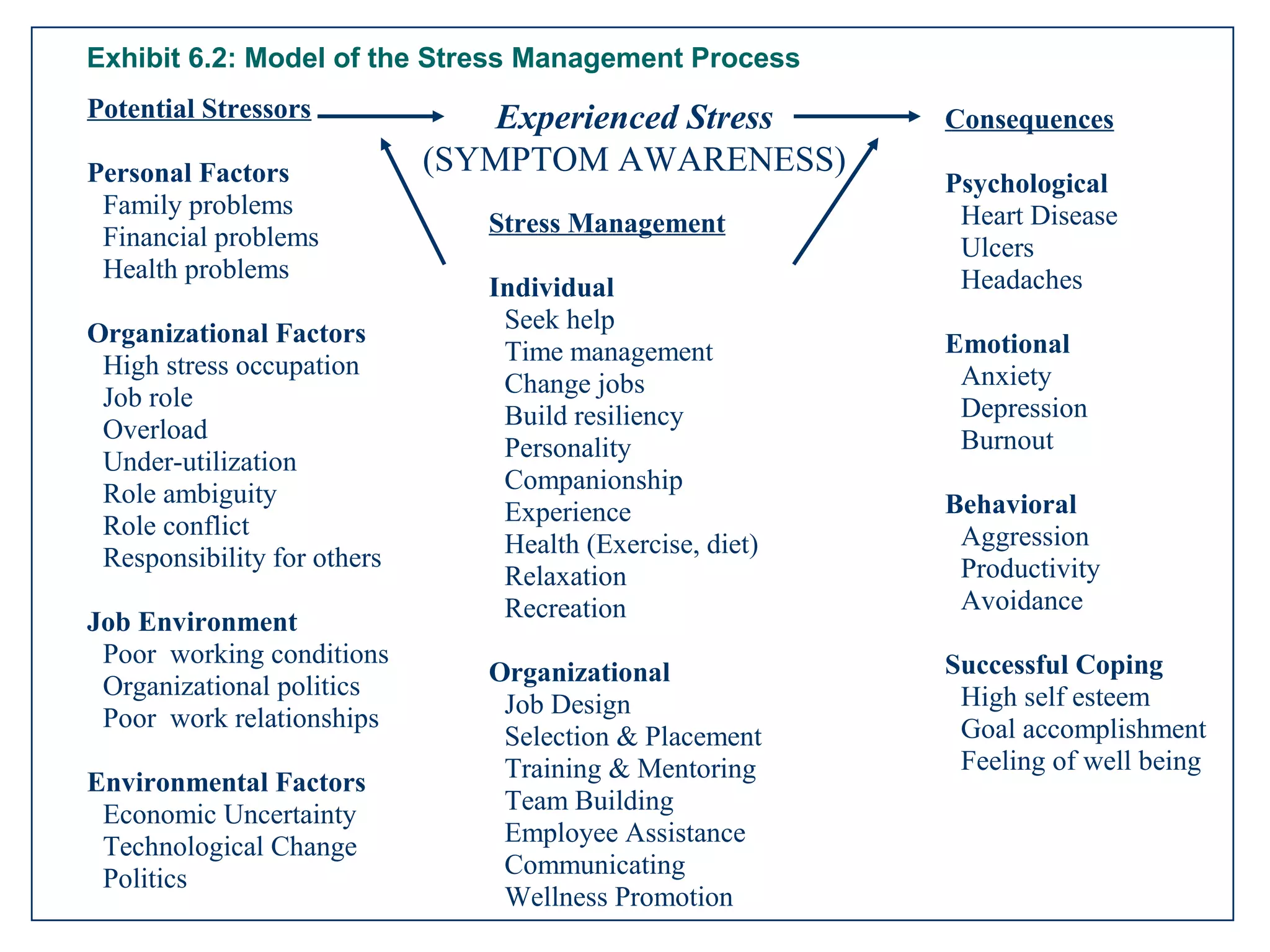
This document discusses time and stress management. It defines stress and stressors, and explains why stress management is important both for organizations and individuals. Stress can negatively impact health, job performance, and burnout. The document presents models of the stress process and factors like stressors, personal resilience, and consequences. It also discusses assessing stress symptoms, sources of stress like work and personal life, and different types of stressors. Finally, it provides strategies for managing stress through eliminating stressors, developing resilience, and temporary coping mechanisms.




![How Can Awareness of Stress
Symptoms Be Enhanced?
Physical Symptoms
Psychological Substitutes
Never Rarely Sometimes Often Always
Constant fatigue [] [] [] [] []
Low energy level [] [] [] [] []
Recurring headaches [] [] [] [] []
Gastrointestinal disorders [] [] [] [] []
Bad breath [] [] [] [] []
Sweaty hands or feet [] [] [] [] []
Dizziness [] [] [] [] []
High blood pressure [] [] [] [] []
Pounding heart [] [] [] [] []](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/timeandstressmanagementskills-130916033521-phpapp02/75/Time-and-stress-management-skills-8-2048.jpg)