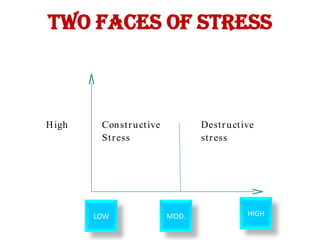
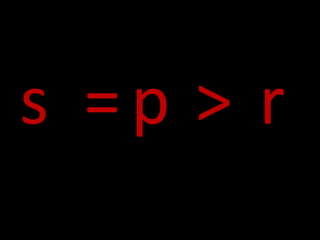1. The document discusses various causes of work stress like occupational demands, role conflicts, ambiguity, overload, interpersonal relationships, and organizational climate.
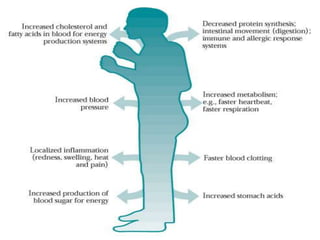
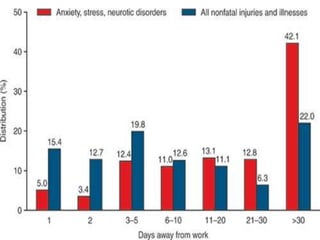
2. It outlines the symptoms and consequences of stress on individuals including lack of appetite, negativism, inability to concentrate, increased blood pressure, and absenteeism.
3. The document provides tips for managing stress through time management, exercise, meditation, relaxation, maintaining role clarity, and developing a supportive organizational climate. It also discusses burnout as a state of frustration from devotion to a cause.