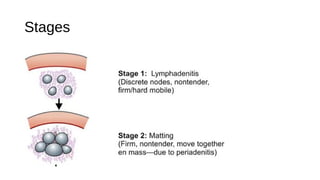
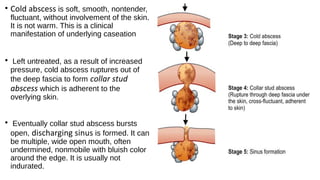
Tuberculous cervical lymphadenitis is caused by Mycobacterium tuberculosis infection of the cervical lymph nodes, usually through the tonsils. Clinically, it presents with fever, cough, and swollen lymph nodes in the neck. Left untreated, the infection can progress from a non-tender cold abscess to a collar stud abscess under the skin that ruptures, forming draining sinus tracts. Diagnosis involves aspiration or biopsy of lesions for staining, culture and cytology. Treatment consists of a 6-9 month course of anti-tuberculosis drugs. Aspiration or incision and drainage may be used for abscesses. Surgery is indicated for drug-resistant cases or persistent sinuses.